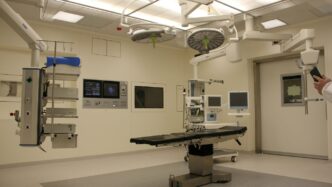
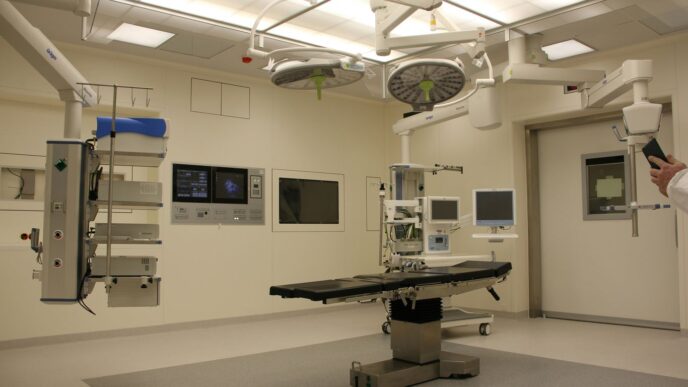
The way we grow food is changing, and fast. With more people living in cities and concerns about our planet growing, traditional farming just doesn’t cut it anymore. That’s where vertical farming comes in. It’s like farming, but stacked up, often indoors, and using smart tech. This approach promises a more sustainable way to get fresh food to our tables, especially in busy urban areas. Let’s look at how this vertical farming future is shaping up.
Key Takeaways
- Vertical farming uses methods like hydroponics and aeroponics to grow plants without soil, saving space and water.
- These indoor farms offer better control over growing conditions, leading to year-round harvests and fewer pesticides.
- By locating farms closer to consumers, vertical farming cuts down on transportation emissions and food waste.
- Technology like AI and smart sensors are making vertical farms more efficient and automated.
- Vertical farming is a key part of urban agriculture, helping cities become more self-sufficient in food production.
Innovations Driving The Vertical Farming Future
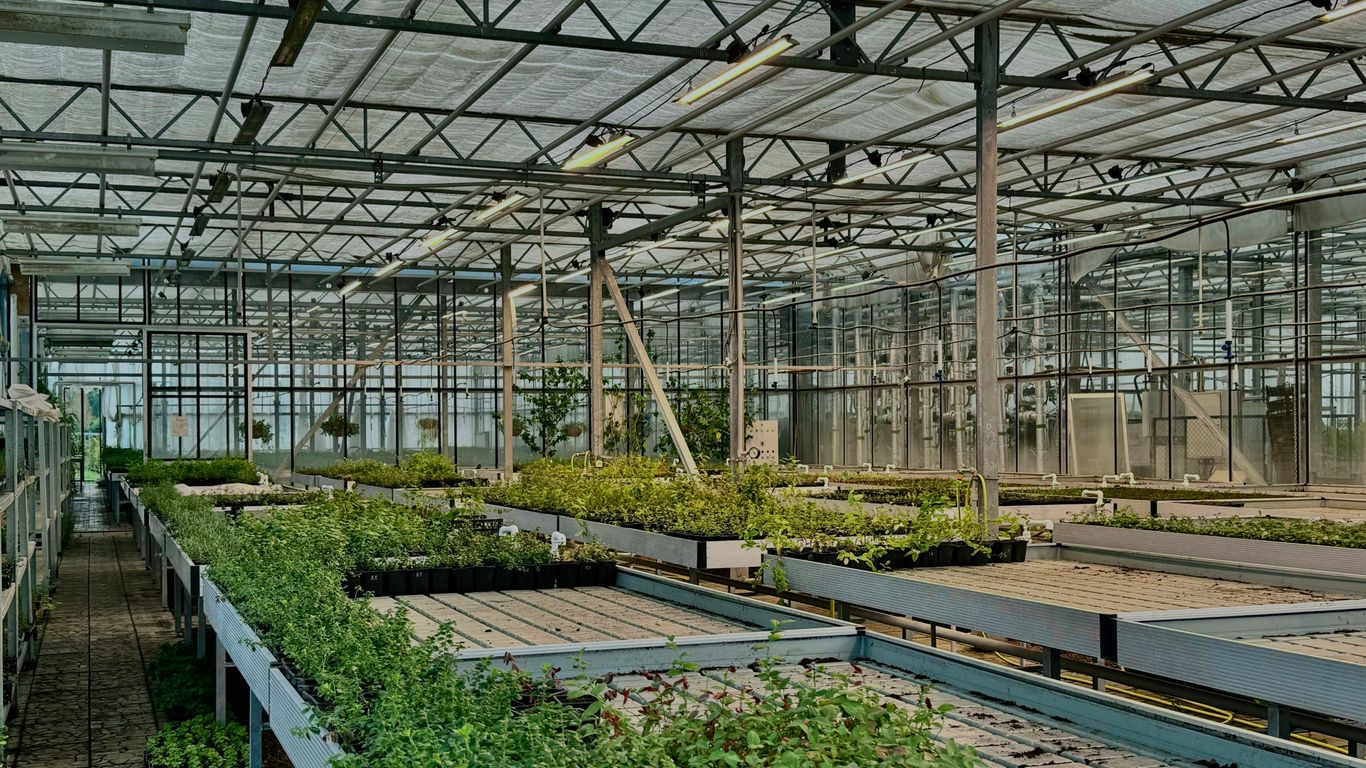

So, what’s actually making vertical farming a thing? It’s not just stacking plants in a warehouse; there are some pretty neat technologies at play that are making it all possible. These aren’t just minor tweaks either; they’re pretty big shifts from how we’ve farmed for centuries.
Hydroponics: Cultivating Without Soil
This is a big one. Hydroponics basically means growing plants using nutrient-rich water instead of soil. Think of it like giving the plants a perfectly balanced meal delivered right to their roots. This method is super efficient because you don’t need to worry about soil quality, pests that live in soil, or the massive amounts of land traditional farming gobbles up. Plus, the water gets recycled, so you’re not just letting it run off into the environment.
Here’s a quick look at how it works:
- Nutrient Solution: A carefully mixed blend of water and essential minerals is provided to the plants.
- Root Support: Plants are often supported by inert materials like rockwool or coco coir, or sometimes just suspended directly in the water.
- Water Efficiency: Because the water is recirculated, it can use up to 90% less water than traditional farming.
Aeroponics: Roots Suspended in Air
If hydroponics is cool, aeroponics is like the next level. Here, plant roots are actually suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution. It sounds a bit sci-fi, right? But it works. This method allows for maximum oxygen exposure to the roots, which can lead to faster growth and healthier plants. It’s also incredibly water-wise, as the misting is very precise.
Key aspects of aeroponics include:
- Misting System: Fine droplets of nutrient solution are sprayed directly onto the roots at regular intervals.
- Air Circulation: Excellent airflow around the roots is vital for their health and growth.
- Rapid Growth: Many growers report faster crop cycles compared to other methods.
Controlled Environments for Optimal Growth
This is the umbrella that covers both hydroponics and aeroponics, really. Vertical farms are essentially high-tech greenhouses or indoor spaces where every single condition can be managed. We’re talking about temperature, humidity, light levels, and even CO2 concentration. This precise control means you can grow crops year-round, regardless of the weather outside, and tailor the environment for the absolute best yield and quality. It’s like having a perfect spring day, every single day, inside the farm.
Sustainability Benefits of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming isn’t just a cool new way to grow food; it’s actually a pretty big deal for the planet. Think about it: we’re facing a world where land is getting tighter and water is becoming more precious. Vertical farms tackle these issues head-on.
Maximizing Land Use Efficiency
This is a huge one. Instead of spreading farms out horizontally, taking up vast amounts of land, vertical farms grow crops in stacked layers. This means you can grow a lot more food in a much smaller footprint. It’s like turning a single-story building into a skyscraper for lettuce. This is especially important in cities where every square foot of land is valuable and often already built upon. We’re talking about getting more food from less space, which is a win-win for feeding growing populations without gobbling up natural habitats.
Conserving Precious Water Resources
Traditional farming can be really thirsty work. Vertical farms, however, use systems like hydroponics and aeroponics that recirculate water. In these setups, water is delivered directly to the plant roots, often with added nutrients. This means significantly less water is lost to evaporation or runoff compared to field farming. Some estimates show vertical farms can use up to 95% less water than conventional methods. That’s a massive saving, particularly in regions already struggling with water scarcity. It’s about making every drop count.
Minimizing Pesticide and Emission Footprints
Because vertical farms are indoors and controlled environments, they’re naturally protected from many pests and diseases that plague outdoor crops. This drastically reduces or even eliminates the need for chemical pesticides. Less pesticide use means healthier food and a healthier environment. Plus, by locating farms closer to where people live, especially in urban areas, we cut down on the long-haul transportation of produce. Fewer trucks on the road means fewer emissions, which is good news for air quality and climate change. It’s a way to get fresher food to your plate with a much smaller environmental impact.
The Technology Behind Vertical Farming
So, how exactly do these vertical farms work? It’s not just stacking plants on top of each other and hoping for the best. There’s some pretty clever tech involved that makes it all possible. These systems are designed to give plants exactly what they need, when they need it, all while using way fewer resources than traditional farming.
Advanced Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponics is a big one. Instead of dirt, plants grow with their roots sitting in or misted by a nutrient-rich water solution. Think of it like a fancy, super-efficient plant spa. The water is carefully mixed with all the minerals and vitamins the plants need to thrive. This means no soil is needed, which is great for space and also means you don’t have to worry about soil-borne pests or diseases. Plus, the water gets recycled, so you’re not just letting it run down the drain.
Here’s a quick look at how it generally works:
- Nutrient Delivery: A pump circulates the water and nutrient mix to the plant roots.
- Root Support: Plants might be held in place by inert materials like rockwool or coco coir, or sometimes just suspended.
- Water Recycling: Excess water is collected and sent back to the reservoir, reducing waste.
Sophisticated Aeroponic Techniques
Aeroponics takes things a step further. Here, the plant roots are actually suspended in the air, inside a growing chamber. They’re not sitting in water constantly. Instead, a fine mist of nutrient-rich water is sprayed directly onto the roots at regular intervals. This gives the roots plenty of oxygen, which they really seem to like, leading to faster growth. It’s like giving the plants a refreshing, nutrient-packed shower.
Key aspects of aeroponics include:
- Misting System: Nozzles spray a nutrient solution onto the roots.
- Air Exposure: Roots hang freely, getting lots of oxygen.
- Minimal Water Use: Only the water needed for misting is used, making it incredibly water-efficient.
LED Lighting and Environmental Controls
And then there’s the lighting and climate control. Forget relying on the sun. Vertical farms use specialized LED lights. These lights can be tuned to give plants the exact spectrum of light they need for different growth stages, from leafy greens to fruiting plants. It’s like giving them a custom-made sunshine experience, 24/7 if needed. On top of that, sophisticated sensors and computer systems monitor and adjust everything – temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, you name it. This creates a perfectly stable environment, year-round, no matter what’s happening outside. It’s all about precision to get the best possible harvest.
Vertical Farming’s Role in Urban Agriculture
Cities are getting bigger, and that means less space for growing food the old way. Traditional farms need a lot of land, which just isn’t available in crowded urban areas. This is where vertical farming really shines. It’s about growing food right where people live, cutting down on all that travel time and making sure we have fresh stuff available.
Think about it: instead of food traveling hundreds, maybe thousands of miles, it can come from a farm just a few blocks away. This not only means fresher produce for us but also a big drop in the carbon emissions from trucks and planes.
Addressing Urban Food Supply Challenges
Cities often struggle with getting enough fresh food to everyone, especially in areas that are far from traditional grocery stores. Vertical farms can pop up in old warehouses, on rooftops, or even in shipping containers. This brings food production closer to home, making it easier to supply neighborhoods with healthy options year-round, no matter the weather outside.
Reducing Food Miles and Enhancing Freshness
This is a big one. When food is grown locally in a city, it doesn’t need to be picked way before it’s ripe and then shipped across the country. Vertical farms can harvest produce and get it to your plate within hours. This means better taste, more nutrients, and less food waste because things don’t spoil as quickly during transit.
Integrating Farms into City Landscapes
We’re starting to see farms become part of the city itself. Imagine buildings with farms built into them, or community gardens on rooftops. This isn’t just about food; it’s about making cities greener and more connected to where their food comes from. It can even help with things like managing rainwater and improving air quality.
Here’s a quick look at how vertical farms fit into the urban picture:
- Local Production: Food grown right in the city.
- Reduced Transport: Less distance from farm to table.
- Year-Round Supply: Consistent availability regardless of season.
- Space Efficiency: Uses vertical space, not sprawling land.
- Fresher Produce: Harvested and delivered quickly.
The Future of Vertical Farming
AI and IoT for Smarter Operations
The next big leap for vertical farms is all about making them smarter. Think of it like upgrading from a flip phone to a smartphone – everything just works better. We’re talking about using artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to keep a super close eye on everything. Sensors scattered throughout the farm will constantly collect data on things like temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and nutrient concentrations. This information gets sent to AI systems that can then make tiny, instant adjustments to keep the plants perfectly happy. This level of precision means less waste and higher yields, which is a win-win for everyone. It’s like having a tiny, expert farmer for every single plant, 24/7.
Expanding Crop Varieties Indoors
For a while, vertical farms were mostly about leafy greens and herbs. But that’s changing, and fast. Researchers are figuring out how to grow a wider range of crops indoors. This includes things like:
- Berries: Strawberries and raspberries are already being grown successfully in some vertical setups.
- Root vegetables: While trickier, advancements are being made to grow things like carrots and radishes.
- Even some fruits: Early experiments are showing promise for growing smaller fruits like certain types of tomatoes and peppers.
This expansion is huge because it means vertical farms can become a more complete food source, not just a supplement. It’s about making sure we can grow more of what people actually want to eat, right where they live.
Government Support and Investment Trends
It’s not just tech companies and farmers getting excited about vertical farming; governments and investors are too. There’s a growing recognition that this type of farming can help with food security, especially in cities, and reduce our environmental impact. Because of this, we’re seeing more government grants and incentives aimed at helping vertical farms get started and expand. Investment firms are also pouring money into the sector, looking for the next big thing in sustainable food production. This financial backing is what allows for the expensive research and development needed to bring new technologies and crop types to market. It’s a positive cycle: more investment leads to more innovation, which in turn attracts even more investment.
Integrating Vertical Farms into the Circular Economy
Vertical farming isn’t just about growing food in new ways; it’s also about fitting into a bigger picture of how we use resources. Think of it like a giant, smart recycling system for food production. The goal is to make sure that what’s left over from one part of the process can be used somewhere else, cutting down on waste and making everything more efficient.
Waste-to-Resource Strategies
Instead of throwing things away, vertical farms are looking at how to turn "waste" into something useful. For example, plant trimmings and leftover organic matter can be composted. This compost can then be used to enrich soil, perhaps for traditional farms or even for smaller community gardens. Another option is using anaerobic digestion, where organic waste breaks down without oxygen to produce biogas, which can be used for energy, and a nutrient-rich digestate that can be a fertilizer.
Creating Closed-Loop Sustainable Systems
This is where things get really interesting. A closed-loop system means that water, nutrients, and energy are reused as much as possible within the farm itself. For instance, water used in hydroponic or aeroponic systems is often recycled after being filtered and re-enriched. Some farms are even looking at integrating with other businesses. Imagine a vertical farm located next to a brewery; the CO2 released from the brewing process could be captured and used to help plants grow faster in the farm. Similarly, heat generated by data centers could be repurposed to maintain optimal growing temperatures.
Maximizing Resource Utilization
It’s all about getting the most out of everything we put in. This means:
- Water Recycling: Advanced filtration systems capture and reuse water, drastically reducing consumption compared to traditional agriculture.
- Nutrient Management: Precise delivery of nutrients means plants get exactly what they need, minimizing excess and waste.
- Energy Efficiency: Using LED lights that are specifically tuned to plant needs and exploring renewable energy sources like solar power helps lower the farm’s overall energy footprint.
- Byproduct Valorization: Finding uses for all parts of the plant, from the leaves to the roots, prevents anything from going to waste.
The Road Ahead for Vertical Farming
So, it looks like vertical farming is really shaping up to be a big deal for how we grow food. It’s not going to replace all the old ways of farming, especially for things like wheat and rice, but it’s a smart way to get fresh stuff grown right where people live, using way less water and land. With all the new tech coming out, like smarter robots and AI helping out, these farms are only going to get better and more productive. Plus, figuring out how to fit them into a system where waste from one part helps another part is pretty neat for keeping things sustainable. It’s definitely a key piece of the puzzle for making sure we have enough food and taking better care of the planet, especially as the world keeps changing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is vertical farming?
Vertical farming is like growing plants in tall buildings or stacked layers, kind of like a skyscraper for veggies! Instead of using soil, it often uses water or mist to feed the plants, all inside a controlled environment where things like light and temperature are just right.
How is vertical farming different from regular farming?
The biggest difference is where and how it’s done. Regular farming uses big fields outside, while vertical farming happens indoors in stacked layers. This means it doesn’t need as much land or water, and you can grow food all year round, no matter the weather.
What are hydroponics and aeroponics?
These are special ways to grow plants without soil. Hydroponics means the plant’s roots sit in nutrient-rich water. Aeroponics is even cooler because the roots hang in the air and get misted with nutrients. Both help plants grow faster and use less water.
Why is vertical farming good for the environment?
It’s great because it uses way less water, often recycling it. Since it’s indoors, fewer pesticides are needed. Plus, growing food closer to cities means less travel for the food, cutting down on pollution from trucks and planes.
Can vertical farms grow all kinds of food?
Right now, they’re best for leafy greens, herbs, and some fruits like strawberries. Growing big crops like wheat or potatoes is still easier in traditional farms because they need a lot of space. But scientists are working on growing more types of food vertically!
Is vertical farming expensive to set up?
Setting up a vertical farm can cost a lot at first because you need special lights, climate control systems, and technology. However, as the technology gets better and more farms are built, the costs are coming down, and they can save money on water and energy in the long run.