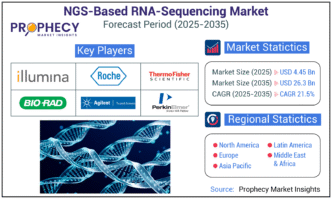
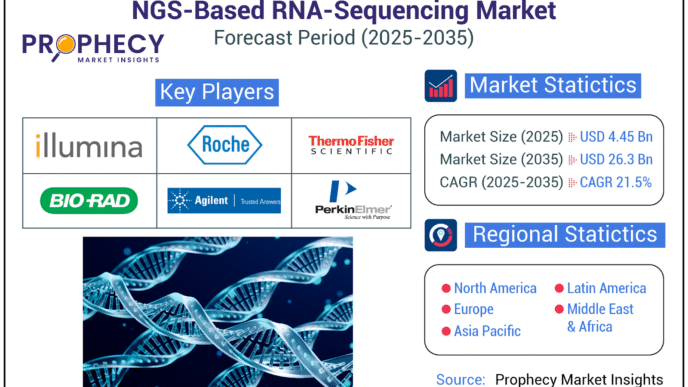
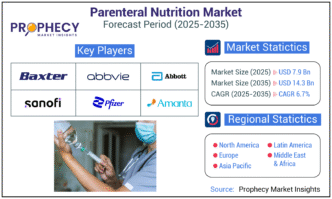
Introduction:
The financial landscape has undergone a profound transformation with the advent of digital finance, reshaping the way individuals and businesses manage, invest, and interact with their finances. From online banking and mobile payment solutions to cryptocurrency and robo-advisors, digital finance has become a cornerstone of the modern economy. In this article, we delve into the dynamic world of digital finance, exploring its key components, benefits, challenges, and the transformative impact it has on the financial industry.
The Pillars of Digital Finance:
- Online Banking:
- Online banking has become a fundamental aspect of digital finance, allowing users to manage their accounts, conduct transactions, and access financial services through secure web portals or mobile apps. The convenience of 24/7 access and the ability to monitor transactions in real-time has made online banking a staple for individuals and businesses alike.
- Mobile Payments and Wallets:
- Mobile payment solutions and digital wallets have revolutionized how we make transactions. From peer-to-peer payments to contactless purchases, platforms like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and various mobile banking apps provide seamless and secure methods for transferring funds.
- Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology:
- Cryptocurrencies, led by the pioneering Bitcoin, have introduced decentralized digital currencies that operate on blockchain technology. Blockchain, a distributed ledger system, ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions. Beyond Bitcoin, a multitude of cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications are reshaping the financial landscape.
- Robo-Advisors:
- Robo-advisors leverage algorithms and artificial intelligence to provide automated, algorithm-driven financial planning services. These digital platforms analyze financial data and user preferences to offer investment advice, manage portfolios, and optimize investment strategies at a fraction of the cost of traditional financial advisors.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms connect borrowers directly with lenders, bypassing traditional financial institutions. This decentralized model offers borrowers competitive interest rates and provides lenders with diversified investment opportunities.
- Open Banking:
- Open banking initiatives promote the secure sharing of financial data among different financial institutions. This enables users to access a consolidated view of their financial information across various accounts and services, fostering competition and innovation in the financial sector.
Benefits of Digital Finance:
- Convenience and Accessibility:
- Digital finance brings unparalleled convenience and accessibility. Users can manage their finances, conduct transactions, and access a wide range of financial services from the palm of their hand, irrespective of location or time.
- Cost-Efficiency:
- Many digital finance solutions offer cost-effective alternatives to traditional financial services. From lower transaction fees to reduced advisory costs through robo-advisors, digital finance often translates into savings for consumers.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Digital finance plays a pivotal role in promoting financial inclusion by providing services to individuals and businesses that may not have access to traditional banking infrastructure. Mobile banking and digital wallets empower underserved populations, enabling them to participate in the economy.
- Security and Fraud Prevention:
- Advanced encryption technologies, biometric authentication, and secure protocols contribute to the robust security of digital finance. Additionally, real-time monitoring and fraud detection tools help mitigate risks and enhance overall security.
- Efficient Investment Strategies:
- Robo-advisors use sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast amounts of financial data, tailoring investment strategies to individual risk profiles. This automated approach allows for efficient and data-driven investment decisions.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Cybersecurity Risks:
- The increased reliance on digital platforms makes the financial sector a target for cyber threats. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is paramount to safeguarding sensitive financial information and maintaining the trust of users.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- The evolving nature of digital finance often outpaces regulatory frameworks. Striking a balance between innovation and regulatory compliance is a challenge, as policymakers strive to create an environment that fosters innovation while ensuring consumer protection.
- Digital Literacy:
- The success of digital finance relies on users’ understanding of the technologies and platforms. Digital literacy becomes a barrier for those who may not be familiar with the intricacies of online transactions, cryptocurrencies, or robo-advisors.
- Privacy Concerns:
- The collection and use of vast amounts of financial data raise concerns about user privacy. Striking a balance between personalized financial services and respecting user privacy is an ongoing challenge in the digital finance landscape.
- Market Volatility:
- Cryptocurrencies, a prominent aspect of digital finance, are known for their price volatility. Investors must navigate this volatility and be aware of the associated risks when engaging in digital currency markets.
The Future of Digital Finance:
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs):
- Central banks are exploring the issuance of digital currencies as a form of legal tender. CBDCs aim to combine the efficiency of digital transactions with the stability and backing of traditional fiat currencies.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- AI is increasingly being integrated into digital finance for enhanced customer experiences, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice. Machine learning algorithms analyze data patterns, improving the accuracy of financial predictions and recommendations.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
- DeFi leverages blockchain technology to recreate and innovate traditional financial systems, providing decentralized alternatives to banking, lending, and trading. DeFi platforms aim to increase accessibility and reduce reliance on centralized financial institutions.
- Cross-Border Transactions:
- Digital finance is facilitating more efficient and cost-effective cross-border transactions. Blockchain and cryptocurrencies are reducing the friction associated with international payments, making global transactions faster and more accessible.
Conclusion:
Digital finance stands at the forefront of a transformative era in the financial industry. From revolutionizing banking and payments to reshaping investment strategies, the digitalization of finance continues to redefine the way individuals and businesses engage with their financial activities. While challenges persist, the ongoing evolution of digital finance holds the promise of increased efficiency, accessibility, and financial inclusion in the years to come.