It’s pretty wild how 3D printing is changing things up in healthcare. You know, it used to be that medical stuff was pretty much one-size-fits-all. But now, with 3D print healthcare, doctors and makers can create things that are made just for one person. This is a huge deal, especially for surgeries and custom parts like fake limbs. We’re seeing this technology pop up in hospitals more and more, helping with everything from planning tricky operations to making new kinds of medical tools. It’s definitely a big shift in how we think about patient care.
Key Takeaways
- The market for 3D print healthcare is growing fast, showing how important custom-made medical items are becoming.
- Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, lets us build complex medical parts layer by layer from digital designs.
- Custom implants and prosthetics are a big win with 3D print healthcare, fitting patients perfectly.
- Surgical precision gets a boost with 3D printed models that let doctors practice before surgery.
- While there are rules to follow and facilities to manage, 3D print healthcare is making care faster, cheaper, and more personal.
Revolutionizing Patient Care With 3D Print Healthcare
It feels like just yesterday we were talking about 3D printers as cool gadgets for hobbyists. Now, they’re seriously changing how doctors and nurses take care of people. This isn’t science fiction anymore; it’s happening right now in hospitals all over.
The Growing Market For 3D Print Healthcare
The world of 3D printing in healthcare is booming. We’re talking about a market that was already worth a good chunk of change a couple of years ago and is projected to keep growing at a really fast pace. Think about it: more and more hospitals are setting up their own 3D printing labs, right where the patients are. This means they can make things on demand, tailored specifically for each person.
- Personalized patient care: Making devices that fit perfectly.
- Faster production: Getting needed equipment made quickly.
- New research: Creating tools for medical breakthroughs.
Understanding Medical Additive Manufacturing
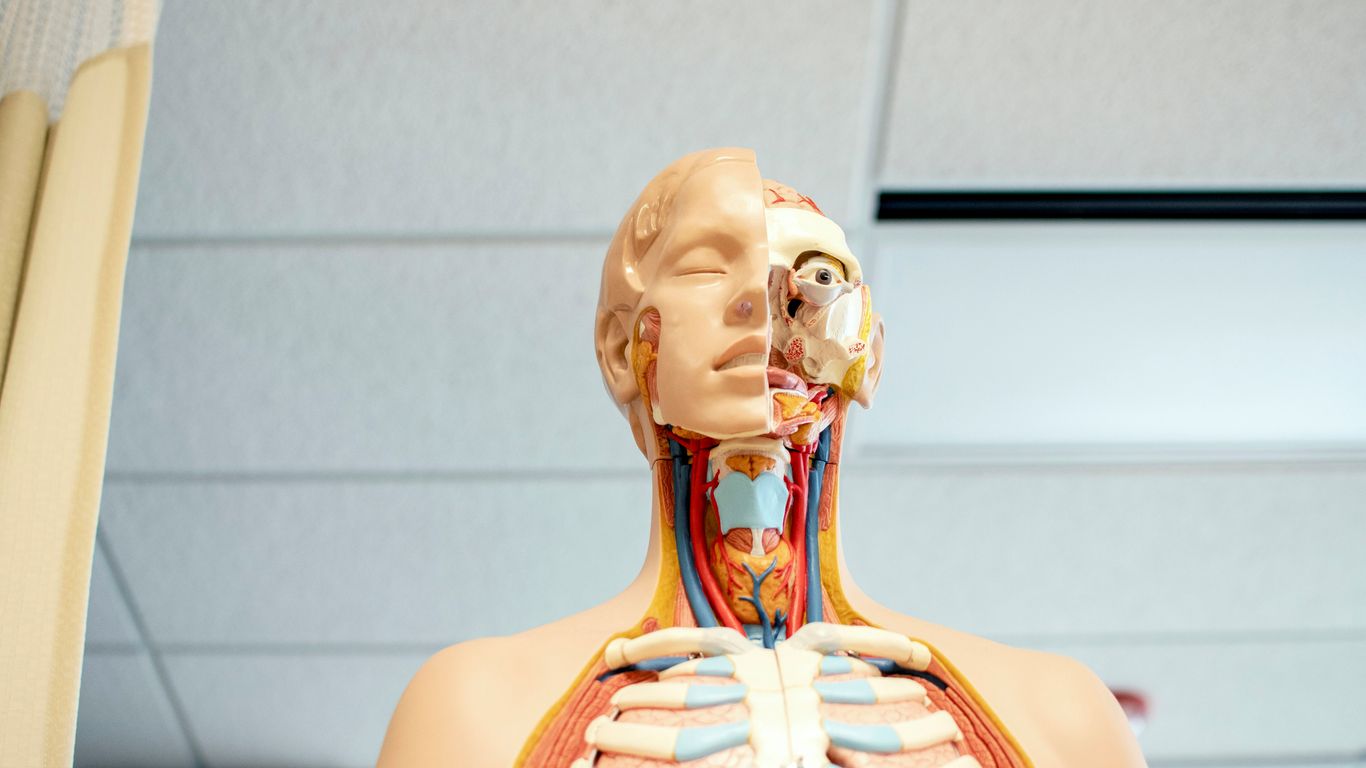
So, what exactly is this "medical additive manufacturing"? Basically, it’s using a digital design to build a physical object, layer by tiny layer. For medicine, this means creating things like custom implants, prosthetic limbs, or even exact models of a patient’s organs. They use special materials, some of which are even safe to put inside the body or are made from living cells. It’s like having a super-precise, on-demand factory for medical needs.
Enhancing Surgical Precision Through 3D Models
Imagine a surgeon about to perform a really tricky operation. Instead of just looking at flat scans, they can now hold a 3D-printed model of the patient’s heart or brain in their hands. This model is made from the patient’s own scan data. It lets the surgeon practice the surgery beforehand, see exactly where the problem is, and plan every step. This kind of preparation can make a huge difference in the operating room, potentially leading to shorter surgery times and better results for the patient. It’s like having a practice run before the main event.
Transforming Medical Devices With 3D Printing
It’s pretty wild how 3D printing is changing the game for medical devices. We’re not just talking about making things faster, but making them way more personal and effective for patients. Think about it – instead of a standard-issue part, you get something made just for you. That’s a huge shift.
Customized Implants and Prosthetics
This is where 3D printing really shines. For folks needing prosthetics, especially kids who are still growing, getting a custom fit is a big deal. Traditional methods can be pricey and don’t always fit perfectly. But with 3D printing, we can make prosthetics that match a person’s exact shape and needs. This makes them more comfortable and way more functional, helping people get back to their lives. It’s not just prosthetics either; custom implants for bones or joints are also becoming a reality. This level of personalization means better outcomes and a higher quality of life for patients.
Accelerated Production Of Medical Equipment
When time is critical, like in an emergency, waiting weeks for a specific medical tool or implant just won’t cut it. Traditional manufacturing can take ages. 3D printing, however, can churn out patient-specific devices in hours or days. This speed is a lifesaver in urgent situations. Plus, making these items on-site at hospitals cuts down on shipping costs and delays. It’s about having what you need, when you need it, without the usual red tape.
Innovations In Dental Applications
Dentistry has seen some pretty cool changes thanks to 3D printing. Imagine going to the dentist and getting a crown or a custom aligner made right there, in the same visit. That’s becoming possible. Dentists can now print highly detailed models, crowns, and even clear aligners in their own offices. This cuts out the need for external labs and drastically reduces waiting times for patients. It makes the whole process smoother and more convenient, which is a win-win for everyone involved.
Pioneering Applications In 3D Print Healthcare
Mayo Clinic’s Surgical Planning Success
Doctors at the Mayo Clinic have really leaned into using 3D printing to get ready for tricky surgeries. They print out exact copies of a patient’s body parts, like organs or bones, using scans. This lets surgeons see exactly what they’re dealing with before they even step into the operating room. It’s like having a practice run. They even used this for a super complicated surgery to separate conjoined twins. Being able to plan it all out beforehand made the operation go much smoother and helped those kids out a ton.
Tissue Engineering Breakthroughs
Researchers are doing some pretty amazing stuff with 3D printing and tissues. Think about creating scaffolds that mimic human tissue. Northwestern University, for example, has been working on 3D-printed ovaries. They actually implanted one in mice, and guess what? The mice were able to have babies and nurse them. It sounds like science fiction, but it’s a huge step forward for figuring out how we might handle reproductive issues down the line.
Veterans Affairs Custom Prosthetics Initiative
The Veterans Affairs (VA) system has also jumped on board with 3D printing, especially for prosthetics. They can now make custom limbs that fit veterans perfectly. This isn’t just about making them look good; it’s about making them work better and feel more comfortable. Plus, it cuts down on the time and money it takes to get these devices made. It really helps give veterans back a sense of normalcy and improves their daily lives.
The Advantages Of 3D Print Healthcare Solutions
Unprecedented Speed And Efficiency
Think about it: when a patient needs something specific, like a custom implant or a model to plan a tricky surgery, waiting weeks or months just isn’t ideal. Traditional manufacturing can be slow, involving lots of steps and specialized factories. But with 3D printing, we’re talking about making things much, much faster. Hospitals can now print patient-specific devices right there, on-site, often in a matter of hours or days instead of weeks. This speed is a game-changer, especially when every minute counts in an emergency. It means less waiting for patients and quicker treatment paths.
Significant Cost Reductions
While setting up a 3D printing lab might seem like a big upfront cost, the savings down the line can be pretty substantial. For starters, you cut out a lot of the middleman costs associated with ordering from external suppliers. Plus, printing on demand means less money tied up in inventory and less waste from unused or outdated parts. Imagine needing a rare surgical tool – instead of stocking a dozen that might never get used, you can just print one when the need arises. This localized production also cuts down on shipping and logistics expenses, making healthcare more efficient financially.
Personalized Patient Treatment Plans
This is where 3D printing really shines. We’re moving away from one-size-fits-all solutions. For example, a child needing a prosthetic limb can get one designed precisely for their body, accounting for growth and specific needs. Surgeons can use 3D printed models of a patient’s anatomy to practice complex procedures beforehand, reducing risks during the actual surgery. This level of customization means treatments are tailored to the individual, leading to better outcomes, improved comfort, and a higher quality of life for patients. It’s about making healthcare fit the person, not the other way around.
Navigating Challenges In 3D Print Healthcare Implementation
So, 3D printing in healthcare sounds pretty amazing, right? We’ve talked about all the cool ways it’s changing things. But, like anything new and exciting, it’s not all smooth sailing. There are definitely some bumps in the road we need to figure out before it becomes totally commonplace.
Addressing Regulatory Hurdles
This is a big one. Getting medical stuff approved is serious business, and for good reason. We need to make sure anything that goes into or onto a patient is safe and actually works. Regulatory bodies, like the FDA, are trying to keep up with how fast this technology is moving. It’s a constant back-and-forth to make sure the rules make sense for things like biocompatible materials, how long a printed device will last, and just generally keeping quality in check throughout the whole printing process. It can be a bit of a maze to get through.
Ensuring Safe And Effective Use
Beyond just the paperwork, there’s the practical side of making sure these printed items are actually good to go. This means:
- Material Science: We’re still learning about all the different materials we can use. They need to be safe for the body, tough enough for medical use, and meet all those strict standards. Researchers are working hard on new stuff, like special ‘bio-inks’ for printing tissues, but making sure they work perfectly inside a person for years is a challenge.
- Precision and Consistency: Sometimes, getting the tiny details just right is tricky. For things like super-small drug delivery systems, achieving that level of precision is tough. Also, being able to print a lot of something while making sure every single piece is exactly the same is an area that needs more work.
- Technical Know-How: You can’t just plug in a 3D printer and expect magic. Hospitals need people who really know their stuff – folks who can design in 3D, operate the printers, and understand the specific needs of medical devices. This means investing in training, which takes time and money.
Strategic Management Of 3D Printing Facilities
Setting up and running a 3D printing operation in a hospital isn’t just about buying a printer. It requires careful planning. Hospitals need to think about:
- Initial Investment: The cost of the printers themselves, plus the software and training, can be pretty high upfront. While it can save money later, that initial outlay is a hurdle for some places.
- Workflow Integration: How does this new tech fit into what the hospital is already doing? It needs to work smoothly with existing systems and not create more work.
- Quality Control: Establishing clear processes for checking the quality of every printed item is non-negotiable. This involves regular checks and sticking to best practices, just like any other medical manufacturing process.
It’s a lot to consider, but by tackling these challenges head-on, healthcare providers can really make 3D printing work for them and, most importantly, for their patients.
The Future Landscape Of 3D Print Healthcare
Advancements In Bioprinting Tissues And Organs
This is where things get really sci-fi, but it’s happening now. We’re talking about printing actual living tissues and, eventually, whole organs. Imagine needing a new kidney and instead of waiting years for a donor, doctors can print one using your own cells. That’s the goal of bioprinting. Researchers are already making progress with simpler tissues, like skin grafts. The idea is to create scaffolds, which are like tiny frameworks, and then layer living cells onto them. It’s a slow process, and there are huge hurdles to overcome, like making sure the printed tissues have blood vessels and can function properly inside the body. But the potential to end organ transplant waiting lists and eliminate rejection issues is enormous.
The Rise Of Custom Pharmaceuticals
Think about your daily medications. Most are one-size-fits-all, right? Well, 3D printing could change that completely. We’re looking at a future where pills can be printed with exact dosages tailored specifically for you. This means if you need a very precise amount of a drug, or a specific release schedule (like a slow-release version), a 3D printer could make it on demand. This could lead to much more effective treatments with fewer side effects because the medication is perfectly matched to your body’s needs. It’s like having a personal pharmacist in a printer.
Integration With Digital Health Platforms
So, how do all these amazing 3D printed medical innovations connect with the rest of your healthcare? That’s where digital health platforms come in. Imagine your doctor using a digital model of your heart, created from scans, to plan surgery. That same digital model could then be sent to an in-hospital 3D printer to create a physical replica for practice. All this information – the scans, the digital models, the printing parameters, and even the final printed device – can be stored and accessed through secure digital health records. This makes it easier for different healthcare providers to share information, track progress, and coordinate care. This interconnectedness is key to making 3D printing a truly integrated part of modern medicine. It means better communication, more informed decisions, and ultimately, a more streamlined patient experience.
The Road Ahead
So, where does all this leave us? It’s pretty clear that 3D printing isn’t just a fancy gadget anymore in the medical world. We’ve seen how it’s already making a real difference, from helping surgeons plan tricky operations to making custom parts for people who need them. It’s not perfect, and there are still some bumps in the road, like figuring out all the rules and how much things will cost long-term. But the potential is huge. Think about custom medicines made just for you, or even new organs printed when you need them. It feels like we’re just scratching the surface of what’s possible, and that’s pretty exciting for how we’ll all get treated in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is 3D printing in healthcare?
Think of 3D printing in healthcare like using a super-smart printer. Instead of just printing flat pictures, it builds real, solid objects layer by layer from a digital design. In medicine, this means we can create custom body parts, models for surgeons to practice on, or even special tools, all made exactly for one person.
How does 3D printing help surgeons?
Surgeons can use 3D printing to make exact copies of a patient’s body parts, like a heart or a bone, before an operation. This is like having a practice run! It helps them see exactly what they need to do, making surgeries safer and quicker.
Can 3D printing make fake limbs (prosthetics) or implants?
Yes, absolutely! 3D printing is fantastic for making custom-fit prosthetic limbs or implants that go inside the body. Because each one is made just for the person, they fit better and work more comfortably than ones made the old way.
Is 3D printing cheaper than making medical stuff the usual way?
Often, yes, in the long run. While setting up the printers can cost money at first, making things one at a time or in small batches can be much cheaper than mass production. Plus, you don’t waste as much material, and you can make things right when you need them.
Are there rules and safety checks for 3D printed medical items?
Yes, there are strict rules. Just like any medical equipment, 3D printed items need to be approved and checked to make sure they are safe and work correctly for patients. This is a very important step before they can be used.
What’s the next big thing for 3D printing in healthcare?
Scientists are working on printing living tissues and even whole organs, which could change how we treat organ failure. They’re also looking into printing medicines with just the right amount of each ingredient for each person. It’s all about making treatments more personal and effective.














