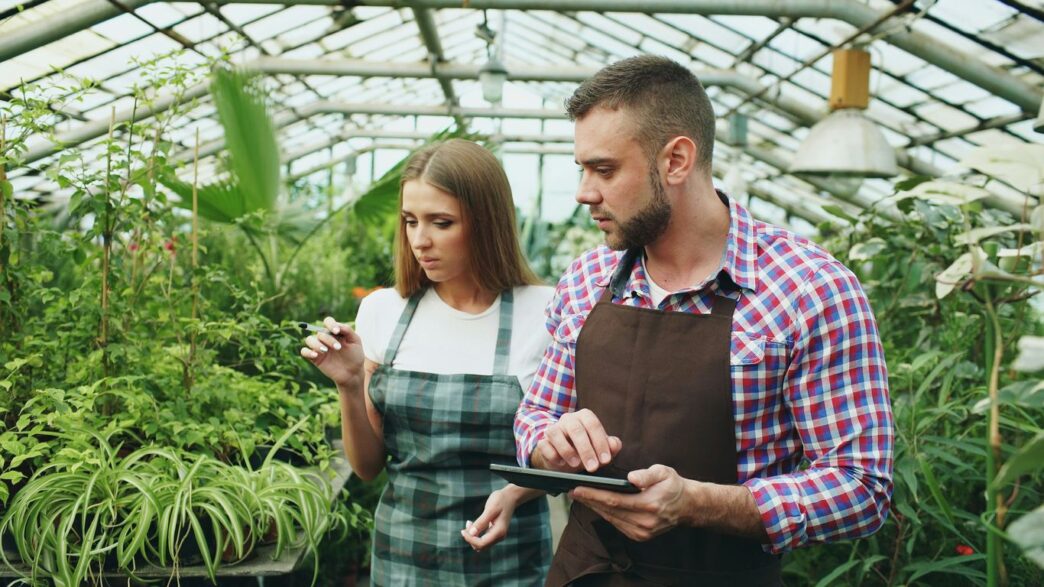
Feeding everyone is a big deal, right? Especially with more people on the planet and less good land to grow on. That’s where greenhouse horticulture comes in. It’s like a high-tech farm inside, using smart gadgets and controlled conditions to grow food better and more reliably. Think sensors, special lights, and smart watering. This approach is changing how we grow everything from your everyday veggies to specialty herbs, making sure we have fresh food all year, no matter what’s happening outside. It’s all about being smarter with our resources and producing food that’s good for us and the planet.
Key Takeaways
- Modern greenhouse horticulture relies heavily on technology like smart sensors and climate control systems to create optimal growing environments.
- Efficient lighting, especially LED solutions, plays a big part in boosting plant growth and yield, supplementing natural light when needed.
- Greenhouse farming allows for a wider variety of crops to be grown, including fruits, vegetables, and even medicinal plants, thanks to advanced growing methods.
- Sustainability is a major focus, with practices like water recycling, energy efficiency, and reduced pesticide use becoming standard in greenhouse operations.
- Controlled environments in greenhouses enable year-round production, making agriculture more resilient to climate challenges and unpredictable weather.
Innovations Driving Greenhouse Horticulture
The way we grow food is changing, and greenhouses are at the forefront of this shift. Gone are the days of simple glass boxes; today’s high-tech greenhouses are packed with smart technology designed to make growing more efficient and sustainable. These advancements are helping us produce more food, using fewer resources, all year round.
Smart Sensors and Climate Control Systems
Think of these as the brains of the operation. Tiny sensors are scattered throughout the greenhouse, constantly measuring things like temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and even soil moisture. This data is fed into sophisticated climate control systems that can automatically adjust heating, cooling, ventilation, and irrigation. It’s like having a personal weather forecaster and a tireless farmhand all rolled into one, making sure plants get exactly what they need, when they need it. This precision means less waste and healthier plants.
Here’s a quick look at what these systems monitor:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) levels
- Light intensity
- Soil moisture and nutrient levels
Energy-Efficient LED Lighting Solutions
Natural sunlight is great, but it’s not always enough, especially during shorter days or cloudy spells. Traditional grow lights used a lot of energy and produced a lot of heat. Now, we’re seeing a big move towards LED lighting. These lights use way less electricity, last much longer, and can be tuned to emit specific light spectrums that plants love for different stages of growth. This means growers can provide the perfect light conditions without breaking the bank on energy bills or overheating the greenhouse.
Some benefits of using LEDs:
- Reduced energy consumption (up to 50% less than older lights)
- Longer lifespan, meaning fewer replacements
- Customizable light spectrums for different crops and growth phases
- Lower heat output, simplifying climate control
Advanced Water and Nutrient Management
Water is precious, and so are the nutrients plants need. Advanced systems in modern greenhouses focus on using these resources wisely. Drip irrigation delivers water and dissolved nutrients directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Sensors monitor nutrient levels in the water, allowing for precise adjustments. Many systems also incorporate water recycling, treating and reusing water that isn’t immediately absorbed by the plants. This not only conserves water but also prevents nutrient loss, making the whole process much more sustainable.
Optimizing Growth Conditions in Greenhouse Horticulture

Getting plants to grow their best in a greenhouse isn’t just about sticking them in a pot and hoping for the best. It’s a careful balancing act, and light is a huge part of that. Think of light as the plant’s energy source; without enough, or with too much of the wrong kind, things just don’t work right. Controlling the light environment is key to getting high yields and top-quality produce.
Maximizing Natural Light Exposure
We all know sunlight is free and plentiful, so using it as much as possible makes a lot of sense. Greenhouses are designed to capture this natural light. Positioning the greenhouse correctly and keeping the glazing clean helps a ton. Sometimes, though, the sun can be a bit too intense, especially during hot summer days. In these cases, growers might use shade cloths or special coatings on the greenhouse panels to diffuse the light, preventing plants from getting scorched.
Strategic Use of Supplemental Lighting
Natural light isn’t always enough, especially during shorter days in fall and winter, or on cloudy days. This is where supplemental lighting comes in. Modern LED lights are pretty amazing for this. They use less energy than older types and can be tuned to give off specific light colors that plants really like for different growth stages. Using these lights strategically means you can keep plants growing strong all year round, no matter what the weather’s doing outside.
Here’s a quick look at why supplemental lighting is so useful:
- Extends Growing Season: Allows for year-round production, even when natural light is limited.
- Boosts Yields: Provides plants with the consistent energy they need to produce more flowers or fruit.
- Improves Quality: Can influence plant shape, color, and overall health.
- Reduces Crop Time: Speeds up the growth cycle, meaning faster harvests.
Controlling Light Intensity and Spectrum
It’s not just about having light; it’s about having the right light. Plants need different amounts of light and different light colors at different times. For example, young seedlings might need gentler light, while fruiting plants need more intense light. The spectrum, or the mix of colors in the light, also matters. Blue light is good for leafy growth, while red light helps with flowering and fruiting. Advanced systems allow growers to precisely control both how bright the light is and its color composition, tailoring it perfectly to the crop’s needs at every stage of its life. This level of control is what really separates modern greenhouse growing from just putting plants outside.
Expanding the Horticultural Crop Spectrum

Greenhouses used to be mostly for tomatoes and cucumbers, right? But things are changing fast. With all the new tech, we’re not just growing the usual suspects anymore. We can grow a whole lot more, and it’s pretty exciting for what we can eat and even what we can use for medicine.
Cultivating Diverse Fruits and Vegetables
It’s not just about staple veggies anymore. Think about berries, for example. Strawberries, once tricky to grow consistently indoors, are now being cultivated in controlled environments with great success. Growers are finding they can get high-quality fruit, nice and big, all year round. This means we can have fresh strawberries even when it’s snowing outside. It’s not just strawberries, either. We’re seeing more exotic fruits and a wider variety of leafy greens being grown this way. This helps make sure we have access to a diverse range of produce, no matter the season or where we live.
Growing Medicinal and Specialty Crops
Beyond food, greenhouses are becoming important for growing plants used in medicine and for special ingredients. Many plants used in pharmaceuticals or for high-value extracts need very specific conditions to grow well. Think about certain herbs or plants that produce compounds used in supplements or traditional remedies. Being able to control the light, water, and temperature precisely means growers can produce these sensitive crops reliably. This is a big deal for industries that depend on a steady supply of these plant-based materials. It also means we can grow things closer to where they’re needed, cutting down on transport.
Advancements in Substrate Technologies
What the plants grow in is changing too. We’re moving beyond just soil. New materials, like rockwool or coco coir, give growers more control over the plant’s root environment. These substrates allow for better water and nutrient delivery, which is key for healthy growth. They also help prevent diseases that can come from soil. Plus, using these inert materials means we can recycle water and nutrients more effectively, which is a big win for sustainability. It’s all about creating the perfect setup for the roots so the rest of the plant can thrive, no matter what kind of crop we’re aiming for.
Sustainable Practices in Greenhouse Horticulture
When we talk about making agriculture greener, greenhouses are really stepping up. It’s not just about growing plants indoors; it’s about doing it in a way that’s kinder to the planet. Think less waste, less pollution, and using resources smarter. This shift is key to feeding more people without using up all our natural resources.
Water Conservation and Recycling
Water is a big deal in growing things, and greenhouses are getting really good at not wasting it. Many are switching to systems like hydroponics, which use way less water than traditional soil farming. Plus, they’re setting up ways to clean and reuse the water and the nutrients that go with it. It’s like a closed loop, so very little gets lost.
Here are some ways greenhouses are saving water:
- Collecting Rainwater: Simple systems can catch rainwater that runs off. This water can then be filtered and used for irrigation.
- Recycling Irrigation Water: Water that drains from the plants isn’t just dumped. It’s collected, treated (sometimes with methods like reverse osmosis to make it super clean), and then used again. This drastically cuts down on the need for fresh water.
- Smart Irrigation: Using systems like drip or micro-irrigation means water goes right to the plant roots, where it’s needed. This avoids water evaporating from the soil surface or running off.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Sources
Greenhouses need energy, especially for heating and lighting, but they’re finding cleaner ways to get it. Many are putting up solar panels to power their operations, which means less reliance on fossil fuels and fewer greenhouse gases. They’re also upgrading their equipment to be more efficient.
Some common energy-saving moves include:
- LED Lighting: Swapping out old, power-hungry lights for efficient LEDs makes a big difference in electricity bills and energy use.
- Better Heating: Using systems that heat the soil or water more directly, and controlling them with sensors, means less wasted heat.
- Insulation: Modern greenhouses use special screens and better insulation to keep the heat in during colder months and out during warmer ones, reducing the need for active heating or cooling.
Reducing Pesticide Use and Contamination Risks
One of the built-in benefits of a greenhouse is that it’s a controlled environment. This naturally means fewer pests can get in from the outside. Because of this, growers often don’t need to use as many pesticides as they would in open fields. This is good for the environment and means the food produced is less likely to have chemical residues. The controlled setting also helps prevent contamination from outside sources, leading to cleaner produce.
Companies are also looking at their own production methods. For example, some are exploring ways to use electricity from cleaner sources to power their manufacturing of growing materials, further reducing their overall environmental impact.
Climate Control for Year-Round Production
Being able to grow crops no matter the season is a big deal for food production. Greenhouses make this possible by letting us control the environment inside. It’s not just about keeping it warm; it’s a whole system working together.
Automated Temperature and Humidity Regulation
Keeping the temperature and humidity just right is key. Modern greenhouses use sensors that constantly check these levels. These systems can automatically adjust heating, cooling, and ventilation to keep things stable. This means plants get what they need, even when it’s freezing outside or sweltering hot. Think of it like a smart thermostat for your plants, but way more advanced. It can even be programmed for different times of day or different stages of plant growth. This precision helps prevent diseases and ensures plants grow strong and healthy, leading to better yields.
Energy Screens and Insulation Strategies
To keep that controlled climate from escaping, good insulation is a must. This includes things like double-layered polycarbonate walls that trap heat, much like a thermos. Then there are energy screens, often made of special fabrics, that can be deployed at night or on cold days to act like a blanket, stopping heat from rising out of the greenhouse roof. Sealing up any cracks or gaps with materials like silicone caulk also makes a big difference. These methods help keep the inside temperature steady without needing to run the heating system constantly, saving a lot of energy and money.
Passive and Active Ventilation Techniques
Airflow is super important. Too much humidity can cause mold, and plants need fresh air too. Ventilation systems handle this. Passive ventilation uses natural forces, like wind and the tendency for hot air to rise, to move air through vents. It’s simple and doesn’t use much energy. Active ventilation, on the other hand, uses fans to force air circulation. This gives growers more control, especially on still days or when they need to cool things down quickly. Often, a mix of both passive and active methods is used to get the best results. This careful management of air movement is vital for plant health and creating the perfect growing space all year long.
Adapting Greenhouse Horticulture to Climate Challenges
The weather outside can be pretty wild these days, right? We’re seeing more intense storms, heatwaves, and just generally unpredictable conditions. This makes growing food the old-fashioned way a lot trickier. But that’s where greenhouses really shine, especially when we think about how to keep things going despite these climate shifts.
Mitigating Extreme Weather Impacts
Greenhouses act like a shield against the elements. Think of them as a sturdy bubble protecting your plants. They can handle strong winds, heavy rain, and even hail that would otherwise flatten crops in an open field. This controlled environment means growers can keep producing food even when the weather outside is doing its worst. We’re talking about using stronger materials for the structure, like reinforced glass or polycarbonate panels, and making sure everything is sealed up tight. Some setups even have systems to quickly drain excess water if there’s a downpour, preventing waterlogged roots.
Developing Resilient Crop Varieties
It’s not just about the building; it’s about what’s growing inside too. Scientists are working on developing plant varieties that can handle a wider range of conditions. This means finding or breeding plants that can tolerate higher temperatures, use water more efficiently, or even resist certain pests that might become more common with climate change. It’s like giving the plants a built-in advantage.
Here are a few ways this is happening:
- Selective Breeding: Looking for plants that naturally show traits like heat tolerance or drought resistance and breeding them.
- Genetic Modification: Using advanced techniques to introduce specific traits that help plants survive challenging environments.
- Hybridization: Crossing different plant varieties to combine desirable characteristics.
The Role of Controlled Environment Agriculture
Controlled Environment Agriculture, or CEA, is basically the fancy term for growing food in these high-tech, protected spaces like greenhouses. It’s a big part of the solution because it gives us so much control. We can manage the temperature, humidity, light, and nutrients precisely. This means we can grow crops year-round, regardless of what’s happening outside. It also allows us to grow a wider variety of crops in places where it might not have been possible before, reducing the need to transport food long distances. This whole approach is key to making our food system more stable and less vulnerable to the unpredictable nature of our changing climate.
Collaboration and Future of Greenhouse Horticulture
Industry Partnerships for Innovation
It’s pretty clear that nobody can do this whole advanced farming thing alone. The future of growing food in greenhouses really hinges on folks working together. Think about it: you’ve got companies making the fancy sensors, others building the efficient lights, and then the growers themselves who know what plants actually need. When these groups team up, that’s when the real magic happens. Companies like Grodan, for example, don’t just make growing stuff; they actively partner with other tech providers and, importantly, with farmers. They run trials, share what they learn through guides and at events. It’s like a big, ongoing experiment to figure out the best ways to grow more, better, and with less waste. This kind of teamwork is what pushes the whole industry forward, making sure we’re all learning and improving.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Gone are the days of just guessing what your plants need. Modern greenhouses are packed with sensors that collect tons of information – temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, nutrient concentrations, you name it. The real game-changer is what happens with all that data. Instead of just having numbers on a screen, growers are starting to use this information to make smarter choices. They can see exactly how a change in lighting affects fruit development or how adjusting the watering schedule impacts yield. This means less guesswork and more precise control over the growing environment. It’s about using the data to fine-tune everything, from irrigation to climate control, leading to healthier plants and bigger harvests. This shift towards data-informed growing is probably one of the biggest leaps we’re seeing.
Ensuring Food Security Through Advanced Growing
So, what’s the big picture here? It’s about making sure everyone has enough to eat, even with a changing climate and more people on the planet. High-tech greenhouses offer a pretty solid answer. They let us grow food reliably, year-round, regardless of what’s happening outside. We can grow a wider variety of crops, including things that might struggle in traditional fields. Plus, these controlled environments mean we can cut down on pesticides and use water and energy much more efficiently. It’s not just about growing more food; it’s about growing it more sustainably and reliably. This technology is a key piece of the puzzle for building a more secure food future for everyone.
Looking Ahead: A Greener Plate
So, what does all this mean for the future? It’s pretty clear that greenhouses are becoming a bigger deal in how we grow food. They let us grow more, year-round, using less water and energy, which is a win for everyone. Plus, they help us grow things closer to home, cutting down on transport. While it’s not a magic bullet for all our food problems, these high-tech farms are definitely a big step towards a more sustainable way of feeding ourselves. It’s exciting to see how these innovations will keep changing what’s on our plates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes greenhouses so special for growing food?
Greenhouses are like super-controlled rooms for plants! They let farmers carefully manage things like temperature, light, and water. This means they can grow healthy food all year long, no matter what the weather is like outside. It’s a smart way to get fresh food consistently.
How do new technologies help greenhouses grow more food?
Think of high-tech greenhouses as having a plant’s personal assistant! Smart sensors watch over the plants, telling computers exactly what the plants need. Special lights help them grow even when the sun isn’t strong, and smart systems make sure plants get just the right amount of water and food. This all helps plants grow better and faster.
Can greenhouses grow more than just common vegetables?
Absolutely! While they’re great for yummy fruits and veggies, greenhouses are also being used to grow special things like plants for medicine and unique food ingredients. With new growing methods, farmers can cultivate a wider variety of crops than ever before.
Are greenhouses good for the environment?
Yes, they can be! Greenhouses use water much more efficiently because they can collect and reuse it. They also use less energy, especially when they use special LED lights and renewable power sources like solar. Plus, because the environment is controlled, farmers don’t need to use as many bug sprays.
How do greenhouses keep plants growing when it’s cold or hot outside?
Greenhouses have built-in systems to control the temperature. They use things like special insulation, covers that can block or let in sun, and fans to keep the air moving. This way, farmers can create the perfect warm or cool spot for their plants, even during heat waves or cold snaps.
What’s the future of growing food in greenhouses?
The future looks bright! Farmers are working together and using lots of data to make greenhouses even smarter. This helps them grow more food in a sustainable way, which is super important for making sure everyone has enough healthy food to eat, especially as our planet faces challenges like climate change.