Introduction
In the realm of medical imaging, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) stands as a vital tool for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. One particular MRI technique that has gained prominence over the years is Short Tau Inversion Recovery, often abbreviated as STIR MRI. This advanced imaging method has proven to be invaluable in clinical practice, offering unique insights into soft tissues and enhancing our ability to detect and characterize abnormalities. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of STIR MRI, exploring its principles, applications, and benefits.
Understanding the Basics
What Is STIR MRI?
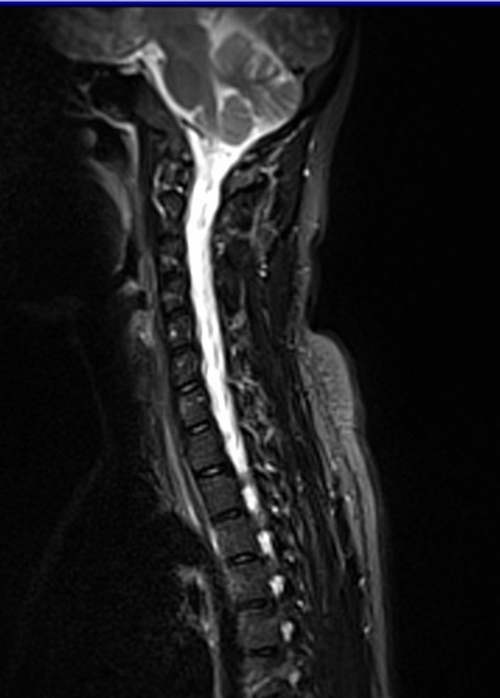
STIR MRI is a specialized MRI technique used to create images with high contrast between different types of soft tissues. It accomplishes this by suppressing the signal from fat tissues, which makes it particularly useful for visualizing structures like muscles, blood vessels, and tumors. Unlike conventional MRI sequences, STIR MRI selectively nullifies the signal from fat while preserving the signal from water-based tissues.
How Does It Work?
STIR MRI employs a technique called “inversion recovery.” In this process, a radiofrequency pulse is used to invert the magnetization of all tissues, effectively flipping their magnetic orientations. Subsequently, a second radiofrequency pulse is applied to selectively excite the water-based tissues while leaving the fat tissues in a “null” state. As a result, the image primarily reflects the distribution of water in the body, offering excellent tissue contrast.
Applications of STIR MRI
STIR MRI has found applications across various medical disciplines, owing to its ability to highlight specific tissues and pathology. Here are some key areas where STIR MRI proves invaluable:
Musculoskeletal Imaging
In orthopedics and sports medicine, STIR MRI is commonly used to visualize musculoskeletal structures such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It provides detailed information about injuries, inflammation, and degenerative changes, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning of conditions like ligament tears and osteoarthritis.
Oncology
STIR MRI plays a crucial role in oncology by helping detect and characterize tumors. Its ability to suppress fat signals enhances the visibility of lesions within the body, making it easier to identify and assess the extent of malignancies. It is particularly useful in breast and prostate cancer imaging.
Vascular Imaging
In vascular imaging, STIR MRI is used to visualize blood vessels and detect vascular anomalies. By suppressing fat signals, it improves the contrast of blood vessels against surrounding tissues, making it easier to diagnose conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and vascular malformations.
Neuroimaging
STIR MRI is employed in neurology to study the brain and spinal cord. It helps visualize lesions, demyelination, and inflammation in conditions such as multiple sclerosis. Additionally, STIR sequences can be useful in identifying brain tumors and abnormalities in the spine.
Benefits of STIR MRI
- Enhanced Soft Tissue Contrast: STIR MRI excels in highlighting soft tissues, offering improved contrast compared to conventional MRI sequences, which can be especially valuable in detecting subtle abnormalities.
- Fat Suppression: By selectively suppressing fat signals, STIR MRI minimizes interference from fat tissue, making it an excellent choice for imaging areas with a high fat content.
- Accurate Diagnosis: The superior tissue contrast provided by STIR MRI enhances diagnostic accuracy, allowing healthcare professionals to make more informed decisions regarding patient care and treatment.
- Non-Invasive: Like standard MRI, STIR MRI is non-invasive and does not involve ionizing radiation, making it safe for patients.
Conclusion
STIR MRI is a powerful imaging technique that has revolutionized the way we examine and diagnose various medical conditions. Its ability to selectively suppress fat signals and emphasize water-based tissues has made it an indispensable tool in fields such as musculoskeletal imaging, oncology, vascular imaging, and neuroimaging. The enhanced soft tissue contrast it offers allows for more accurate diagnoses and better treatment planning. As technology continues to advance, STIR MRI is likely to play an even more significant role in the future of medical imaging, contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.