Artificial intelligence, or AI, is changing how we do things in medicine. It’s showing up in all sorts of medical tools and devices, making them smarter and more helpful. We’re seeing these ai medical devices pop up everywhere, from helping doctors figure out what’s wrong to planning out treatments. It’s a big shift, and it’s important to get a handle on what’s happening, what the rules are, and what it all means for patients and doctors alike. This is a look at how these tools are changing healthcare now and what we can expect down the road.
Key Takeaways
- AI is making medical tools better at spotting diseases and looking at scans, helping doctors make faster, more accurate calls.
- These smart tools can help create treatment plans made just for you, based on your specific health info.
- New rules are being made to keep up with how fast AI is changing, with groups like the FDA working on ways to approve these new ai medical devices.
- Figuring out who’s responsible when an AI makes a mistake is a big question, and we need clear rules for trust and safety.
- AI is not just about replacing people; it’s about working together, with AI helping doctors so they can focus more on patient care.
Advancements in AI Medical Devices
Artificial intelligence is really changing how we do medicine, and it’s happening fast. It’s not just about fancy new gadgets; it’s about making healthcare smarter and more effective for everyone involved.
Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Imaging
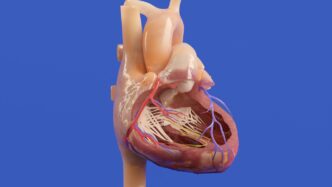
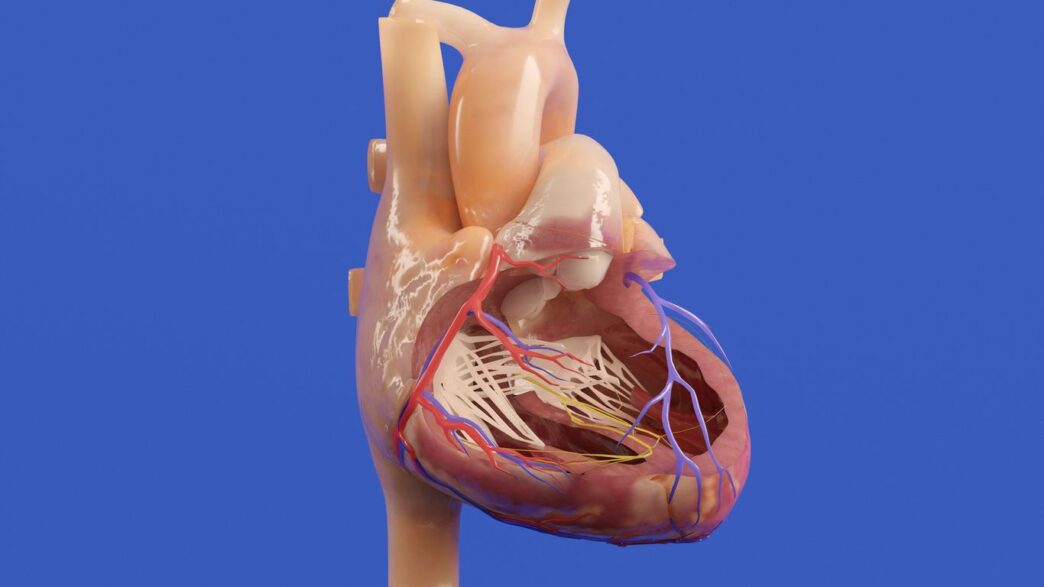
Think about looking at medical scans like X-rays or MRIs. AI can now look at these images and spot things that might be really hard for a human eye to catch. It’s like having a super-powered assistant that’s been trained on millions of images. This means doctors can get to a diagnosis quicker and with more certainty. It’s a big deal for catching diseases early when they’re easiest to treat.
Personalized Treatment Planning
We’re all different, right? So why should our medical treatments be one-size-fits-all? AI is helping to change that. By looking at a patient’s unique health history, genetic makeup, and even how they’ve responded to past treatments, AI can help doctors figure out the best plan for that specific person. This isn’t just about picking the right drug; it’s about tailoring the whole approach to get the best results and avoid side effects. It makes healthcare feel much more focused on the individual.
Predictive Analytics for Patient Outcomes
This is where AI gets really interesting for preventing problems before they happen. By sifting through tons of patient data, AI can start to predict who might be at risk for certain health issues down the line. This gives doctors a heads-up, allowing them to step in early with preventative measures. It’s a shift from just treating sickness to actively keeping people healthy. This proactive approach can really make a difference in how well people do over time and can also help hospitals manage their resources better.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape for AI

AI in medicine isn’t just a tech story—it’s a legal and regulatory challenge, too. As smart algorithms show up in exam rooms, radiology labs, and even virtual care apps, the rules are rushing to catch up. Lately, the US government and global regulators are paying much more attention, especially as AI tools become less predictable and keep learning after deployment.
FDA’s Adaptive Framework for AI
The FDA has long been the gatekeeper for new medical tools in the US. But AI isn’t like a drug or a traditional device—it changes over time. Right now, the FDA mostly reviews what are called "locked algorithms," which stay the same after approval. But AI that adapts in real-world use is pushing the FDA to rethink its rules. Draft frameworks talk about pre-launch checks and also keeping tabs on devices after they hit the market.
Main features of the FDA’s approach:
- Focus on transparency: Companies may need to explain how and why their AI makes certain choices.
- Life-cycle oversight: Ongoing monitoring is being discussed to keep up with changes in adaptive algorithms.
- Emphasis on collaboration: The FDA wants input from industry, hospitals, and even patients before finalizing any new rules.
Navigating Challenges with Locked Algorithms
A "locked" algorithm is set in stone once it leaves the factory. That’s simple to regulate. But as hospitals and software companies demand more adaptable AI, the older frameworks don’t always work.
Key challenges with locked vs. adaptive algorithms:
- Locked algorithms are easy to audit but can’t learn from new data or surprises.
- Adaptive models can keep improving, but regulators worry they might change in dangerous or unpredictable ways.
- Hospitals using locked models may end up falling behind on best practices if they can’t update their tools quickly enough.
Regulators are walking a tightrope—balancing safety with innovation, and that means constant tweaks to existing rules.
The FTC’s Growing Role in AI Oversight
The FDA isn’t the only agency interested in AI medical devices. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is stepping up, especially where patient privacy and data ethics are concerned. Recently:
- The FTC started using tools like algorithmic discouragement, which lets them force companies to delete harmful algorithms and any related data sets.
- They’re keeping a close eye on how companies claim their AI works, trying to spot false marketing or promises.
- The FTC may get more power to act in AI cases that cross from mere "health tech" into regulated healthcare services.
Here’s a simple table showing which agency does what:
| Agency | Focus Area | Example Actions |
|---|---|---|
| FDA | Device safety and performance | Approving new devices, inspecting for compliance |
| FTC | Fair marketing, protecting users | Investigating misleading ads, enforcing data privacy |
As this all plays out, expect more rules, more public comments, and—for companies—more paperwork. In 2026, the rules of yesterday may not fit the devices of tomorrow.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Bringing AI into healthcare isn’t just about new tech; it’s a whole new ballgame when it comes to who’s responsible and what’s right. It gets complicated fast.
Liability and Accountability in AI-Driven Decisions
So, what happens when an AI makes a mistake? Who takes the blame? Is it the doctor who used the AI, the company that made it, or the hospital that installed it? These are the big questions we’re wrestling with. We need clear rules about this. Right now, it’s a bit of a gray area. Establishing who is accountable when AI systems are involved in patient care is a major hurdle. It’s not as simple as pointing a finger; the decision-making process can be so complex.
Here’s a breakdown of who might be in the hot seat:
- AI Developers: They built the system. Did they test it enough? Were there flaws in the code?
- Healthcare Providers: They used the AI. Did they follow the guidelines? Did they override it when they should have, or trust it too much?
- Healthcare Institutions: They bought and implemented the AI. Did they provide proper training? Was the system properly maintained?
Ensuring Transparency and Trust
People are naturally wary of things they don’t understand, and AI can be a black box. If a doctor can’t explain why an AI suggested a certain treatment, it’s hard for patients to trust it. And honestly, it’s hard for the doctor to trust it too. We need AI systems that can show their work, so to speak. This means being able to explain how the AI arrived at its conclusion. It’s not just about making the AI work; it’s about making it understandable.
Building trust involves a few key things:
- Clear Communication: Explaining to patients how AI is being used in their care, what data it uses, and what the potential outcomes are. This is part of getting informed consent, which is a big deal.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Developing AI that can provide reasons for its recommendations. This helps clinicians validate the AI’s output.
- Auditable Systems: Having systems in place that can track AI decisions and the data used, making it easier to investigate issues if they arise.
Ethical Frameworks for AI Integration
We can’t just throw AI into hospitals and hope for the best. We need a plan, a set of rules that guide how we use it. This includes thinking about things like patient privacy and making sure AI doesn’t introduce new biases into healthcare. For example, if an AI is trained on data that mostly represents one group of people, it might not work as well for others. That’s not fair, and it’s not ethical.
Key ethical considerations include:
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive patient information is non-negotiable. Robust encryption and strict access controls are a must.
- Bias Mitigation: Actively working to identify and remove biases in AI algorithms to ensure equitable care for all patients.
- Human Oversight: Always keeping a human in the loop. AI should assist, not replace, the judgment of healthcare professionals. They need to be able to question and override AI recommendations when necessary.
Future Trends in AI Medical Devices
Looking ahead, the world of AI in medical devices is set to get even more interesting. We’re talking about technologies that will make AI easier to understand, protect patient data better, and really fine-tune treatments to each person.
Explainable AI for Enhanced Understanding
One big area is something called Explainable AI, or XAI. Right now, some AI can feel like a black box – it gives an answer, but we don’t always know how it got there. XAI aims to change that. The goal is to make AI’s decision-making process clear and understandable to doctors and patients. This is super important in healthcare. If an AI suggests a certain diagnosis or treatment, clinicians need to know why. XAI can show the data points and logic that led to that conclusion, building more trust and allowing for better collaboration between human experts and the AI. It’s like having a smart assistant that can actually show its work.
Federated Learning for Data Privacy
Data privacy is a huge concern, especially with sensitive medical information. Federated learning is a clever way to train AI models without actually moving or sharing raw patient data. Imagine multiple hospitals wanting to train an AI to spot a rare disease. Instead of sending all their patient records to one central place, the AI model travels to each hospital. It learns from the local data there and then sends back only the learned patterns, not the actual patient details. This way, the AI gets smarter from a larger pool of information, but each hospital’s data stays put. It’s a big step for privacy-preserving AI in research and clinical practice.
Predictive Genomics and Personalized Medicine
This is where AI really starts to get personal. By combining AI with genomic data – essentially, our DNA – we can predict health risks with more accuracy. AI can sift through vast amounts of genetic information to identify patterns linked to certain diseases. This isn’t just about predicting problems, though. It’s also about figuring out the best treatment for you, based on your unique genetic makeup. Think of it as moving beyond one-size-fits-all medicine to treatments that are tailored specifically to an individual’s biology. This could mean more effective therapies with fewer side effects, truly ushering in an era of precision medicine.
Human-Machine Collaboration in Healthcare
It’s pretty wild to think about how much AI is changing things in hospitals and clinics, right? It’s not about robots taking over, though. The real story is how doctors, nurses, and other healthcare folks are starting to work with these AI tools. Think of it like a super-smart assistant that can sift through mountains of patient data way faster than any human ever could.
AI as a Supportive Tool for Clinicians
This is where AI really shines. It can spot patterns in scans or patient histories that might be easy to miss, giving clinicians a heads-up. It’s not making the final call, though. The idea is that AI handles the heavy lifting of data analysis, freeing up the human expert to do what they do best: connect with the patient, understand their unique situation, and make the final, informed decision. It’s about augmenting, not replacing, the human touch.
Balancing Human Expertise with AI Capabilities
Finding that sweet spot between what AI can do and what a human can do is key. AI is great with numbers and data, but it doesn’t have empathy or the ability to read a room. A doctor can pick up on subtle cues from a patient’s body language or tone of voice that an AI wouldn’t even register. So, the goal is to use AI for what it’s good at – processing information – and let humans handle the parts that require emotional intelligence and real-world context. It’s a partnership.
Enhancing Patient Care Through Collaboration
When humans and AI work together, the patient often benefits the most. Imagine a doctor having AI-generated insights at their fingertips during a consultation. This can lead to quicker, more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans that are more tailored to the individual. Plus, AI-powered tools can help streamline a lot of the behind-the-scenes work, like managing appointments or sending out reminders, which means less waiting and a smoother experience for everyone involved. It’s all about making healthcare work better for the person at the center of it all.
Impact on Clinical Operations and Patient Experience
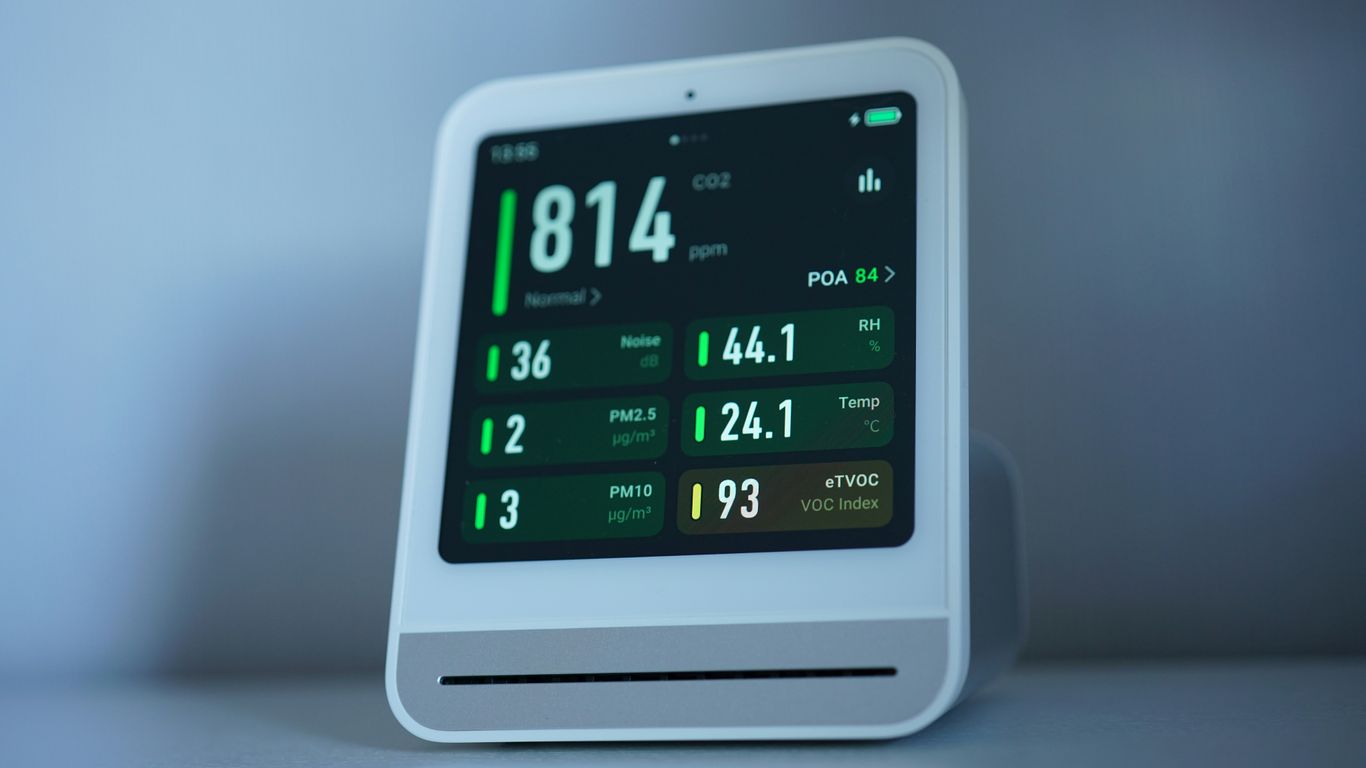
AI is really changing how hospitals run day-to-day and how patients feel about their care. It’s not just about the fancy new tech; it’s about making things smoother for everyone involved.
Streamlining Workflows with AI
Think about all the paperwork and repetitive tasks that bog down healthcare staff. AI can step in here. It can help sort through patient records faster, manage appointment scheduling, and even assist with billing. This means doctors and nurses can spend less time on administrative stuff and more time actually caring for people. It’s like giving them a super-efficient assistant.
Here’s a quick look at how AI can speed things up:
- Faster Image Analysis: AI can review X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans in minutes, flagging potential issues that a human might miss or take much longer to find. This speeds up diagnosis significantly.
- Automated Reporting: Generating reports can be time-consuming. AI can help draft initial reports based on data, which clinicians can then review and finalize.
- Resource Management: Predicting patient flow and managing staff schedules becomes more accurate with AI, reducing wait times and optimizing the use of hospital beds and equipment.
Improving Patient Engagement with Virtual Assistants
Patients often have questions or need reminders about their care. AI-powered virtual assistants can handle a lot of this. They can answer common questions 24/7, send out appointment reminders, provide medication instructions, and even help patients track their progress at home. This constant availability and personalized communication can make patients feel more connected and in control of their health. It’s a big step up from just waiting on hold or trying to remember what the doctor said.
The Rise of Digital Therapeutics
Beyond just helping with operations, AI is also leading to new kinds of treatments themselves. Digital therapeutics, often powered by AI, are software programs designed to treat, manage, or prevent a disease or disorder. These can range from apps that help manage chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease to virtual reality programs used for pain management or mental health therapy. They offer a way to deliver care directly to patients, often in their own homes, making treatment more accessible and convenient. It’s a whole new way of thinking about medicine, moving beyond pills and procedures to include digital tools as legitimate forms of therapy.
Looking Ahead
So, where does all this leave us? AI in medical devices isn’t just a futuristic idea anymore; it’s here and it’s changing things fast. We’ve seen how it can help doctors spot problems earlier, figure out the best treatments for each person, and even help manage appointments. But it’s not all smooth sailing. We still need to figure out the tricky parts, like making sure these AI systems are safe, fair, and that we know who’s responsible if something goes wrong. Plus, getting everyone on board with these new tools takes time and effort. The future looks bright, with AI likely becoming an even bigger part of how we get healthcare, but we’ve got to keep working on the details to make sure it benefits everyone.