Indian agriculture is going through a big change. For years, farming here has been the same, but now, new ideas and technology are popping up everywhere. It’s not just about planting seeds and hoping for the best anymore. We’re seeing smart tools, better seeds, and even robots start to show up in fields across India. This shift is really important for feeding everyone and making sure farming can handle things like weird weather. Let’s take a look at some of the cool stuff happening.
Key Takeaways
- Precision agriculture and digital tools, like satellite imaging and IoT sensors, are helping farmers manage crops better and use resources more wisely in Indian agriculture India.
- Biotechnology is leading to new crop varieties that can handle tough weather and pests, while also promoting the use of natural farming inputs.
- Automation and robotics, including drones and self-driving machines, are making farm work more efficient and less labor-intensive.
- Vertical farming and controlled growing methods offer new ways to produce food, especially in cities, using less water and land.
- Developing crops that can survive climate challenges and adopting sustainable farming methods are key to making Indian agriculture India resilient for the long term.
Precision Agriculture and Digital Farming Innovations
It feels like just yesterday that farming was all about gut feelings and what your grandfather taught you. Now, things are changing fast. We’re seeing a big shift towards what they call precision agriculture and digital farming. Basically, it means using a whole bunch of new tech to farm smarter, not just harder.
Leveraging Satellite Imaging and IoT for Enhanced Crop Management
Think about looking down on your fields from space. That’s kind of what satellite imaging lets farmers do. These images can show you things like how healthy your crops are, if they’re getting enough water, or if there’s a problem brewing that you can’t see from the ground. Then there’s the Internet of Things, or IoT. This involves putting little sensors all over the farm – in the soil, on equipment, you name it. These sensors collect all sorts of data, like soil moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content. All this information gets sent to the farmer, usually on their phone or computer. This data helps farmers make really specific decisions about where and when to water, fertilize, or apply pest control, instead of just doing it everywhere. It’s about using just what’s needed, where it’s needed.
AI-Driven Advisory Services for Farmers
So, you’ve got all this data coming in from satellites and sensors. What do you do with it? That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) comes in. AI can look at all that information, along with weather forecasts and historical data, and give farmers advice. It’s like having a super-smart farming consultant available 24/7. These AI systems can predict potential crop diseases before they become a big problem, suggest the best time to plant, or even give tips on how to get the best price for your produce at market. Many of these services are delivered through simple mobile apps, making them accessible even to farmers with smaller plots of land.
The Growing Adoption of Smart Farming Technologies in Indian Agriculture
It’s not just a few big farms getting in on this either. Smart farming tech is starting to spread across India. We’re seeing more farmers use:
- Soil moisture sensors: To make sure they’re not over or under-watering crops.
- Weather forecasting apps: To plan fieldwork around rain or extreme heat.
- Digital record-keeping: To track inputs and yields more accurately.
- Online marketplaces: To connect directly with buyers and cut out middlemen.
This move towards digital tools and data-driven farming is helping farmers manage risks better, use resources more efficiently, and hopefully, improve their incomes. It’s a big change, but one that seems to be gaining serious momentum.
Biotechnology’s Role in Advancing Indian Agriculture
Biotechnology is really shaking things up in Indian farming, and honestly, it’s about time. We’re talking about using science to make crops tougher, more nutritious, and better for the environment. It’s not just about tweaking things a little; it’s a pretty big deal for the future.
Genome Editing for Climate-Resilient and Improved Crop Varieties
Think about crops that can handle tough weather. That’s where genome editing, like CRISPR, comes in. Scientists can now make very specific changes to a plant’s DNA. This means we can develop varieties of rice, wheat, and millets that can better survive dry spells or heavy rains. This ability to create climate-resilient crops is becoming super important as weather patterns get more unpredictable. It also helps in making crops resistant to common pests and diseases, meaning less need for chemical sprays.
The Rise of Biological Inputs for Sustainable Farming
Beyond just the seeds, biotechnology is also giving us better ways to manage soil and pests. Instead of relying heavily on chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can harm the soil and water, we’re seeing more biological inputs. These are things like biofertilizers made from helpful microbes that boost soil fertility naturally, and biopesticides that use natural organisms to control pests. Using these helps keep the soil healthy for the long run and reduces our environmental footprint.
Enhancing Food Security and Nutrition Through Genetic Innovation
So, what does all this mean for us? Well, it’s a big step towards making sure everyone has enough to eat and that the food we eat is good for us. By improving crop yields and making them more nutritious – like developing rice with extra vitamins – biotechnology plays a key role. It’s about creating a more stable food supply that can feed a growing population while also improving the health benefits of our staple foods.
Automation and Robotics Transforming Farm Operations
Farming in India is getting a serious upgrade, moving way beyond just tractors and plows. We’re talking about machines and robots that can do a lot of the heavy lifting, and often, with more accuracy than we can manage by hand. This isn’t science fiction anymore; it’s becoming a real part of how farms operate, especially for bigger operations or those growing high-value crops.
Autonomous Tractors and AI-Guided Implements
Imagine tractors that drive themselves. That’s what autonomous tractors are all about. They use GPS and AI to plow fields, plant seeds, or apply fertilizer with incredible precision. This means less overlap, less wasted seed or fertilizer, and a more uniform crop. AI-guided implements, like planters or sprayers, can adjust their settings on the fly based on what they’re seeing in the field, making sure each plant gets exactly what it needs. This level of automation is a game-changer for efficiency and reducing the need for manual labor, which is becoming harder to find.
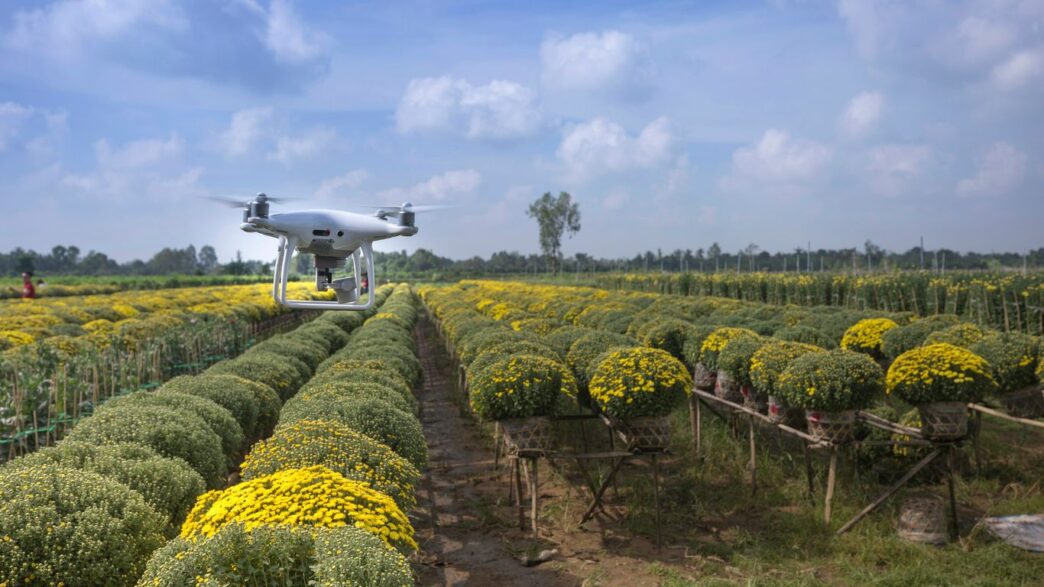
Drones for Crop Surveillance and Targeted Application
Drones are becoming indispensable tools. They can fly over vast fields, taking high-resolution pictures that help farmers spot problems like pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies early on. But they do more than just look; many drones are equipped to spray pesticides or fertilizers precisely where they’re needed, rather than blanket-spraying the whole field. This saves a lot on chemicals and reduces environmental impact. Some drones can even be used for seeding in hard-to-reach areas.
Robotic Systems for Harvesting and Field Tasks
Harvesting is often the most labor-intensive part of farming. Robotic systems are starting to tackle this, especially for delicate crops like fruits and vegetables. These robots can identify ripe produce, pick it gently without bruising, and even sort it. While still developing, especially for India’s diverse crops, these systems promise to reduce post-harvest losses and make harvesting more consistent. Beyond harvesting, robots are also being developed for tasks like weeding, which can be a back-breaking job for farmworkers.
Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture
With cities growing and less land available for farming, new ways of growing food are popping up, especially near big towns. Vertical farming and controlled environment agriculture (CEA) are changing how we produce food in India. Think of it like stacking farms on top of each other. These systems use modular towers to grow crops, which is a smart way to use space when land is tight. This is a big deal for places with lots of people.
Optimizing Space with Vertical Farming Towers
Vertical farms stack crops in layers, often in towers. This means you can grow a lot of food in a small footprint. It’s perfect for urban areas where land is expensive and scarce. Imagine a building dedicated to growing fresh produce right in the middle of a city. This approach cuts down on the need for vast farmlands and brings food production closer to where people live.
Hydroponics and Aeroponics for Water-Efficient Cultivation
These methods grow plants without soil. Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water, while aeroponics mists the plant roots with water and nutrients. Both use way less water than traditional farming – sometimes up to 90% less. This is a huge advantage in a country like India, where water can be a problem. It also means you can grow crops in places that don’t have good soil.
Here’s a quick look at how they compare:
| Feature | Hydroponics | Aeroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use | Low (recirculated nutrient solution) | Very Low (misted roots) |
| Nutrient Delivery | Roots submerged in nutrient solution | Roots suspended and misted |
| System Complexity | Moderate | High (requires precise misting control) |
| Suitability | Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, peppers | Leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, root crops |
Year-Round Production with LED Lighting Systems
Controlled environments mean you’re not at the mercy of the weather. Using LED lights, farmers can control the light spectrum and duration, mimicking ideal growing conditions. This allows for consistent, year-round harvests, regardless of the season or external climate. It also means you can grow specific crops that might not normally do well in the local climate. This technology helps ensure a steady supply of fresh produce, reducing reliance on seasonal availability and imports.
Climate-Resilient Crops and Sustainable Farming Practices

The weather’s been pretty wild lately, right? We’re seeing more floods, longer dry spells, and just generally unpredictable patterns. This is hitting Indian farms hard. So, it makes total sense that a lot of the new ideas in farming here are all about making crops tougher and farming gentler on the land.
Developing Seeds for Drought and Flood Tolerance
Scientists are working hard to create new kinds of seeds. They’re breeding crops like rice, wheat, and millets that can handle tough conditions. Think seeds that don’t need as much water or can survive when fields get waterlogged. This means farmers can keep growing food even when the weather doesn’t cooperate. Some of these new varieties are showing promise for better yields, maybe even up to 25% more in some cases, and they often need fewer chemicals too.
Conservation Agriculture for Soil Health and Sustainability
This is all about treating the soil right. Instead of plowing fields heavily, which can damage the soil structure, conservation agriculture uses methods like minimal tillage. Farmers also use cover crops – planting things like clover or vetch between main crops – to protect the soil and add nutrients. Crop rotation, where you switch what you plant in a field each season, is another big part of it. These practices help keep the soil healthy, hold onto water better, and make the whole farm more sustainable over time.
Agroforestry for Biodiversity and Long-Term Resilience
Agroforestry is a pretty neat idea: mixing trees and shrubs into farmland. It’s not just about planting trees for shade. These trees can help improve soil quality, provide habitats for helpful insects and birds, and even offer additional products like fruit or timber. This approach builds a more diverse and stable farming system that can bounce back better from problems and keep producing for years to come. It’s a way to work with nature, not against it, for a more robust future.
Blockchain for Transparent Agricultural Supply Chains

You know, it’s wild how much we worry about where our food comes from these days. Is it organic? Was it grown ethically? Did it travel halfway around the world? For a long time, figuring that out was a real headache, especially with so many people involved between the farm and your plate. But that’s where blockchain is starting to make a big difference in Indian agriculture.
Think of it like a super secure digital notebook. Every single step a product takes – from the seeds planted, to the fertilizer used, to when it was harvested, and how it was transported – gets written down. And here’s the cool part: once it’s written, you can’t erase or change it. This makes it really hard for anyone to mess with the information.
Ensuring Traceability from Farm to Market
This digital record-keeping means we can actually track food all the way back to the farm it came from. For consumers, this is huge. You can scan a QR code and see the exact farm, the date of harvest, and maybe even details about the farming practices used. This is especially important for things like organic produce or high-value exports where authenticity really matters. It builds trust, plain and simple.
Facilitating Fair Pricing and Reducing Middlemen
Another big win is how blockchain can help farmers get a fairer deal. By creating direct links between farmers and buyers, and using something called ‘smart contracts’ (which are basically automated agreements), payments can be made much faster and more reliably once certain conditions are met. This cuts out a lot of the middlemen who often take a big chunk of the profit, meaning more money stays with the farmer. It also helps reduce waste and fraud, especially with perishable goods, because the whole process is more streamlined and accountable.
Enhancing Trust Through Digital Ledger Technology
Ultimately, blockchain is all about building trust in the food system. It creates a shared, unchangeable record that everyone involved can see. This transparency helps prevent issues like food adulteration and ensures that quality standards are met. For India, with its massive agricultural sector, this technology is a game-changer for making the entire supply chain more reliable, efficient, and fair for everyone involved, from the farmer in the field to the person buying groceries.
The Road Ahead for Indian Farms
So, looking at everything that’s happening, it’s pretty clear Indian agriculture is on the move. We’re seeing a big shift, with new tech like smart sensors, AI, and even robots starting to show up in fields. It’s not just about getting more crops; it’s about doing it smarter, using less water and fewer chemicals, and making sure the land stays healthy for the future. Plus, things like blockchain are starting to make the whole process from farm to table more open and fair. It’s a lot to take in, but the goal is simple: a stronger, more reliable food system for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main new technologies helping Indian farms?
Indian farms are getting help from many new technologies! Think of smart farming tools like sensors and satellites that tell farmers exactly what their crops need. We also have super smart computer programs that give advice, special seeds that can handle tough weather, robots that do farm work, and even ways to grow food in tall buildings. Plus, new ways to track food from the farm to your plate are making things more honest.
How does smart farming help farmers grow more food?
Smart farming, also called precision agriculture, uses technology to give crops exactly what they need, when they need it. Satellites and sensors watch the soil and plants closely. This means farmers can use just the right amount of water and fertilizer, and deal with pests quickly. It’s like giving each plant personal attention, which helps them grow better and produce more food.
What is biotechnology and how is it used in farming?
Biotechnology is like using nature’s own tools to make plants better. Scientists can now make tiny changes to a plant’s ‘instructions’ (its DNA) to make it stronger. This means they can create seeds that don’t need much water, can fight off bugs better, or even have more vitamins. It’s a way to improve crops without using as many chemicals.
Are robots and machines starting to work on Indian farms?
Yes, they are! We’re seeing more robots and smart machines helping out. Self-driving tractors can plant seeds perfectly, and drones can spray crops or check on their health from the sky. Robots are even being developed to pick fruits and vegetables. These machines help farmers do tough jobs faster and more accurately, saving time and effort.
What is vertical farming and why is it important?
Vertical farming is a cool way to grow food indoors, stacking plants in layers, like in a tall building. It uses much less land and water than regular farming, which is great for cities where space is limited. These farms can grow food all year round, even in bad weather, and the food is often grown without pesticides, making it super fresh and healthy.
How does blockchain help make food safer and fairer?
Blockchain is like a super secure digital diary for food. It keeps a record of every step a food item takes, from when it was planted on the farm all the way to when it reaches the store. This makes it easy to see where your food came from and proves it’s real. It also helps farmers get paid fairly because it cuts out some of the people in the middle.