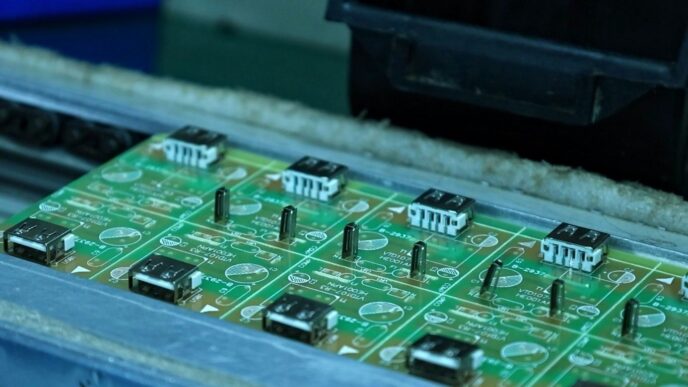
So, you’re trying to figure out the whole silicon carbide wafer scene, huh? It’s a pretty big deal these days, especially with all the buzz around electric cars and new tech. We’re looking at what’s happening in 2026, who’s making the wafers, what’s new with the tech, and why everyone suddenly needs them. It’s not just about the big companies; there’s a lot going on behind the scenes too. Let’s break it down.
Key Takeaways
- Big names like Wolfspeed, Coherent, and STMicroelectronics are major players in the silicon carbide wafer market, with companies like Resonac and SK Siltron also growing their presence globally.
- The industry is moving towards bigger wafers, like 8-inch ones, and working on better ways to grow the crystals to make production smoother and cheaper.
- Demand for these wafers is really taking off, mostly because of electric vehicles and the need for more efficient power electronics in general.
- Making silicon carbide wafers isn’t cheap, and getting enough of them can be tough due to supply chain issues, which is something companies are working to fix.
- New uses for these wafers are popping up in areas like 5G, and there’s a growing focus on making the whole process more sustainable and looking at recycling options.
Leading Silicon Carbide Wafer Manufacturers in 2026
Alright, let’s talk about who’s really making waves in the silicon carbide (SiC) wafer scene as we hit 2026. It’s a pretty dynamic market, and a few big names are definitely leading the charge, shaping how things are made and what’s even possible.
Wolfspeed Inc.: A Dominant Force
Wolfspeed has really cemented its position as a major player. They’ve been investing heavily in expanding their manufacturing capacity, especially for larger diameter wafers, which is a big deal for efficiency. Their focus on vertical integration, from raw materials to finished devices, gives them a solid advantage. They’re not just making wafers; they’re pushing the boundaries of SiC technology itself, particularly for high-power applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. You see their name popping up a lot when discussing next-gen power electronics.
Coherent Corp. and STMicroelectronics NV: Key Industry Players
These two are also right in the thick of it. Coherent Corp., through its acquisitions and internal development, has built a strong portfolio in SiC materials and devices. They’re known for their material quality and their ability to scale production. STMicroelectronics, on the other hand, is a giant in the semiconductor world, and their move into SiC is significant. They’re leveraging their existing semiconductor expertise and customer base to bring SiC solutions to a wider market, especially in automotive and industrial sectors. It’s interesting to see how they’re integrating SiC into their broader product offerings.
Resonac Holdings Corporation and SK Siltron Co., Ltd.: Expanding Global Reach
Resonac and SK Siltron are both making serious moves to grow their global footprint. They’re investing in new fabrication facilities and R&D to keep up with demand. SK Siltron, for instance, has been quite active in expanding its production capabilities, aiming to meet the surging need for SiC wafers from various industries. Resonac is also focusing on material innovation and increasing its output. Both companies are key to the global supply chain, and their expansion efforts are critical for the overall market growth.
SiCrystal GmbH and GlobalWafers Co., Ltd.: Strategic Market Positions
SiCrystal, now part of Infineon, has a long history and strong reputation in SiC technology, particularly in Europe. Their focus on high-quality wafers and advanced manufacturing processes makes them a reliable supplier. GlobalWafers, a major player in the silicon wafer industry, has also made significant strides in SiC. By applying their vast experience in wafer manufacturing to SiC, they are rapidly increasing their market share. Their strategy often involves strategic partnerships and capacity expansions to secure their position in this competitive landscape.
Technological Advancements Shaping Silicon Carbide Wafer Production
Making silicon carbide (SiC) wafers isn’t exactly a walk in the park. It’s a complex process, and manufacturers are constantly trying to figure out how to do it better, faster, and cheaper. The push for larger wafer diameters is a big deal right now.
Transitioning to Larger Wafer Diameters
For a long time, 4-inch (100mm) wafers were the standard. But the industry is moving towards 6-inch (150mm) and even 8-inch (200mm) wafers. Why? Think about baking cookies. If you have a bigger baking sheet, you can fit more cookies on it at once. It’s the same idea here. Making bigger wafers means you can produce more individual chips from a single slice of silicon carbide. This naturally helps bring down the cost per chip, which is a huge win, especially for things like electric cars and power grids that need a lot of these components.
Innovations in Crystal Growth Technologies
Growing the actual silicon carbide crystal is a really delicate step. It’s like trying to grow a perfect, giant gemstone. Companies are working on new ways to grow these crystals more efficiently and with fewer imperfections. This involves tweaking the temperatures, pressures, and the mix of gases used in the growth process. Some newer methods are looking at using plasma or special catalytic reactions to make the process more energy-efficient. We’re seeing reports of energy savings of around 20% per ton of SiC synthesized, which is pretty significant when you’re talking about industrial-scale production. Plus, better crystal growth means fewer defects, which leads to higher yields and better performance in the final devices.
Addressing Fabrication Challenges and Material Defects
Even with better crystal growth, SiC wafers can still have issues. Think of tiny cracks or impurities that can mess up how the electronic components built on them work. Manufacturers are getting smarter about identifying and fixing these problems. This includes better quality control during manufacturing and even developing ways to recycle waste SiC material. Some advanced thermal treatments can recover up to 80% of usable SiC powder from waste, which is great for both supply and sustainability. The goal is to get closer to the kind of near-perfect material you get with traditional silicon, but with all the advantages of SiC.
Market Dynamics and Growth Drivers for Silicon Carbide Wafers
So, what’s really pushing the silicon carbide (SiC) wafer market forward right now? It’s not just one thing, but a few big trends that are really making waves. Think of it like a perfect storm, but for semiconductors.
Surging Demand in Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure
This is probably the biggest driver, no surprise there. Electric vehicles (EVs) are everywhere now, and everyone’s talking about them. SiC power devices are a big reason why EVs are getting better. They help make the inverters more efficient, which means less energy wasted and longer driving ranges. Plus, with more charging stations popping up, especially fast chargers, the demand for reliable power electronics that can handle the load just keeps going up. It’s a cycle: more EVs mean more charging, which means more demand for the SiC that makes it all work.
The Role of High-Efficiency Power Electronics
Beyond just EVs, there’s a general push for more efficient electronics across the board. We’re talking about everything from industrial equipment to data centers. SiC is just plain better than traditional silicon for handling high voltages and high temperatures while losing less energy. This efficiency isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s becoming a requirement, especially as energy costs rise and companies look to cut down on their power bills. The drive for lower energy consumption is making SiC a go-to material for next-generation power systems.
Government Policies Supporting Clean Energy Technologies
Governments around the world are really pushing for cleaner energy, and that includes supporting things like EVs and renewable energy sources. Many countries have set targets for reducing emissions and increasing the use of green technologies. These policies often translate into incentives for manufacturers and consumers, which in turn boosts the demand for components like SiC wafers. It’s like a nudge from the government that helps the market grow faster. Plus, there are stricter rules about energy efficiency in many places, and SiC helps meet those standards.
Navigating Supply Chain and Cost Considerations
Okay, so let’s talk about the tricky parts of getting silicon carbide wafers – the supply chain and, well, the cost. It’s not exactly like picking up a loaf of bread, you know?
Understanding High Manufacturing Costs
Making these SiC wafers is a complex process. We’re talking about super high temperatures and really pure materials. This all adds up. The equipment needed is expensive, and the whole process takes a lot of energy. Plus, you need highly skilled people to run everything. It’s a recipe for high costs, plain and simple. The price of raw materials, especially the super-pure silicon and carbon, can really fluctuate, making it hard to pin down exact manufacturing expenses. Sometimes, you see price wars, like with 6-inch wafers dropping below $500, but that doesn’t mean the underlying costs are low; it’s often a sign of overcapacity.
Addressing Limited Availability and Supply Chain Constraints
Getting your hands on SiC wafers can sometimes feel like a treasure hunt. There aren’t that many places that make them, and they often rely on a few key suppliers for the really pure stuff. This can create bottlenecks. If one supplier has an issue, it can ripple through the whole system. We saw this a bit when electric vehicle sales slowed down temporarily in 2024; it made companies rethink their production plans. Building more resilient supply chains means looking at different suppliers and maybe even bringing some production closer to home. It’s about having backup plans.
The Impact of Global Trade and Local Sourcing
International trade rules and tariffs definitely play a role. Some countries put tariffs on imported SiC materials to help their own manufacturers. This can make things more expensive for everyone and complicate how companies get their materials. It also affects how easily companies can sell their products in different parts of the world. For smaller companies, dealing with these trade rules and the added costs can be a real challenge. Finding a balance between global sourcing and supporting local production is something many companies are thinking about right now.
Emerging Trends and Future Opportunities in the Silicon Carbide Market

Integration in 5G and High-Frequency Applications
So, silicon carbide isn’t just for electric cars, you know? It’s also becoming a big deal for the next generation of wireless tech. Think 5G and even faster stuff. SiC’s ability to handle high power and high frequencies means it’s perfect for the components that make these super-fast networks work. We’re talking about base stations, antennas, and all sorts of radio frequency (RF) devices. As we push for more data and quicker connections, the demand for SiC in this area is only going to grow. It’s a pretty exciting space to watch.
Strategic Partnerships Between OEMs and Foundries
What’s really interesting is how companies are teaming up. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) – the big brands you know – are working more closely with the foundries that actually make the silicon carbide wafers and chips. This isn’t new, but it’s getting more intense. Why? Because getting the right SiC components is super important for their products, whether it’s a car or a power supply. These partnerships help make sure that the foundries are making exactly what the OEMs need, and that the supply chain stays steady. It’s all about making sure everyone gets what they need, when they need it.
The Growing Importance of Sustainability and Recycling
And then there’s the green angle. Everyone’s talking about sustainability these days, and the SiC industry is no different. Making silicon carbide takes a lot of energy, so companies are looking for ways to be more eco-friendly. This includes:
- Using cleaner energy sources for manufacturing.
- Developing more efficient production processes that use less power.
- Exploring ways to recycle old SiC components and materials.
The push for greener manufacturing is becoming a major factor in how companies are chosen and how they operate. It’s not just good for the planet; it’s also becoming a business necessity as customers and investors pay more attention to environmental impact.
Regional Landscape of Silicon Carbide Wafer Manufacturing
When we talk about silicon carbide (SiC) wafers, it’s not really a one-size-fits-all global market. Different areas have their own strengths and focus. Understanding these regional differences is pretty important if you’re involved in this industry.
North America’s Role in Silicon Carbide Innovation
North America is really pushing the envelope when it comes to new ideas in SiC technology. While it might not be the biggest manufacturing hub right now, the region is a hotbed for research and development. Companies here are focused on creating next-generation SiC devices and improving the underlying manufacturing processes. The push for electric vehicles and advanced power electronics is a big driver, and you see a lot of investment going into R&D to meet these demands. The US, in particular, is seeing a projected fast compound annual growth rate for SiC, suggesting a significant expansion in the coming years.
Asia-Pacific’s Manufacturing Prowess
When it comes to actually making the wafers, Asia-Pacific is the undisputed leader. This region, especially China, Japan, and South Korea, accounts for a huge chunk of the global SiC wafer market share. They’ve got the established infrastructure and the sheer volume of production down pat. In 2024, Asia-Pacific brought in a massive 52.87% of the revenue for SiC wafers. This dominance is fueled by strong demand from the electronics sector and a well-developed supply chain. Companies here are also looking at expanding into larger wafer sizes, like 8-inch, to keep up with demand and improve cost-effectiveness. It’s a dynamic area where production capacity is constantly being scaled up.
Europe’s Focus on Automotive and Industrial Solutions
Europe is carving out its niche, particularly in the automotive and industrial sectors. The continent has a strong base in car manufacturing and industrial equipment, both of which are increasingly adopting SiC technology for better performance and efficiency. Think electric cars, high-speed trains, and advanced power grids. While Europe might not match Asia-Pacific’s sheer manufacturing volume, it’s a significant market for SiC wafers, with countries like Germany and the UK showing steady growth. The region is also looking at ways to secure its supply chain, with some interest in local sourcing and production to reduce reliance on other regions. The European market is expected to see substantial growth, with sales revenue projected to increase significantly over the next decade.
Looking Ahead: The SiC Wafer Scene in 2026
So, where does all this leave us as we look towards 2026? The silicon carbide wafer market is definitely heating up, with big players like Wolfspeed, Coherent, and STMicroelectronics leading the charge. We’re seeing a clear move towards bigger wafers, like 8-inch ones, which should help bring costs down and make things more efficient. Plus, SiC is becoming super important for things like 5G and electric cars. It’s not all smooth sailing, though. Making these wafers is still pretty expensive, and getting enough of them can be tricky. There are also some technical hurdles to jump over. But, with companies teaming up and investing more, it looks like the supply will get better. Keep an eye on this space, because SiC is set to play a huge role in the tech of tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Silicon Carbide (SiC) wafers and why are they important?
Silicon Carbide wafers are special discs made from a tough material called silicon carbide. They are super important because they help make electronic parts that can handle more power and work better, especially in hot conditions, compared to regular silicon. Think of them as the building blocks for advanced electronics used in things like electric cars and super-fast internet.
Which companies are the biggest makers of SiC wafers?
Some of the top companies making these wafers are Wolfspeed, Coherent Corp., and STMicroelectronics. Others like Resonac Holdings and SK Siltron are also growing fast and selling their wafers around the world. These companies are key players in making sure we have enough of these important materials.
Why is there such a big demand for SiC wafers right now?
The demand is booming mainly because of electric cars! SiC wafers help make electric car parts more efficient and allow them to charge faster. They are also used in power electronics that save energy and in new 5G technology. Basically, anything that needs high-powered and efficient electronics benefits from SiC.
Are SiC wafers easy to make and buy?
Making SiC wafers is tricky and costs a lot of money, which can make them hard to get. There aren’t as many factories making them as there are for regular silicon, and sometimes there are problems with the manufacturing process. This means supply can be limited, and prices can be high.
What’s new in the world of SiC wafer production?
Companies are working on making bigger wafers, like 8-inch ones, which helps lower costs and make more at once. They’re also finding better ways to grow the silicon carbide crystals and fix any tiny flaws. Plus, they’re looking into ways to reuse SiC materials to be more eco-friendly.
Where are most SiC wafers made and used?
While companies all over the world are involved, North America is a hub for new ideas and innovation in SiC. Asia-Pacific, especially places like China and Japan, is a huge manufacturing center. Europe is focusing on using SiC for cars and industrial machines. So, you see production and use happening in many different parts of the world.