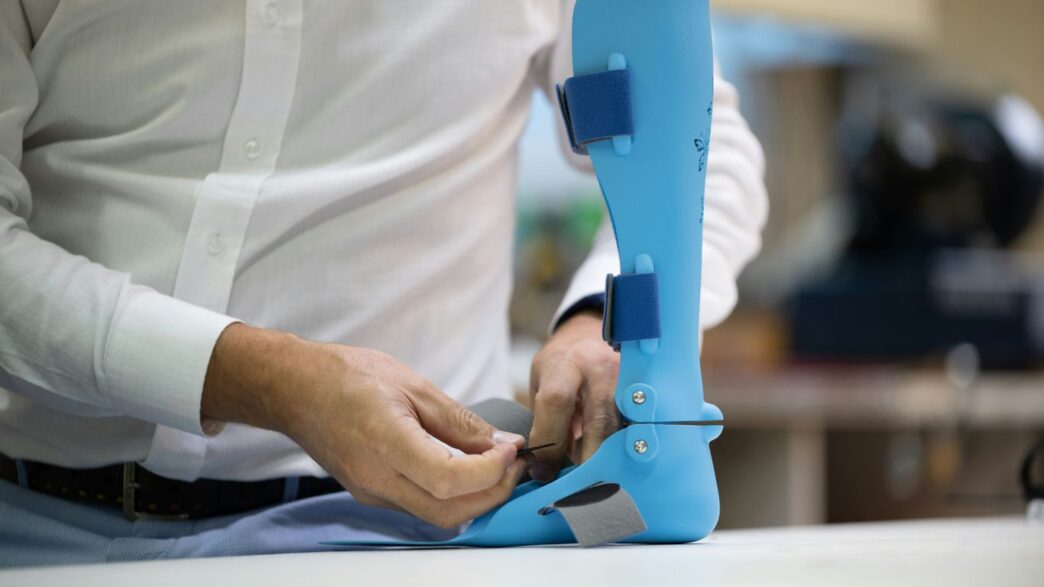
It’s pretty wild how much 3D printing is changing things in medicine. You know, the stuff that used to take ages or was just impossible to make? Now it’s becoming a reality, layer by layer. This technology isn’t just a cool gadget; it’s actually making a big difference in how doctors treat people and how new medical tools are made. We’re talking about custom parts for patients, better ways to plan surgeries, and even growing tissues. It’s a huge shift for the whole 3d printing medical industry.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing is totally changing how medical devices are made, allowing for custom prosthetics and implants that fit just right.
- Surgeons can use 3D printed guides for more precise operations, leading to better results for patients.
- The technology means treatments can be tailored to each person’s body, improving how well they recover.
- Bioprinting is opening doors to creating biological structures and tissues, which could revolutionize regenerative medicine and drug testing.
- In the future, 3D printing will likely be integrated with AI and other smart tech for even more advanced and accessible healthcare solutions.
Revolutionizing Medical Device Manufacturing

It’s pretty wild how 3D printing is shaking things up in making medical stuff. For ages, we’ve been stuck with pretty standard ways of making things, which meant devices were mostly one-size-fits-all. But now? We can actually make things that fit you perfectly. This whole process is changing the game, making devices that are way more effective and often less expensive to produce.
Pioneering Personalized Prosthetics and Implants
Think about prosthetics. Before, getting a prosthetic limb meant dealing with generic shapes and sizes that might not feel quite right. Now, with 3D printing, we can scan a person’s limb and create a prosthetic that’s molded exactly to their body. It’s not just about looks; it’s about comfort, function, and how well it integrates. The same goes for implants, like hip replacements or cranial plates. Instead of using standard sizes, doctors can now get implants printed that match a patient’s unique bone structure. This means a better fit, less chance of complications, and a quicker recovery. It’s a huge step up from the old methods.
Enhancing Surgical Precision with Custom Guides
Surgeons are also getting in on this. Imagine a complex surgery where every millimeter counts. 3D printing allows for the creation of custom surgical guides. These are like little jigs that fit precisely onto a patient’s anatomy during surgery, showing the surgeon exactly where to cut or place a screw. They’re made based on the patient’s scans, so they’re incredibly accurate. This level of precision can really help avoid mistakes and make surgeries go more smoothly. It’s a big deal for tricky procedures, helping to improve patient outcomes and reduce risks. This technology is really changing how complex medical components are made.
Overcoming Traditional Manufacturing Constraints
Traditional manufacturing has its limits. Making intricate shapes or highly customized parts can be really expensive and time-consuming, sometimes even impossible. You often need special molds or tooling, which adds a lot of cost and takes a long time to set up. 3D printing, on the other hand, builds things layer by layer directly from a digital file. This means:
- Complex Geometries: You can create shapes that would be impossible with older methods.
- Reduced Waste: Often, less material is wasted compared to subtractive manufacturing.
- Faster Prototyping: Designs can be tested and refined much more quickly.
- On-Demand Production: Devices can be made as needed, reducing the need for large inventories.
This flexibility means that manufacturers can respond faster to new needs and create devices that were previously out of reach. It’s a real game-changer for innovation in the medical field.
Transforming Patient-Specific Care
It’s pretty amazing how 3D printing is changing the game when it comes to treating people as individuals. You know, the old way of doing things often meant a sort of ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach, which, let’s be honest, doesn’t always work out great for everyone. But now, we’re seeing treatments and medical tools made just for you. This is a huge step forward.
Tailoring Treatments to Individual Anatomy
Think about it: everyone’s body is different. Your bones, your organs, they all have unique shapes and sizes. 3D printing lets doctors create things that fit perfectly. For example, surgical guides can be printed based on a patient’s specific scans. This means the surgeon knows exactly where to cut or place something before even stepping into the operating room. It’s like having a custom map for a complex journey. This technology is really about making sure medical devices fit exactly right for optimal function, which is a big deal for patient outcomes.
Improving Patient Outcomes Through Customization
When things fit better and are designed for a specific person, patients tend to do better. This applies to everything from artificial limbs to implants. Instead of a standard prosthetic that might feel awkward or not quite right, a 3D-printed one can be shaped and sized precisely for the individual. This not only improves comfort but also how well the device works. We’re seeing a shift towards solutions that are:
- More comfortable for the patient.
- Better suited to their daily activities.
- Potentially leading to faster recovery times.
The Rise of Bespoke Medical Solutions
This move towards custom-made medical items is really picking up steam. It’s not just about prosthetics anymore. We’re talking about custom-fit braces, specialized tools for complex surgeries, and even models of a patient’s own anatomy to help plan procedures. The ability to produce these unique items on demand, without the massive tooling costs of traditional manufacturing, is opening up possibilities that were just science fiction a few years ago. It’s a move away from mass production and towards truly personalized healthcare.
Advancing Bioprinting and Regenerative Medicine
This is where things get really futuristic. Bioprinting is basically using 3D printing technology to create biological structures, like tissues and even organs. It’s a huge step forward for regenerative medicine, aiming to repair or replace damaged body parts.
Creating Complex Biological Structures
Imagine printing a piece of skin for burn victims or a scaffold that helps nerves regrow. That’s what bioprinting is working towards. Researchers are developing special "bioinks" – think of them as inks made from living cells, growth factors, and biocompatible materials. These inks can be precisely layered to build intricate tissue architectures. The goal is to create functional biological constructs that mimic natural tissues. This technology is still developing, but it holds promise for creating everything from simple cell cultures for drug testing to more complex tissues.
Accelerating Drug Discovery and Development
Testing new drugs on animals isn’t always ideal, and human trials are expensive and time-consuming. Bioprinting offers a solution by creating realistic 3D tissue models. These models, like printed heart tissue, can be used to test drug efficacy and toxicity in a more human-like environment. This could significantly speed up the process of finding new medicines and make drug development more efficient. It’s a powerful tool in advanced manufacturing, particularly useful for fabricating drug delivery systems, such as implants or scaffolds with controlled release properties. This capability is crucial for developments in medical treatments and therapies [b412].
Engineering Tissues for Future Therapies
Looking further ahead, the dream is to bioprint entire organs for transplantation. This could solve the critical shortage of donor organs and eliminate the risk of rejection. While printing a whole, complex organ is still a long way off, progress is being made. Researchers are working on printing different cell types together, along with supportive materials, to build functional tissue units. The potential applications are vast, from creating patient-specific tissues for personalized treatments to developing new ways to repair injuries. It’s a complex field, but the potential to change lives is enormous.
Innovations in Pharmaceutical Applications
Personalized Drug Dosages and Formulations
Forget the one-size-fits-all approach to medicine. 3D printing is really changing the game here, letting us make drugs that are exactly what a specific person needs. Think about it – instead of getting a standard pill that might be too strong or too weak, we can print a dose that’s just right for your body. This is a big deal for folks who have trouble with standard dosages, like kids or older adults, who often need very specific amounts. We can also tweak how the medicine is released. Some drugs need to work fast, others need to release slowly over hours. 3D printing lets us build these complex release profiles right into the pill itself. It’s like having a custom-made delivery system for every single patient.
On-Demand Medication Production
This technology also means we don’t have to rely on massive factories churning out tons of the same drug. We can print medications right where and when they’re needed. Imagine a hospital pharmacy or even a local clinic being able to print a specific medication on demand. This cuts down on waste and makes sure that hard-to-get or specialized drugs are available without needing huge stockpiles. It’s a more efficient way to manage drug supplies, especially for rare conditions or during emergencies. Plus, it opens the door for making smaller batches of drugs that might not be profitable for big manufacturers but are vital for certain patient groups.
Developing Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Beyond just pills, 3D printing is letting scientists get really creative with how drugs get into the body. We’re seeing things like microneedle patches printed with incredible precision, designed to deliver medication through the skin without a shot. There are also complex structures being developed that can dissolve in the stomach or release drugs in very specific ways. It’s all about making treatments more effective and easier for patients to use. The ability to create intricate, multi-layered designs means we can combine different drugs or control their release in ways that just weren’t possible before. This really pushes the boundaries of what we can do with medication.
Enhancing Medical Research and Education
3D printing is really changing how we learn about the human body and how we figure out new ways to treat people. It’s not just for making actual medical stuff anymore; it’s become a big deal in classrooms and labs.
Detailed Anatomical Modeling for Training
Forget those old plastic skeletons or flat diagrams. Now, we can print incredibly detailed models of human organs, bones, and even complex systems like the heart or brain. These aren’t just pretty models; they’re built from real patient scans, so they show actual anatomy, including any unique quirks or problems. Medical students can get their hands on these models, turning them around, seeing how things fit together in three dimensions. It’s a much better way to grasp complex structures than just looking at a book. Plus, for rare conditions or specific patient cases, you can print a model that shows exactly what a doctor might encounter.
Developing New Surgical Techniques
Surgeons can now practice complex procedures before they even step into the operating room. Imagine printing a replica of a patient’s tumor or a damaged joint. A surgeon can then use this 3D printed model to plan their approach, figure out the best angles, and even rehearse the steps. This practice run helps them get a feel for the instruments and anticipate any tricky spots. It’s like having a dress rehearsal for surgery, which can really cut down on surprises and improve the actual operation. This also means less risk for the patient because the surgeon is already familiar with the specific anatomy they’ll be working with.
Inspiring Innovation in Medical Devices
When people can easily create and test new ideas, innovation tends to happen faster. 3D printing makes it way simpler and cheaper to prototype new medical tools or devices. Instead of waiting months and spending a fortune on traditional manufacturing, a researcher or engineer can design something, print it out, test it, tweak it, and print it again, all within days or weeks. This rapid iteration cycle is huge for coming up with better surgical instruments, diagnostic tools, or even parts for advanced medical equipment. It lowers the barrier to entry for inventors and allows for more creative solutions to emerge.
The Future of 3D Printing in Healthcare
So, where is all this 3D printing stuff in medicine heading? It’s pretty exciting, honestly. We’re looking at a future where technology is even more woven into our health, making things more personal and effective.
Integrating AI and IoMT for Enhanced Devices
Think about devices that can actually talk to each other and learn. That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) come in. We’re talking about implants that can monitor your body’s signals and send that data straight to your doctor, or even adjust themselves based on what they’re sensing. Imagine a pacemaker that learns your heart’s rhythm and fine-tunes its output automatically. Or a prosthetic limb that uses AI to predict your next movement, making it feel more natural. This fusion of 3D printing with smart tech means medical devices will become more responsive and predictive. It’s like giving your medical gear a brain.
Addressing Regulatory Frameworks and Safety
Of course, with all these cool new advancements, there are big questions about safety and how we regulate them. Making sure that a 3D-printed implant is just as safe, if not safer, than one made the old way is a huge deal. Regulatory bodies are working hard to keep up, creating new guidelines for these custom-made devices. It’s a balancing act: we want innovation, but we absolutely need to make sure everything is tested and approved properly.
Ensuring Accessibility and Ethical Considerations
Another big piece of the puzzle is making sure everyone can benefit from these technologies, not just a select few. How do we make sure that personalized treatments and custom devices are affordable and available to people who need them, no matter where they live? There are also ethical questions to consider, like data privacy when devices are constantly collecting information about our bodies. We need to think about how to use this powerful technology responsibly, making sure it helps more people and doesn’t create new divides.
The Road Ahead
So, looking at everything, it’s pretty clear that 3D printing isn’t just some futuristic idea anymore, especially in medicine. We’ve seen how it’s already changing how doctors make custom implants and guides, making treatments way more personal. Plus, the work being done with bioprinting and custom drugs? That’s huge for developing new ways to fight diseases and help people get better. It’s not perfect yet, and there are still hurdles to jump, like making sure everyone can get these new treatments and figuring out all the rules. But honestly, the potential is massive. This technology is really just getting started, and it’s going to keep reshaping healthcare in ways we’re only beginning to imagine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3D printing, and how is it used in medicine?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is like building something layer by layer with a special printer. In medicine, it’s used to create custom body parts like fake limbs (prosthetics) or replacement joints (implants), tools for surgeons, and even models of organs to help doctors plan operations. It’s like having a super-precise way to make exactly what a patient needs.
How does 3D printing help make medical devices better?
Instead of making generic parts, 3D printing lets doctors and engineers design medical devices that fit a person’s body perfectly. This means prosthetics feel more natural, implants fit better, and surgical tools can be made to perform specific tasks during an operation, making everything safer and more effective.
What is bioprinting, and why is it important?
Bioprinting is a type of 3D printing that uses special ‘bio-inks’ made of living cells. Scientists are using it to create simple tissues and, in the future, might be able to print whole organs. This could help us test new medicines more accurately and eventually solve the problem of organ shortages for people who need transplants.
Can 3D printing change the way we get medicines?
Yes! Imagine getting medicine printed just for you, with the exact right amount and a special way of releasing it in your body. 3D printing can make this happen, allowing for personalized doses and even printing medications right when and where they are needed, which is super helpful for rare diseases or places far from big pharmacies.
How does 3D printing help doctors and students learn?
Doctors and students can use 3D-printed models of real body parts to practice surgeries or learn about complex anatomy. These models are very detailed and realistic, making learning and training much more hands-on and effective than just looking at pictures or diagrams. It’s like having a practice dummy for almost any medical situation.
What’s next for 3D printing in healthcare?
The future looks exciting! We’ll likely see 3D-printed devices that can connect to the internet to monitor health, smarter ways to make sure these devices are safe and approved, and efforts to make sure everyone can get access to these amazing new technologies. It’s all about making healthcare more personal, effective, and available to more people.














