In the world of laboratory management, two software solutions often come up in discussions: Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS). While both serve essential functions in managing laboratory workflows and data, they have distinct purposes and features that set them apart. This article will explore the differences between LIS and LIMS to help you determine which system is best suited for your laboratory’s needs.
What is a Laboratory Information System (LIS)?
A Laboratory Information System (LIS) is a software solution designed primarily for clinical laboratories to manage patient data, test orders, and results. It streamlines the process of collecting, processing, and reporting patient test data, ensuring accuracy and efficiency throughout the laboratory workflow. LIS is specifically tailored to the needs of medical professionals, focusing on patient care and diagnosis.
Key Features of LIS:
- Patient-centric data management: LIS focuses on managing patient data, including demographic information, test orders, and results.
- Integration with Electronic Medical Records (EMRs): LIS can integrate with EMRs, ensuring seamless data exchange and facilitating communication between healthcare providers and laboratory staff.
- Clinical decision support: LIS can include clinical decision support tools, such as flagging abnormal results or providing reference ranges, to aid healthcare professionals in interpreting test results and making informed decisions about patient care.
- Regulatory compliance: LIS is designed to comply with clinical laboratory regulations, such as the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
What is a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)?
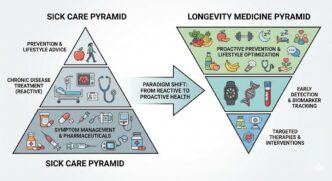
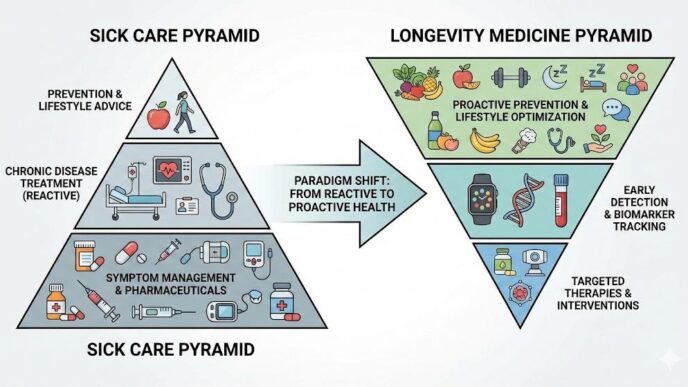
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a software solution designed to manage laboratory workflows, samples, and data in a wide range of laboratory settings, including research, industrial, environmental, and clinical labs. LIMS focuses on optimizing laboratory processes, enhancing data integrity, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Unlike LIS, LIMS is not limited to clinical laboratories and can be implemented in various laboratory environments.
Key Features of LIMS:
- Sample-centric data management: LIMS primarily focuses on managing sample data, including sample tracking, storage, and analysis.
- Integration with laboratory instruments: LIMS can integrate with a wide range of laboratory instruments, automating data collection and reducing manual data entry errors.
- Quality control and assurance: LIMS includes features to monitor and manage quality control processes, such as control charts, statistical analysis, and instrument calibration.
- Regulatory compliance: LIMS supports compliance with various industry-specific regulations and standards, such as Good Laboratory Practice (GLP), Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards.
Comparing LIS and LIMS: Key Differences
While both LIS and LIMS serve essential functions in laboratory data management, there are several critical differences between the two systems:
1. Primary Focus
The primary focus of LIS is managing patient data, test orders, and results in clinical laboratories. In contrast, LIMS focuses on managing sample data, laboratory workflows, and quality control processes in various laboratory settings.
2. Target Users
LIS is specifically designed for clinical laboratories, catering to the needs of medical professionals involved in patient care and diagnosis. On the other hand, LIMS caters to a broader range of laboratory environments, including research, industrial, environmental, and clinical labs.
3. Data Management Approach
LIS primarily manages patient-centric data, integrating with Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and providing clinical decision support tools. In contrast, LIMS manages sample-centric data and integrates with laboratory instruments to streamline workflows and ensure data integrity.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Both LIS and LIMS support regulatory compliance; however, the specific regulations they adhere to may differ. LIS is designed to comply with clinical laboratory regulations, such as CLIA and HIPAA. In contrast, LIMS supports compliance with various industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GLP, GMP, and ISO standards.
Choosing the Right System for Your Laboratory
When deciding between a LIS and LIMS, it’s essential to consider your laboratory’s specific needs and requirements. Here are some factors to take into account when making your decision:
- Type of laboratory: If you operate a clinical laboratory focused on patient care and diagnosis, a LIS may be better suited to your needs. However, if you work in a research, industrial, or environmental laboratory, a LIMS may be more appropriate.
- Data management requirements: Consider whether your laboratory primarily deals with patient data (LIS) or sample data (LIMS) and which system best aligns with your data management needs.
- Integration capabilities: Evaluate the compatibility of each system with your existing laboratory infrastructure, such as EMRs, laboratory instruments, and other software solutions.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensure that the system you choose supports the specific regulatory requirements and standards relevant to your laboratory operations.
Conclusion
Both Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) play crucial roles in managing laboratory workflows and data. While LIS is tailored to the needs of clinical laboratories and focuses on patient care, LIMS caters to a broader range of laboratory environments and emphasizes sample management and quality control processes. By understanding the key differences between LIS and LIMS, you can make an informed decision about which system best suits your laboratory’s unique requirements.