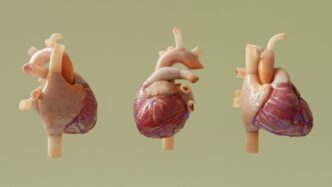
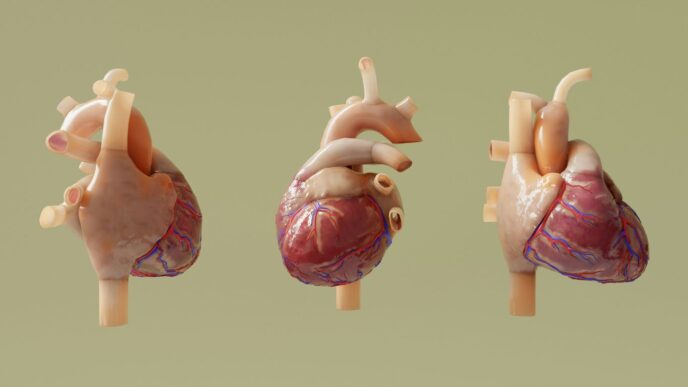
Boston Scientific’s FARAPULSE Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) system is making waves in how doctors treat irregular heart rhythms, specifically atrial fibrillation. This new approach uses electricity in a special way to target problem areas in the heart without harming the surrounding tissue. It’s a big step forward from older methods and is getting a lot of attention from doctors and patients alike. We’ll look at what makes this boston scientific pfa system so different and why it’s becoming a go-to option.
Key Takeaways
- The Boston Scientific FARAPULSE PFA system has received FDA approval for treating certain types of atrial fibrillation, offering a new option for patients.
- This system uses pulsed electric fields, a ’tissue-selective’ method, to target and eliminate abnormal heart tissue without causing thermal damage.
- Clinical trials like ADVENT and MANIFEST 17K have shown positive results for the FARAPULSE PFA system’s effectiveness and safety.
- Boston Scientific is continuing to explore broader uses for its PFA technology, including for more complex forms of atrial fibrillation and other heart conditions.
- The FARAPULSE PFA system includes advanced components like the FARAWAVE catheter and FARASTAR generator, designed to work together for better patient outcomes.
Boston Scientific FARAPULSE PFA System Overview
So, what exactly is this FARAPULSE PFA system from Boston Scientific? It’s a pretty big deal in the world of heart rhythm treatments, specifically for atrial fibrillation (AFib). Basically, it’s a new way to do cardiac ablation, which is a procedure to fix irregular heartbeats. Instead of using heat or cold, this system uses something called pulsed field ablation (PFA).
Introduction to Pulsed Field Ablation Technology
Pulsed Field Ablation, or PFA, is a newer approach that’s really changing the game. Instead of burning or freezing the heart tissue, PFA uses short, controlled bursts of electrical energy. These pulses are designed to be really specific, targeting the cells that cause AFib without harming the surrounding healthy tissue. Think of it like a very precise zap that disrupts the faulty electrical signals in the heart. This tissue-selective approach is what makes PFA so interesting and potentially safer than older methods. It’s a big step forward in how we treat conditions like AFib.
Components of the FARAPULSE PFA System
The FARAPULSE system isn’t just one piece of equipment; it’s a collection of tools working together. The main parts include:
- FARAWAVE Ablation Catheter: This is the part that actually goes into the heart. It’s designed to deliver the electrical pulses precisely where they’re needed. There are a couple of versions, like the FARAWAVE and FARAWAVE Nav, which offer different ways to get to the right spot.
- FARASTAR Ablation Generator: This is the machine that powers the whole thing. It creates and controls the electrical pulses that the catheter delivers. It’s designed to be pretty straightforward to use, with simple controls for preparing and delivering the therapy.
- FARADRIVE Steerable Sheath: This is like a guide that helps the doctors get the catheter exactly where it needs to go in the heart. It allows for precise navigation.
- VersaCross Connect Access Solution: This is an extra piece that helps doctors safely get to the left side of the heart, which is often where the problem areas are for AFib.
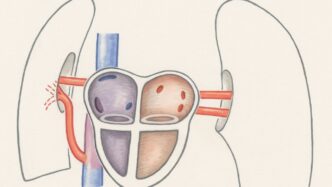
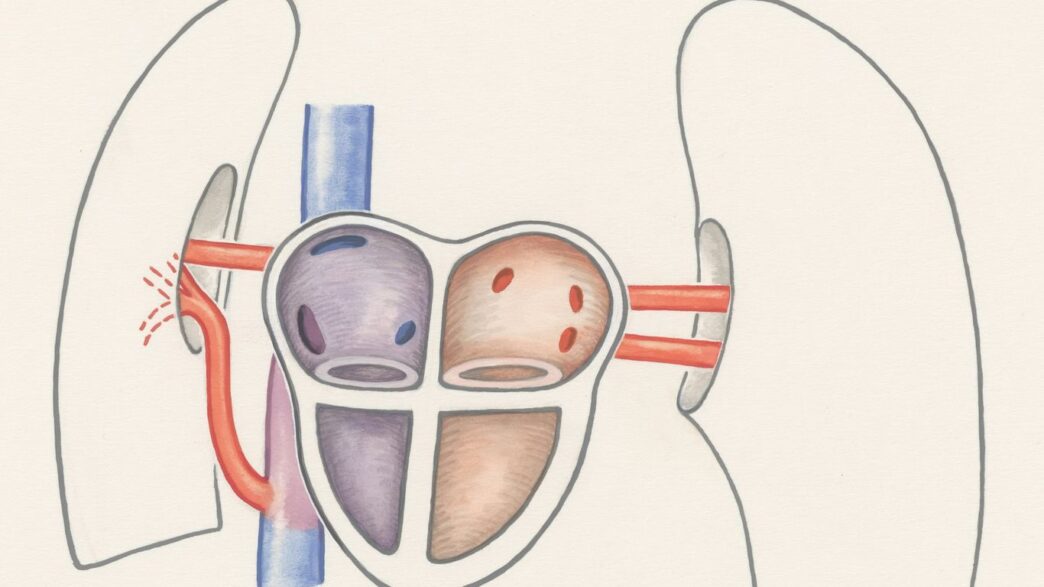
Mechanism of Action: Tissue-Selective Ablation
How does it actually work? The FARAPULSE system uses pulsed electric fields to create tiny holes in the cell membranes of the heart muscle cells. This process, called electroporation, disrupts the normal function of those cells. The key is that these electrical pulses are designed to affect the heart muscle cells much more than the cells in the surrounding tissues, like nerves or blood vessels. This means the system can effectively isolate the areas of the heart causing AFib without causing collateral damage. It’s a way to create scar tissue in very specific spots to block those irregular electrical signals, all without relying on extreme temperatures. This targeted approach is what makes it so promising for patients.
FDA Approval and Clinical Validation
Getting the green light from the FDA is a pretty big deal, and Boston Scientific’s FARAPULSE PFA System got just that. This approval is specifically for treating paroxysmal atrial fibrillation that hasn’t responded well to other medications. It’s a major step forward, offering a new option for folks dealing with this heart rhythm issue.
Introduction to Pulsed Field Ablation Technology
Pulsed Field Ablation, or PFA, is a newer way to handle AFib. Instead of using heat or cold to create scar tissue in the heart, PFA uses short, controlled electrical pulses. The idea is that these pulses can destroy the problematic heart tissue while leaving other nearby tissues, like the esophagus or nerves, unharmed. It’s a more targeted approach, which is pretty neat.
Components of the FARAPULSE PFA System
The system itself isn’t just one piece of equipment. It’s a collection of devices designed to work together. You’ve got the FARAWAVE Ablation Catheter, which is the part that actually delivers the energy to the heart. Then there’s the FARASTAR Ablation Generator, the machine that powers the catheter. To get the catheter where it needs to go, there’s the FARADRIVE Steerable Sheath. And to make sure doctors can safely access the left side of the heart, they use the VersaCross Connect Access Solution. It’s a whole setup.
Mechanism of Action: Tissue-Selective Ablation
So, how does it actually work? The FARAPULSE system uses what they call tissue-selective ablation. This means the electrical pulses are designed to affect only the heart muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes. They create tiny holes in the cell membranes, causing the cells to die. This process is supposed to be very specific, aiming to avoid damaging other important structures around the heart. The goal is to create lesions that block the abnormal electrical signals causing AFib without causing collateral damage.
FDA Approval for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
As mentioned, the FDA gave its nod for the FARAPULSE PFA System to treat paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. This is the type of AFib that comes and goes. The approval was based on solid data showing how well the system worked and how safe it was.
ADVENT Trial: Pivotal Study Results
The ADVENT trial was a big study that helped get the FARAPULSE system approved. It looked at patients with paroxysmal AFib and compared the PFA system to traditional ablation methods. The results at 12 months showed that the FARAPULSE system was effective in isolating the pulmonary veins, a common target for AFib ablation. It also showed a good safety profile.
MANIFEST 17K Registry: Real-World Data
Beyond the controlled ADVENT trial, the MANIFEST 17K registry provided real-world data. Registries like this collect information from actual patient cases as they happen in regular clinical practice. This helps confirm that the system performs as expected outside of a strict trial setting. The data from MANIFEST 17K supported the findings from the ADVENT trial, adding more confidence in the system’s performance.
Expanding Indications and Future Trials
So, the FARAPULSE PFA system got the green light from the FDA for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, which is great news. But what’s next? It’s not just about treating the most common type of AF anymore. Boston Scientific is looking at how this technology can help more people with different kinds of AF and even other heart rhythm issues.
Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: ADVANTAGE AF Trial
One of the big areas they’re exploring is persistent atrial fibrillation. This type of AF is trickier to treat than paroxysmal AF because the heart rhythm has been irregular for a longer time. The ADVANTAGE AF trial is designed to see if the FARAPULSE PFA system can be effective in these more complex cases. Early results are promising, suggesting that pulsed field ablation might offer a way to isolate the pulmonary veins and other areas causing the irregular rhythm, even when the AF has been going on for a while. This could mean a new treatment option for a significant number of patients who haven’t responded well to other therapies.
Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablations: FARAPOINT PFA
Beyond AF, the team is also investigating the FARAPULSE system for other procedures. The FARAPOINT PFA study is looking into using this technology for cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI) ablations. The CTI is a specific area in the heart that can be involved in certain types of arrhythmias, particularly typical atrial flutter. Using PFA here could offer a more targeted approach, potentially reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional thermal ablation methods. This expansion shows the versatility of the PFA technology.
First-Line Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation
There’s also a lot of talk about whether PFA, and specifically the FARAPULSE system, could become a go-to treatment right from the start for atrial fibrillation. Instead of patients trying medications first, the idea is that PFA could be offered as an initial therapy. This would be a pretty big shift. The ongoing research and real-world data collection are key to building the case for this. If PFA proves to be safe and effective as a first-line option, it could change how AF is managed for many patients, potentially leading to better long-term outcomes and fewer medication side effects.
Technological Advancements and System Integration
Boston Scientific hasn’t just brought a new ablation method to the table with FARAPULSE; they’ve also put a lot of thought into how it all works together. It’s not just about the catheter or the generator in isolation. They’ve focused on making the whole system user-friendly and effective.
FARAWAVE Ablation Catheter Innovations
The FARAWAVE catheter is pretty neat. It’s designed to deliver pulsed electric fields in a way that targets the specific tissue causing the arrhythmia, leaving surrounding tissues pretty much alone. This tissue-selective approach is a big deal because it means less collateral damage. The catheter itself has a unique structure that helps create a consistent electrical field, which is key for reliable ablation. They’ve also worked on making it flexible and easy to maneuver, which is always a plus for the doctors using it.
FARASTAR Ablation Generator Features
This is the powerhouse behind the FARAPULSE system. The FARASTAR generator is built to deliver those precise electrical pulses. It’s got a straightforward interface, making it easier for clinicians to set up and control the energy delivery. The generator is designed to work seamlessly with the FARAWAVE catheter, ensuring that the right amount of energy is delivered at the right time. It also includes safety features to monitor the procedure and provide feedback.
VersaCross Connect Access Solution
Getting to where you need to be in the heart is half the battle, right? The VersaCross Connect is an access solution that helps with this. It’s designed to make it easier and safer to cross the septum and get the ablation catheter into position. Think of it as a specialized tool that simplifies a complex part of the procedure. It’s all about improving workflow and reducing the time it takes to get the job done.
Integration with Mapping Systems
One of the really smart things Boston Scientific has done is integrate the FARAPULSE system with their existing mapping technology, like the OPAL HDx™ Mapping System and the FARAVIEW™ Software Module. This means doctors can see exactly where they are in the heart and visualize the electrical activity in real-time. When you combine this detailed mapping with the FARAPULSE ablation, it allows for a more precise and personalized treatment. They’ve even had workshops where people can get hands-on experience with this integration, showing how it can streamline procedures like pulmonary vein isolation.
Clinical Applications and Patient Outcomes
So, what does this all mean for patients? The FARAPULSE PFA system is really making waves when it comes to treating atrial fibrillation (AFib). It’s designed to be super precise, targeting the heart tissue causing the irregular heartbeat without messing with the surrounding areas. This tissue-selective approach is a big deal.
Pulmonary Vein Isolation Efficacy
One of the main jobs of ablation is to isolate the pulmonary veins, which are often the source of AFib signals. The FARAPULSE system has shown some really good results here. Studies have indicated high rates of successful pulmonary vein isolation, meaning the signals from those veins are effectively blocked. This is key to restoring a normal heart rhythm. The goal is to create a durable block, and early data suggests this is happening.
Posterior Wall Ablation Success Rates
The back wall of the left atrium can also be a tricky spot for AFib. Ablating this area can be challenging with older methods. However, the FARAPULSE system, with its flexible catheter design, seems to handle these complex anatomies pretty well. Reports suggest good success rates when targeting the posterior wall, which is great news for patients who might have had AFib originating from that region.
Safety Profile: Adverse Event Analysis
When you’re talking about heart procedures, safety is always top of mind. The FARAPULSE PFA system is designed with safety in mind, aiming to reduce the risks associated with traditional thermal ablation methods like radiofrequency or cryoablation. While all medical procedures have some level of risk, the data coming out about FARAPULSE shows a favorable safety profile. This includes looking at things like esophageal injury, phrenic nerve issues, and other complications. The aim is to make the procedure as safe as possible for the patient.
The Competitive Landscape of PFA
So, Boston Scientific’s FARAPULSE PFA system is out there, and it’s definitely shaking things up. But they aren’t the only ones playing in the pulsed field ablation (PFA) sandbox. It’s a pretty exciting space right now, with a few big players really pushing the technology forward. Think of it like a race, and everyone’s trying to get to the finish line first with the best solution for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Boston Scientific’s Position in the Market
Boston Scientific snagged FDA approval for their FARAPULSE PFA System, which is a pretty big deal. It means they’ve got a solid product that’s been through the hoops and shown it works for paroxysmal AF. They’ve got the FARAWAVE catheter, the FARASTAR generator, and the FARADRIVE sheath all working together. Plus, they’re already looking at expanding its use, like for persistent AF and even cavotricuspid isthmus ablations. They’re also testing it out as a first-line treatment, which could really change how AF is managed if it pans out.
Comparison with Other PFA Systems
It’s not just Boston Scientific, though. Johnson & Johnson’s Biosense Webster is another major player. They’ve got their VARIPULSE catheter and TRUPULSE generator, and they’ve seen good results from their inspIRE and admIRE trials. Medtronic is also in the mix with their PulseSelect system, which is being studied in the big PULSED AF trial. Each company has its own approach to the catheter design and generator technology. For instance, Biosense Webster’s catheters have different shapes, and Medtronic’s system is also being evaluated in large-scale studies. The key difference often comes down to the specific waveform technology, catheter maneuverability, and how well the system integrates with existing electrophysiology lab setups.
Here’s a quick look at some of the systems:
| System Name | Company | Key Components | Status/Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| FARAPULSE PFA | Boston Scientific | FARAWAVE Catheter, FARASTAR Generator, FARADRIVE Sheath | FDA Approved (Paroxysmal AF), trials for persistent AF, CTI, first-line tx |
| VARIPULSE/TRUPULSE | Biosense Webster (J&J) | VARIPULSE Catheter, TRUPULSE Generator | European trials completed, US trials underway |
| PulseSelect | Medtronic | PulseSelect PFA System | Investigational device trials underway (PULSED AF trial) |
Future of Cardiac Ablation Technologies
Looking ahead, PFA is definitely the hot topic. It seems like it’s going to become a standard option, maybe even replacing some of the older methods like radiofrequency ablation because it’s so good at targeting just the heart tissue without harming the stuff around it. We’re seeing trials that are pushing the boundaries, like looking at PFA for persistent AF, which is trickier than paroxysmal AF, and even using it as the very first treatment option before drugs. It’s going to be interesting to see how these technologies evolve and how they get integrated into everyday procedures. The goal is always to make things safer and more effective for patients, and PFA seems to be a big step in that direction.
A New Chapter in Heart Ablation
So, Boston Scientific’s FARAPULSE system getting the green light from the FDA is pretty big news. It’s a different way to handle atrial fibrillation, using electrical pulses instead of heat or cold. Early studies, like the ADVENT trial, showed it works well for isolating parts of the heart that cause AFib, and it seems to be pretty safe too, with good results at the one-year mark. This technology is still being explored in more trials, looking at different types of AFib and even as a first-line treatment. It really feels like we’re seeing a shift in how these heart rhythm issues are treated, and the FARAPULSE system is right at the forefront of that change.