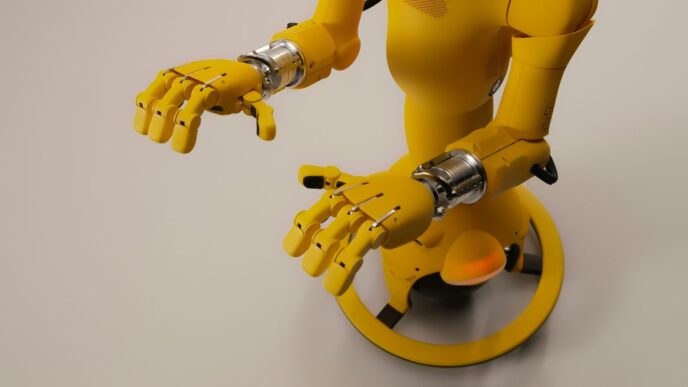
Right then, so OpenAI has gone and done it again, this time with robots. They’ve brought out this new humanoid robot called Neo, which is powered by their fancy GPT-5 language model. It’s a bit like they’ve taken AI out of the computer and given it a body. This whole openai robotics thing is meant to change how we think about machines interacting with the world. It’s pretty wild when you think about it, moving from just typing prompts to actually seeing a robot do things based on what you say.
Key Takeaways
- OpenAI’s new humanoid robot, Neo, uses GPT-5, marking a big step in openai robotics.
- Neo is designed to learn and adapt, moving beyond simple pre-programmed tasks.
- The robot has a human-like shape to make it easier to work alongside people and in human spaces.
- It can take instructions in plain language, making it simpler to use than older robots.
- This development opens up new possibilities for how robots can help in homes, industries, and research.
The Groundbreaking Fusion of OpenAI Robotics and Language Models

For ages, robots have been the stuff of science fiction, and while they’ve become more common in our lives, the idea of truly intelligent, interactive machines still felt a bit like a dream. That is, until now. OpenAI has really shaken things up by merging their advanced language models with physical robots, creating something quite special. It’s like taking the brains behind chatbots and giving them bodies that can actually do things in the real world.
Transforming AI from Code to Physical Form
Traditionally, robots have been programmed with very specific instructions. Think of it like giving a computer a list of commands it has to follow exactly. This works fine for repetitive tasks, but it means robots can’t really adapt when something unexpected happens. They’re stuck doing what they were told, even if the situation changes. OpenAI’s approach is different. By integrating powerful language models, they’re moving AI from just being lines of code on a screen to something that can perceive, understand, and act in the physical world. This means robots can start to grasp context and respond in more flexible ways, much like humans do.
The Role of GPT-5 in Humanoid Robotics
OpenAI’s latest language model, GPT-5, is a big part of this new wave. Imagine a model that doesn’t just write text but can also understand complex instructions and translate them into physical actions. That’s what GPT-5 brings to the table for humanoid robots. Instead of needing a programmer to write thousands of lines of code for every single movement, you can simply tell the robot what you want it to do in plain English. GPT-5 can then figure out the best way to achieve that goal, whether it’s picking up an object or performing a more intricate task. This ability to understand and act on natural language commands is a massive step forward, allowing for a much more intuitive way to interact with robots. It’s a bit like having a conversation with your machine, and it understands.
How Embodied AI Enhances Real-World Interaction
Embodied AI is the term for AI that has a physical presence and can interact with its environment. When you combine this with advanced language models, you get robots that can learn and improve through experience. Think about how a child learns to walk; they fall, they get up, and they adjust. Embodied AI works in a similar way. The robot observes its surroundings, tries out actions, and uses the feedback to get better. This continuous learning process means robots can become more capable and useful over time, adapting to new situations and tasks without needing constant reprogramming. This is a significant shift from older robots that were essentially just sophisticated tools. The potential for these machines to assist us in various tasks, from household chores to complex industrial jobs, is truly immense. You can find more information on the integration of large language models into service robotics in this overview paper.
The fusion of advanced language models with physical robotic forms marks a significant departure from traditional AI. It moves us towards machines that can not only process information but also interact meaningfully with the physical world, learning and adapting as they go. This opens up a vast landscape of possibilities for how humans and robots can collaborate.
Here’s a quick look at what this fusion enables:
- Natural Language Understanding: Robots can now interpret and respond to spoken or written commands, making them far more accessible.
- Adaptability and Learning: Through interaction, robots can refine their actions and learn new tasks, moving beyond pre-programmed routines.
- Complex Task Execution: Language models help break down complex goals into manageable physical steps for the robot.
- Zero-Shot Learning: Robots can perform actions they weren’t explicitly trained for, based on their understanding of language.
Neo: OpenAI’s Revolutionary Humanoid Robot
So, OpenAI has gone and done it again, haven’t they? They’ve taken their incredible language models, the ones that can write poems and explain quantum physics, and given them bodies. Meet Neo, their new humanoid robot. It’s not just another clunky machine; Neo is designed to be a real presence in our world, a physical manifestation of advanced AI. Think of it as the next step, moving AI from just being software on a screen to something that can actually, you know, do things.
Distinctive Humanoid Design and Functionality
Neo looks the part, which is pretty important if it’s going to work alongside us. It’s got the whole humanoid setup – head, torso, arms, legs – all designed to help it move around and interact with environments built for people. This isn’t just for show, though. Having a body like ours means it can potentially do tasks that require dexterity, like picking up objects or even navigating cluttered spaces. It’s built to be capable, not just clever.
Adaptability and Autonomous Decision-Making
This is where Neo really starts to shine. Unlike older robots that needed every single move programmed, Neo can figure things out on its own. It learns from its surroundings and can adjust its actions as it goes. If it makes a mistake, it can correct itself. This ability to make decisions autonomously means it can handle unexpected situations much better than a robot stuck to a script. It’s a big change from robots that only do what they’re told, exactly when they’re told.
Safety Protocols and Human-Centric Interfaces
OpenAI knows that putting advanced robots into the world brings up questions, especially about safety. They’ve put a lot of thought into making sure Neo is safe to be around. This includes built-in safeguards to prevent accidents and ensure it behaves predictably. Plus, the way we interact with Neo is designed to be straightforward. The goal is to make it easy for people to communicate their intentions and for Neo to understand them, creating a more natural partnership.
The development of Neo represents a significant shift, moving AI from abstract concepts to tangible interactions. It’s about creating machines that can not only process information but also act upon it in the physical world, learning and adapting as they go.
Here’s a quick look at some of Neo’s key features:
- Learning Capability: Adapts to new tasks and environments through experience.
- Physical Dexterity: Capable of manipulating objects and navigating complex spaces.
- Autonomous Operation: Makes independent decisions to achieve goals.
- Safety Integration: Designed with multiple layers of safety for human interaction.
- Intuitive Control: Aims for natural language interaction and user-friendly interfaces.
Expanding Possibilities: Applications of OpenAI Robotics
It’s not just about having a fancy robot that can walk and talk; it’s about what these machines can actually do for us. OpenAI’s robots, powered by advanced language models, are poised to make a real difference across a surprising range of areas. Think about it: we’re moving beyond robots that just follow pre-programmed instructions to machines that can understand, adapt, and act in complex, real-world situations.
Industry Integration: From Logistics to Manufacturing
In warehouses and factories, the potential is enormous. Imagine robots that can not only move goods but also understand nuanced instructions for sorting, packing, or even performing delicate assembly tasks. They could learn new processes quickly, reducing the time and cost associated with retraining human workers for new product lines. This adaptability means they can be deployed in dynamic environments where tasks change frequently. For instance, a robot could be instructed to "organise these incoming shipments by destination, prioritising fragile items" and then, with a follow-up command, switch to "prepare the assembly line for the new widget model." This kind of flexibility is a game-changer for efficiency. We’re seeing early developments in this area, with companies exploring how AI can assist in complex software development projects through collaborative agents, hinting at the broader integration of AI into industrial workflows.
Domestic Assistance and Support for Disabilities
At home, these robots could become invaluable assistants. For individuals with mobility issues or disabilities, a robot that can understand spoken requests and perform physical tasks – like fetching items, assisting with meal preparation, or even providing companionship – could significantly improve independence and quality of life. The ability to learn and adapt to an individual’s specific needs and routines is key here. A robot might learn the best way to help someone get dressed or remind them to take medication, all through natural language interaction and observation.
Research, Education and Emerging Use Cases
Beyond industry and home, the applications stretch into research and education. Robots could assist scientists in labs by performing repetitive experiments, handling hazardous materials, or even collecting data in difficult-to-reach environments. In education, they could serve as interactive tutors, demonstrating complex concepts or providing personalised learning experiences. The possibilities are quite broad, and we’re likely to see entirely new use cases emerge as the technology matures and becomes more accessible.
The true power lies in the robot’s ability to interpret intent and adapt its actions, moving beyond simple command execution to a more collaborative form of interaction. This means a robot can be told what needs to be done, and it can figure out the best way to do it, even if it hasn’t been specifically programmed for that exact scenario.
Here’s a look at some potential roles:
- Logistics: Autonomous package sorting, inventory management, and last-mile delivery assistance.
- Manufacturing: Quality control, assembly line support, and tool handling.
- Healthcare: Assisting nurses with patient mobility, delivering medication, and providing remote monitoring.
- Education: Interactive teaching aids, laboratory assistants, and personalised learning companions.
- Elderly Care: Companionship, medication reminders, and assistance with daily living activities.
Enhancing Human-Robot Interaction with Advanced Language Models
It’s quite something, isn’t it? We’re moving past robots that just follow rigid commands. Now, thanks to big language models, robots can actually understand what we’re saying, and even talk back in a way that makes sense. This is a massive leap from the old days of complex coding for every single action.
Natural Language Commands and Zero-Shot Learning
Imagine telling a robot, "Could you fetch me that book from the shelf?" Instead of needing a programmer to map out every step, a language model can interpret that request. It figures out what a "book" is, where the "shelf" might be, and how to physically move to retrieve it. This is what they call "zero-shot learning" – the robot can do things it wasn’t specifically programmed for. It’s like giving instructions to a very capable assistant who can figure out the details on their own. This means robots can adapt to new tasks much more quickly, without needing a complete reprogramming session. It’s a bit like how humans learn new skills by understanding the goal, rather than being shown every single tiny movement.
- Understanding context: The language model helps the robot grasp the nuances of human speech.
- Task decomposition: It breaks down complex requests into manageable steps for the robot.
- Adaptability: Enables robots to perform tasks they haven’t encountered before.
Bridging Human Intent and Robotic Action
So, how does this actually work? Think of the language model as a translator, but for intentions. You have an idea in your head, you express it in words, and the language model converts that into a plan the robot can execute. It’s not just about understanding the words, but the underlying goal. For instance, if you ask a robot to "tidy up the living room," the language model can infer that this involves picking up objects, putting them away, and perhaps even dusting. It’s this ability to bridge the gap between abstract human desires and concrete physical actions that makes these new robots so promising. We’re seeing robots that can produce natural language responses by interacting with these models, making communication much smoother.
The real magic happens when the robot doesn’t just follow orders but can also explain what it’s doing or ask clarifying questions, much like a human collaborator.
Teleoperation and Virtual Reality Integration
Beyond direct commands, language models are also opening doors for more sophisticated remote control. Imagine a scenario where a human operator, perhaps miles away, can guide a robot through a complex task using voice commands. The language model acts as an intermediary, translating the operator’s spoken instructions into precise robotic movements. This is particularly useful in dangerous environments or for tasks requiring fine motor skills that are difficult to program directly. Furthermore, integrating these systems with virtual reality could allow for incredibly immersive teleoperation, where the operator feels like they are physically present, guiding the robot with both voice and gesture, all interpreted by advanced AI.
- Remote guidance: Voice commands can direct robots in hazardous or inaccessible locations.
- Enhanced precision: Language models help translate nuanced instructions into accurate robotic movements.
- Immersive control: VR integration allows for a more intuitive and hands-on remote operation experience.
Addressing Public Concerns: Ethics, Safety and the Future of OpenAI Robotics
It’s completely understandable that the rapid advancements in AI, especially with something as tangible as robots, bring up a lot of questions. People are naturally curious, and sometimes a bit worried, about what this all means for us. We’re talking about machines that can learn, adapt, and interact with the world in ways we’re only just beginning to grasp. This isn’t just about cool new gadgets; it’s about how these intelligent machines will fit into our lives and society.
Managing Fears of AI Dominance and Job Disruption
One of the biggest worries people have is about jobs. Will robots take over all the work? It’s a valid concern, and one that OpenAI is taking seriously. The idea isn’t to replace people, but to create tools that can help us. Think of it like this: a calculator didn’t make mathematicians obsolete; it just made them more efficient. Similarly, these robots could handle the repetitive or dangerous tasks, freeing up humans for more creative and complex work. We’re seeing a lot of discussion about this, and it’s important that we have open conversations about how to manage this transition. It’s not just about the technology itself, but how we choose to implement it.
- Focus on Augmentation: The goal is to build robots that work alongside humans, not instead of them.
- Skills Development: Investing in training programmes to help people adapt to new roles is key.
- Economic Impact Studies: Continuous research into the economic effects of AI is vital to inform policy.
The speed of progress can be startling. What once seemed like science fiction is now becoming reality, and it’s natural to feel a sense of uncertainty about what comes next. This is why transparency and careful consideration are so important as we move forward.
Ensuring Responsible Development and Deployment
Safety and ethics are at the forefront of our minds. When you’re building something as powerful as an intelligent robot, you have to think about all the potential outcomes. This means rigorous testing, clear guidelines, and a commitment to building systems that are aligned with human values. We’re not just building machines; we’re building trust. This involves:
- Robust Safety Protocols: Implementing multi-layered safety checks and fail-safes.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing clear ethical guidelines for AI behaviour and decision-making.
- Transparency in Design: Making the workings of these robots as understandable as possible to the public.
We are committed to responsible AI development, and that means being upfront about the challenges and working collaboratively to find solutions. It’s a complex area, and there’s no single easy answer, but we believe in a future where humans and intelligent machines can coexist safely and productively.
Navigating the Path to Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the idea of AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can, is still a long way off. While current AI is incredibly capable, it’s a far cry from human-level consciousness or general problem-solving. The focus right now is on building useful, specialised AI that can help us with specific tasks. Worrying about a robot uprising is a bit like worrying about overpopulation on Mars before we’ve even landed there. It’s important to consider the long-term possibilities, but our immediate efforts are concentrated on the practical applications and safety of the AI we have today. The journey towards AGI, if it ever happens, will be gradual, allowing society time to adapt and set appropriate boundaries. For now, the focus remains on making current AI systems beneficial and safe for everyone.
Redefining Research and Development Through AI-Powered Robots
It’s pretty wild to think about, but these new AI-powered robots aren’t just for factories or helping around the house. They’re starting to change how we do science and create new things. Imagine a lab assistant that never gets tired, can sift through mountains of data in minutes, and even suggest new experiments. That’s what we’re talking about here.
Acceleration of Scientific Discovery
Think about how much information is out there. Scientists spend ages just trying to keep up, let alone find new connections. AI robots, especially those linked to advanced language models, can process and analyse research papers, experimental results, and datasets at a speed humans simply can’t match. This means we can spot patterns, identify promising avenues for research, and even generate hypotheses much faster. This rapid processing is like giving scientific progress a massive turbo boost. It’s not just about doing things quicker; it’s about uncovering insights that might have been missed entirely.
Collaborative Innovation Between Humans and Robots
This isn’t about robots replacing scientists. It’s more like a partnership. Humans bring creativity, intuition, and the big-picture thinking. The robots, on the other hand, handle the heavy lifting of data crunching, repetitive tasks, and complex simulations. This frees up human researchers to focus on the more creative and strategic aspects of their work. It’s a bit like having a super-smart intern who can do all the tedious bits, leaving you to focus on the exciting breakthroughs.
Here’s a look at how this collaboration might play out:
- Idea Generation: AI suggests novel research questions based on existing literature.
- Experiment Design: Robots help plan and optimise experimental setups.
- Data Analysis: AI processes vast amounts of data, identifying trends and anomalies.
- Hypothesis Testing: Robots can run simulations to test theories proposed by humans.
The Evolution of Autonomous Research Tools
We’re moving towards a future where AI robots can conduct research with minimal human oversight. They can be programmed with research goals and then autonomously design experiments, gather data, analyse results, and even report their findings. This is particularly useful for research in hazardous environments or for long-term, continuous studies. It’s a bit like setting a highly intelligent agent loose on a problem, trusting it to find solutions.
The ability for AI-powered robots to operate autonomously in research settings presents a significant shift. It means that complex scientific inquiries can proceed around the clock, unhindered by human limitations like fatigue or the need for sleep. This continuous operation has the potential to dramatically shorten the timeline for discoveries.
This new era of AI-driven research tools promises to accelerate the pace of innovation across all scientific fields. It’s a fascinating time to be alive, watching these intelligent machines help us understand the world better and faster than ever before.
The Road Ahead
So, what does all this mean for us? Well, OpenAI’s work with robots like Neo, powered by advanced AI, is really changing things. It’s not just about making machines do tasks anymore; it’s about creating partners that can learn and adapt. We’re moving towards a future where these intelligent machines could help us out in all sorts of ways, from doing chores to assisting in complex jobs. It’s an exciting, and perhaps a little bit strange, new chapter. We’re only just starting to see what’s possible, and it’s going to be fascinating to watch how this technology develops and fits into our lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is OpenAI Robotics and Neo?
OpenAI Robotics is like a new chapter in making smart machines. They’ve created a robot called Neo, which is a humanoid robot. Think of it as a robot that looks and acts a bit like a person. It’s powered by a very advanced AI called GPT-5, which helps it understand and interact with the world in a clever way.
How is Neo different from other robots?
Most robots follow strict instructions. Neo is special because it can learn and figure things out on its own, much like how we learn from our experiences. Its AI brain, GPT-5, allows it to adapt to new situations and make smart decisions without being told exactly what to do every single time.
What can Neo do?
Neo is designed to be really useful in many ways. It can help with tasks in factories, deliver things, and even assist people at home. Because it’s a humanoid robot, it can do things like walk, pick up objects, and potentially even help people who need extra support.
How do we talk to Neo?
Instead of complicated computer codes, you can simply tell Neo what to do using normal language, like you’re talking to a friend. The AI understands your words and turns them into actions for the robot. It can even learn new tasks just by being told once, which is pretty amazing!
Is Neo safe to be around?
OpenAI has put a lot of effort into making Neo safe. They’ve built in special safety features to make sure it behaves predictably and doesn’t cause harm. The goal is for robots like Neo to work alongside people safely and reliably.
Will robots like Neo take our jobs?
It’s understandable to worry about jobs when new technology arrives. While robots might change how some jobs are done, they can also create new opportunities and help us with difficult or dangerous tasks. The idea is for robots to help humans, not replace them entirely, and to work together to solve bigger problems.