Understanding The Core Components Of How Does A Robot Works
So, how does a robot actually do its thing? It might seem like magic, but it’s really just a combination of a few key parts working together. Think of it like building with LEGOs, but way more complicated and with actual movement involved.
Mechanical Engineering: The Robot’s Structure
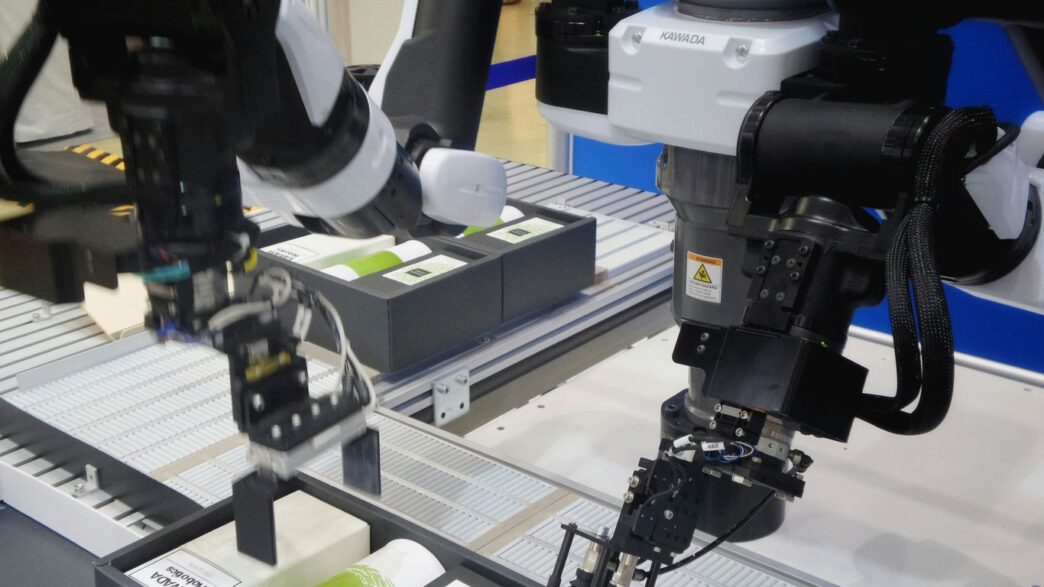
This is all about the robot’s body. It’s the metal, plastic, and wires that give the robot its shape and allow it to move around. Engineers in this field design everything from the robot’s arms and legs to its wheels and joints. They figure out how to make sure the robot can reach, grab, or move without falling apart. It’s like designing the skeleton and muscles of a creature.
Electronics: The Robot’s Nervous System
If the mechanics are the body, then electronics are the nervous system. This is where all the wires, circuits, sensors, and motors come together. Sensors are like the robot’s eyes and ears, letting it know what’s going on around it – is there an object in the way? How hot is it? Motors are what make the robot move, turning electrical signals into physical action. This intricate network of electronic components allows the robot to sense its environment and react to it.
Programming: The Robot’s Brain
Finally, we have the programming, which is the robot’s brain. This is the code that tells the robot what to do. It takes the information from the sensors and decides how the motors should move. Programmers write instructions that guide the robot through its tasks, whether it’s picking up a box, welding a car part, or exploring a new planet. It’s like giving the robot a set of commands to follow.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Structure (Mechanical): The physical body, limbs, and movement parts.
- Sensing & Acting (Electronics): The eyes, ears, nerves, and muscles that interact with the world.
- Decision Making (Programming): The instructions that tell the robot what to do and how to do it.
Foundational Steps To Learning Robotics
So, you’re curious about how robots work and maybe even want to build one yourself? That’s awesome! It might seem like a huge mountain to climb, but honestly, getting started is more about taking things one step at a time. Think of it like learning to cook; you don’t start by making a five-course meal, right? You begin with simple recipes.
Utilizing Robotics Kits For Beginners
One of the best ways to jump in is with a robotics kit. These kits are like a pre-packaged adventure. They usually come with all the bits and pieces you need – motors, sensors, wires, and sometimes even a little controller board. Plus, they often have instructions that are pretty easy to follow. Building a simple robot from a kit lets you get your hands dirty with the mechanics and see how things fit together. It’s a really hands-on way to learn without getting overwhelmed. You get to see your creation come to life, which is super rewarding.
Exploring Tutorials And Books
Beyond kits, there’s a whole universe of learning materials out there. Online, you’ll find tons of video tutorials that walk you through specific projects or explain concepts step-by-step. Some are really well done and make complex ideas seem simple. Then there are books. While maybe not as flashy as videos, books can offer a more structured and in-depth look at the theory behind robotics. You can find resources that cover everything from basic electronics to programming languages used in robotics. Finding a mix of visual and text-based learning often works best for most people.
Building A Sturdy Foundation
No matter how you choose to start, the main goal is to build a solid base. This means getting comfortable with the core ideas. What makes a robot move? How does it sense its surroundings? How do you tell it what to do? Answering these questions through your initial projects will make tackling more advanced topics much easier down the road. It’s like laying the groundwork for a building; if it’s strong, you can build something amazing on top of it. Don’t be afraid to start small and celebrate each little success along the way. That’s how you build confidence and keep the momentum going.
Robotics Education In And Beyond The Classroom
Demystifying Robotics In Schools
Lots of schools are starting to bring robotics right into the classroom these days. It’s a neat way to make subjects like physics or math feel more real. Instead of just reading about how things move, students can program a robot to actually do it. This hands-on approach helps make abstract ideas click. It’s not just about building robots, either; it’s about learning how to think through problems and work with others to find solutions. These practical experiences are a big step in showing kids how science and technology work in the real world.
Extracurricular Opportunities
Beyond the regular school day, there are tons of ways to get more involved with robotics. Think summer camps or weekend workshops. These can be super intense and let you tackle projects that are a bit more complex than what you might do in class. Robotics clubs are also popping up everywhere. They’re great places to meet other people who are into robotics, share ideas, and maybe even get ready for competitions. These events are often where you see students go from just learning about robots to actually creating their own.
Online Courses And Real-World Projects
If you can’t make it to a physical club or camp, the internet is a massive resource. There are countless online courses available, covering everything from the basics of coding to more advanced robot design. You can learn at your own pace, which is pretty handy. Then there are real-world projects. This could be something you start on your own, like trying to build a small automated helper for your room, or even joining a community project. Working on actual projects is where you really get to apply what you’ve learned and see how it all fits together. It makes learning stick way better than just reading about it.
Types Of Robots And Their Applications
When we talk about robots, they generally fall into two main categories: the ones that stay put and the ones that move around. It sounds simple, but understanding the differences here is pretty important if you’re thinking about how robots can actually help out.
Fixed Articulated Arms
These are the robots you often see in factories, the ones with the bendy arms. They’re great for doing the same job over and over again, really fast. Think of them like a super-precise, tireless worker for specific tasks. They can be:
- Industrial Arms: These are the heavy hitters. They need a lot of space and safety measures because they move quickly and can lift heavy things. They’re perfect for big jobs where speed is key, like moving lots of items from one place to another very quickly. However, they can be tricky to set up in smaller places or if your workflow changes a lot.
- Collaborative Arms (Cobots): These are designed to work alongside people. They’re usually smaller and slower, and they can move out of the way when a human needs to get by. They’re good for tasks like packing items into boxes at a workstation, where a human might also be working.
These arms are getting smarter, too. Many now have "eyes" (vision systems) and "brains" (intelligent controllers) that help them understand what’s going on around them and adjust their actions. Some are even using AI to get better at their jobs.
Mobile Robots: AGVs And AMRs
These robots are all about getting from point A to point B. The two main types you’ll hear about are AGVs and AMRs.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Imagine a robot following a set path, like a train on tracks. That’s basically an AGV. They’re predictable and great for moving things along a fixed route, especially in busy areas where you need things to move quickly and reliably. They used to be mostly for brand-new setups, but newer versions can work in existing facilities too.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): These are the more independent movers. AMRs don’t need a set path. They can figure out how to get around on their own, dodging obstacles, other machines, and people. They’re really flexible and can handle different jobs, like bringing items to a person who’s working. They’re becoming more common because they can adapt to changing environments easily.
Choosing the right robot, whether it’s a fixed arm or a mobile one, really depends on what you need it to do. It’s not a one-size-fits-all situation, and often, talking to experts can help you figure out the best fit for your specific needs.
The Importance Of Continuous Learning In Robotics
Look, the world of robotics isn’t exactly standing still. New tech pops up faster than you can say "actuator." If you’re serious about this stuff, you can’t just learn it once and call it a day. It’s like trying to keep up with the latest phone models – you gotta keep reading, keep tinkering.
Staying Updated With New Technologies
Think about it. Just when you get comfortable with one type of sensor, a whole new generation comes out, way better and cheaper. Or maybe a new programming language becomes the go-to for AI in robots. You need to know about these things. It’s not just about knowing the old stuff; it’s about knowing what’s next.
- Keep an eye on industry news: Follow robotics companies and research labs online.
- Experiment with new tools: If a new development kit comes out, try to get your hands on it.
- Attend webinars or online talks: Many companies and universities host free sessions.
Leveraging Online Platforms And Journals
There are tons of places online where people share what they’re working on. You’ve got academic journals, sure, but also forums, blogs, and even YouTube channels where engineers show off their projects. It’s a goldmine of information if you know where to look. You can find detailed breakdowns of how someone solved a tricky problem, or get early looks at upcoming tech.
| Platform Type | Example Resources |
|---|---|
| Academic Journals | IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, Science Robotics |
| Online Forums | Reddit (r/robotics), Stack Exchange Robotics |
| Developer Blogs | Company engineering blogs (e.g., Boston Dynamics) |
Becoming A Leader In The Field
Honestly, if you’re always learning and trying new things, you’re naturally going to get ahead. People notice when you’re up-to-date and can talk intelligently about the latest advancements. It’s not just about being good at building robots; it’s about being someone who understands where the field is going. That’s how you move from just being a participant to actually shaping what happens next. It takes effort, sure, but the payoff is huge.
Tracking Progress And Quantifying Achievements
So, you’ve been building robots, tinkering with code, and generally getting your hands dirty in the world of robotics. That’s awesome! But how do you actually show what you’ve accomplished? It’s not just about having a cool project; it’s about being able to point to concrete results. This is where tracking your progress and quantifying your achievements really comes into play.
Measuring Project Outcomes
Think about it like this: if you build a robot arm to help with a repetitive task, did it actually speed things up? By how much? Maybe you implemented a new algorithm that cut down on errors. Quantifying these improvements turns your work from just ‘a thing I built’ into ‘a thing I built that achieved X result’. This could look like:
- Efficiency Gains: Did your robot complete a task 15% faster than before?
- Error Reduction: Did a software update decrease the number of mistakes by 10%?
- Cost Savings: Did your automated solution reduce material waste by a measurable amount?
Keeping a logbook or a digital record of these metrics is super helpful. It’s easy to forget the exact numbers after a while, but having them written down makes a big difference.
Demonstrating Skills To Employers
When you’re looking for a job or even just trying to impress a mentor, you need more than just a resume listing skills. You need proof. Those quantified achievements we just talked about? They’re your proof. Instead of just saying ‘I know Python,’ you can say, ‘I used Python to develop a control system that improved robot navigation accuracy by 20%.’ That’s way more impactful.
Here’s a quick way to think about presenting your work:
| Skill Area | Project Example | Quantifiable Result |
|---|---|---|
| Programming (C++) | Autonomous Navigation System | Reduced pathfinding time by 30% |
| Mechanical Design | Gripper Mechanism for Delicate Objects | Increased successful pick-and-place rate to 98% |
| Sensor Integration | Object Detection for Obstacle Avoidance | Decreased collision incidents by 50% |
This kind of detail shows employers you understand not just the theory but also the practical impact of your work.
Validating Expertise
Ultimately, tracking your progress helps you see how far you’ve come and validates your growing knowledge. It’s a way to build confidence in your abilities. When you can look back at a project and say, ‘I solved this specific problem, and here’s the data to prove it,’ you know you’re not just dabbling; you’re genuinely developing expertise. This self-validation is important, and it naturally leads to greater confidence when you’re discussing your projects or taking on new challenges in the robotics field.
So, What’s Next?
Look, robotics might seem like something out of a sci-fi movie, but it’s really just a mix of making things move, giving them senses, and telling them what to do. We’ve broken down the basics – the nuts and bolts, the wires and circuits, and the code that makes it all happen. It’s not magic, it’s engineering. Whether you’re tinkering with a kit at home, learning in a classroom, or even just curious about how those warehouse robots work, the core ideas are the same. The world of robots is growing, and understanding how they function is the first step to being a part of it. So, don’t be intimidated. Start small, keep learning, and who knows, maybe you’ll be building the next big thing.