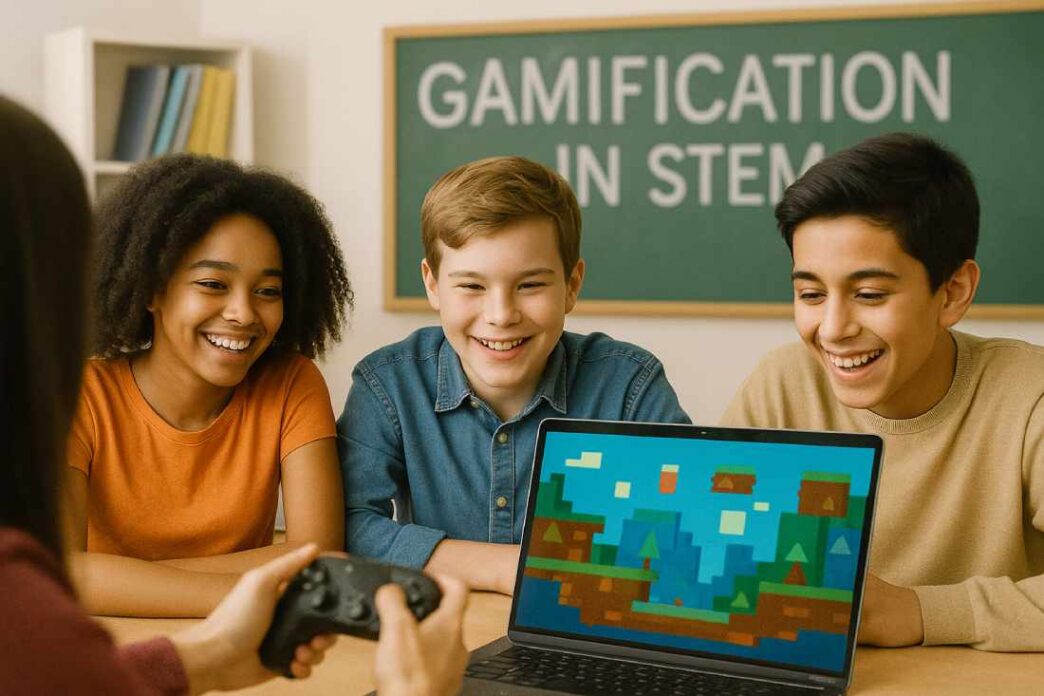
Game-based learning is reshaping the landscape of STEM education. It combines the excitement of games with the rigor of academic learning. This approach fosters engagement and enhances retention among students.
In recent years, gamification in education has gained traction. Many game development companies are innovating ways to create educational gaming experiences. These interactive tools not only make learning fun but also cater to diverse learning styles.
In this article, we explore the benefits of game-based learning for STEM. We’ll also look at pioneering educational games developers and their contributions to the field.
Engaging the Learner
The intrinsic motivation that games instill in players can be paralleled with educational objectives. By integrating game mechanics into learning, educators can captivate students’ attention and encourage active participation. This engagement is crucial in STEM subjects, where traditional learning methods may fail to ignite curiosity or maintain interest. Games provide a platform where students can explore concepts at their own pace, making learning a personalized experience.
Furthermore, game-based learning can cater to different learning styles. Visual learners, for instance, benefit from the graphical elements of games, while kinesthetic learners engage with interactive tasks. This adaptability ensures that all students can find a foothold in their learning journey.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
STEM education inherently involves problem-solving and critical thinking. Games designed for educational purposes simulate complex scenarios requiring players to apply scientific principles, solve mathematical problems, and employ engineering concepts. These games often present challenges that require strategic thinking and decision-making. The iterative nature of gaming allows learners to experiment, fail, and retry, mirroring real-world scientific inquiry processes.
In addition, games can introduce students to real-world problems, encouraging them to think critically about solutions. This not only enhances their problem-solving skills but also prepares them for future challenges in their careers. By tackling these virtual problems, students learn perseverance and adaptability, skills that are invaluable in the STEM fields.
Facilitating Deep Learning
Games have the potential to facilitate deep learning, where students move beyond rote memorization to truly understand and apply concepts. In a game-based learning environment, students are more likely to engage in higher-order thinking. They analyze, evaluate, and create new understanding based on the scenarios presented in the game.
By fostering an environment where exploration and experimentation are encouraged, game-based learning promotes a deeper understanding of STEM subjects. Students are not just passive recipients of information; they are active participants in their education, constructing knowledge through experience. This approach aligns with constructivist theories of learning, which emphasize the importance of learners building their own understanding.
Gamification in Education: Bridging the Gap
Gamification in education involves applying game-design elements in non-game contexts. It is a powerful strategy to enhance student motivation and involvement, particularly in STEM education. By incorporating elements familiar from games into educational settings, educators can create an environment that feels less like a classroom and more like a collaborative, exciting challenge.
Game Elements in STEM Learning
Gamification incorporates elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, and levels to create a competitive yet collaborative learning environment. These elements serve to motivate students by providing clear goals and tangible rewards for their achievements. This structure not only makes the learning process enjoyable but also provides immediate feedback, an essential component in educational psychology.
Immediate feedback helps students understand their progress and areas that need improvement. It encourages a growth mindset, where students view challenges as opportunities to learn and grow. The use of levels and badges can also help break down complex subjects into manageable tasks, allowing students to build their knowledge progressively.
Real-World Applications
The application of gamification extends beyond the classroom. For instance, engineering students might engage in virtual labs where they can design, test, and refine models, akin to real-world engineering tasks. Such experiences are invaluable, as they prepare students for future careers in STEM fields. By simulating real-world scenarios, gamification helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Incorporating gamification also facilitates the development of soft skills such as teamwork and communication. Many gamified learning experiences require students to work together, share ideas, and solve problems collaboratively. These skills are crucial in the modern workplace, where collaboration and effective communication are key to success.
Encouraging Lifelong Learning
Gamification in education can also foster a culture of lifelong learning. By making learning an enjoyable and rewarding experience, students are more likely to continue seeking knowledge beyond the classroom. This is particularly important in STEM fields, where continuous learning is essential due to the rapid pace of technological advancement.
Through gamification, educators can instill a sense of curiosity and a love for learning in their students. This passion for discovery can drive students to pursue further education and career opportunities in STEM, contributing to the development of a knowledgeable and skilled workforce.
Pioneering Game Development Studios in Educational Gaming
Several game developing companies are at the forefront of creating STEM-focused educational games. These companies are pushing the boundaries of traditional education by blending cutting-edge technology with pedagogical principles. By doing so, they are transforming the educational landscape and offering students new ways to engage with complex subjects.
Merging Education and Entertainment
Educational gaming companies are employing sophisticated graphics, compelling narratives, and real-time feedback to create games that are both educational and entertaining. The challenge lies in balancing these elements to ensure that the educational content is not overshadowed by the gameplay. An experienced educational games developer plays a crucial role in maintaining this balance, ensuring that the game design supports learning objectives while keeping players engaged.
The integration of storytelling in educational games is particularly effective in maintaining student interest. A well-crafted narrative can provide context for the educational content, making it more relatable and easier to understand. By embedding STEM concepts within engaging stories, educational game developers can transform abstract ideas into concrete, memorable experiences that support long-term knowledge retention and enjoyment.
Notable Innovations
Companies like Osmo and Tynker are making waves in the educational gaming sector. Osmo’s interactive learning games utilize tangible objects to teach math and coding, offering a unique hands-on approach to learning. This tactile element enhances the learning experience by allowing students to physically interact with the content.
Meanwhile, Tynker offers coding courses that empower students to create their own games, thereby learning programming fundamentals. This approach not only teaches technical skills but also encourages creativity and innovation. By enabling students to become creators rather than just consumers of technology, Tynker is helping to cultivate the next generation of tech-savvy individuals.
Collaborations and Partnerships
The success of educational gaming companies is often bolstered by collaborations with educators, researchers, and technology experts. By partnering with schools and educational institutions, these companies can ensure that their products align with curriculum standards and address the needs of both teachers and students.
Collaborations with technology companies can also enhance the capabilities of educational games. By integrating the latest advancements in artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and data analytics, educational gaming companies can create more personalized and effective learning experiences. These partnerships are crucial for driving innovation and ensuring that educational games remain at the forefront of modern education.
Virtual Environments: The Future of STEM Education
Virtual environments are revolutionizing STEM education by providing immersive experiences that were once considered science fiction. These environments allow for exploration and experimentation in a risk-free setting, making complex STEM concepts more accessible. As technology continues to advance, virtual environments hold the potential to transform the way we teach and learn STEM subjects.
Immersive Learning Experiences
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are creating new possibilities in STEM education. Imagine a biology student exploring the human body from the inside, or a physics student witnessing the laws of motion in action within a virtual lab. These experiences make abstract concepts tangible and understandable. By immersing students in realistic simulations, virtual environments can enhance comprehension and retention of complex ideas.
The use of VR and AR also allows for experiential learning, where students can learn by doing rather than passively receiving information. This hands-on approach is particularly effective in STEM education, where practical application of knowledge is key. Virtual environments provide a safe space for students to experiment, make mistakes, and learn from them without real-world consequences.
Collaborative Learning
Virtual environments foster collaboration among students, even when they are miles apart. Through shared virtual spaces, students can work together on projects, exchange ideas, and solve problems collectively, thus enhancing their learning experience. This collaborative aspect of virtual environments mirrors the teamwork required in real-world STEM professions.
Moreover, virtual environments can connect students with experts and peers from around the world, expanding their learning network. This global perspective can provide valuable insights and inspire innovation. By facilitating collaboration and communication, virtual environments prepare students for the interconnected and globalized nature of modern STEM careers.
Overcoming Barriers to Access
One of the significant advantages of virtual environments is their ability to overcome geographical and resource barriers. Students in remote or underserved areas can access the same high-quality educational experiences as those in well-resourced schools. This democratization of education is a crucial step towards achieving equity in STEM education.
Virtual environments can also accommodate diverse learning needs and preferences. By offering customizable and adaptive learning experiences, these environments ensure that all students, regardless of their background or abilities, can engage with STEM content. This inclusivity is essential for fostering a diverse and talented STEM workforce.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of game-based learning in STEM are immense, there are challenges that educators and developers must address. As with any educational innovation, careful consideration and thoughtful implementation are necessary to ensure that game-based learning is effective and equitable.
Balancing Educational Content and Gameplay
One of the primary challenges is ensuring that the educational value is not lost in the pursuit of entertainment. The goal is to create games that are engaging yet educationally robust. Developers must strike a balance between fun and learning, ensuring that gameplay mechanics enhance rather than detract from the educational objectives.
This balance requires a deep understanding of both game design and pedagogy. Collaboration between educators and game developers is essential to create games that are both entertaining and educational. By working together, they can design experiences that are aligned with curriculum standards and learning goals.
Accessibility and Equity
Ensuring that all students have access to these innovative educational tools is crucial. Developers and educators must work together to address disparities in technology access and ensure that game-based learning is inclusive and equitable. This includes providing resources and support for schools and students with limited access to technology.
Additionally, considerations must be made for students with diverse learning needs. Game-based learning should be designed to accommodate different abilities and preferences, ensuring that all students can benefit from these innovative approaches. By prioritizing accessibility and inclusivity, educators can ensure that game-based learning reaches its full potential.
Measuring Educational Outcomes
Assessing the effectiveness of game-based learning poses another challenge. Traditional assessment methods may not adequately capture the skills and knowledge gained through game-based learning experiences. Educators must develop new assessment strategies that align with the goals of game-based learning, focusing on skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity.
Data analytics and learning analytics can play a role in measuring educational outcomes. By analyzing data generated through gameplay, educators can gain insights into student progress and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach can inform instructional strategies and enhance the overall effectiveness of game-based learning.
Conclusion
Game-based learning for STEM is a promising frontier in education, offering dynamic and engaging ways to learn complex concepts. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for educational games to transform STEM education becomes even more profound. By leveraging the power of games, educators can inspire the next generation of scientists, engineers, and innovators, equipping them with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in an increasingly complex world.
In this rapidly evolving landscape, game developers, educators, and policymakers must collaborate to harness the full potential of game-based learning, ensuring that it remains an effective and inclusive tool for STEM education. As we continue to explore and expand the possibilities of game-based learning, the future of STEM education looks bright, with endless opportunities for innovation and growth. Through collaboration and a commitment to equity, we can create an educational environment where all students have the opportunity to thrive.