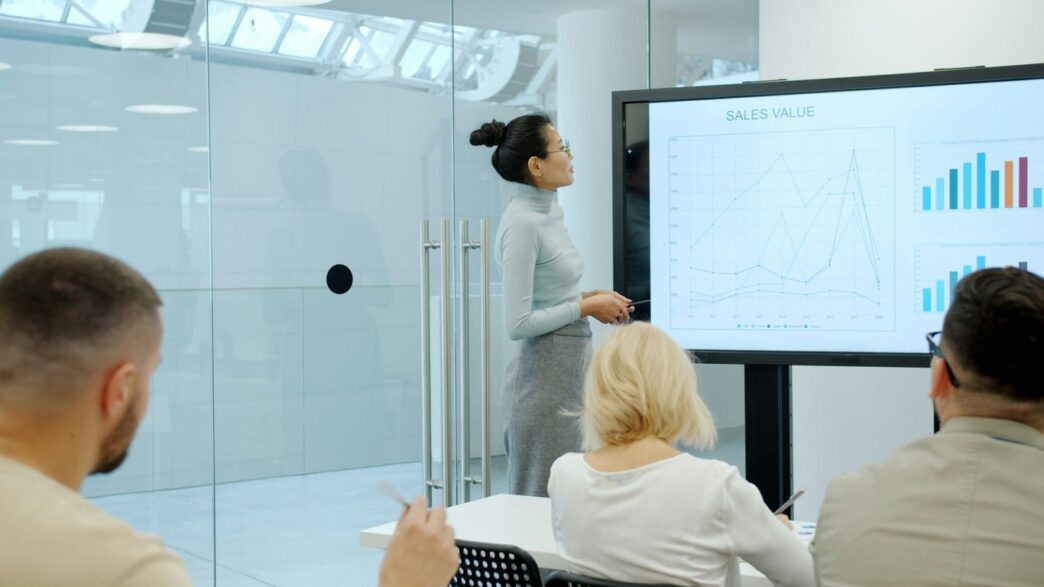
Modern healthcare is all about being more efficient and looking after patients better. For ages, medical gear just sat there, not talking to anything else. Now, we’ve got medical device integration (MDI) to sort that out. Basically, it’s about getting all your different medical gadgets to share information with your computer systems, especially the patient records. This means everyone can see the full picture, all in one place. It’s not just a nice-to-have anymore; it’s becoming a standard part of how hospitals work, helping us make better decisions with all the data we’re collecting.
Key Takeaways
- Medical device integration (MDI) connects various medical gadgets to digital health records, creating a unified patient data view.
- The benefits of MDI include better patient care, smoother hospital operations, and cost savings through automation and fewer errors.
- Implementing MDI involves tackling challenges like getting different systems to work together and keeping patient data safe.
- A good MDI strategy needs to consider all types of devices, how they connect to systems like EHRs, and the use of middleware.
- MDI plays a role in cybersecurity by helping to spot and stop threats related to user identities and access.
Understanding Medical Device Integration (MDI)
The Evolving Healthcare Landscape
Healthcare isn’t what it used to be, is it? We’re seeing more and more sophisticated gadgets popping up in hospitals and even at home, all designed to keep us healthier. Think smart infusion pumps, continuous glucose monitors, and advanced bedside monitors. The problem is, these devices often work in isolation, like little islands of data. This makes it tough for doctors and nurses to get a complete picture of what’s going on with a patient. The whole system is shifting towards using data to make better decisions, and these disconnected devices are a real roadblock. We need a way for all these different pieces of technology to talk to each other and share information effectively. It’s about moving from just having devices to actually using the information they provide.
Bridging Devices and Digital Records
So, what exactly is Medical Device Integration, or MDI? At its heart, it’s about creating a connection. It’s the process and the technology that allows medical devices – from the big machines in the ICU to smaller, wearable sensors – to send their data to other systems. The most common destination is the Electronic Health Record (EHR), but it can also be other hospital information systems. This connection is what turns raw data from a device into useful information within a patient’s digital chart. Imagine a patient’s vital signs from a monitor appearing directly in their EHR without anyone having to type them in. That’s MDI in action. It’s the bridge that links the physical world of medical equipment to the digital world of patient records.
Beyond Connectivity: Actionable Insights
Just connecting devices isn’t the end goal, though. The real magic happens when we can do more with the data that flows from them. MDI isn’t just about getting data from point A to point B; it’s about making that data work harder for us. When information from various devices is collected and organised, it can be analysed in ways that weren’t possible before. This can lead to spotting trends, predicting potential problems before they become serious, and tailoring treatments more precisely to individual patients. It’s about transforming raw numbers into meaningful insights that can genuinely improve patient care and make healthcare operations run more smoothly. Think of it as giving clinicians better tools to understand and act on patient information.
Here’s a look at what MDI aims to achieve:
- Improved Data Accuracy: Reduces manual entry errors.
- Faster Decision Making: Provides real-time data to clinicians.
- Enhanced Patient Monitoring: Allows for continuous observation of vital signs.
- Streamlined Workflows: Automates data collection, freeing up staff time.
The shift towards integrated medical devices is driven by the need for more efficient, accurate, and patient-focused healthcare. It’s about making sure the technology we use actually helps us provide better care, rather than just adding complexity.
The Transformative Benefits of MDI
Enhancing Patient Care and Safety
Getting real-time information from medical devices straight into a patient’s record makes a massive difference. Doctors and nurses can see what’s happening with a patient right now, not just when they remember to write it down. This means quicker decisions, fewer mistakes, and a better chance of spotting if someone’s condition is worsening before it becomes a serious problem. Think about it: if a patient’s heart rate monitor starts acting up, and that data goes straight into their chart, the care team can react much faster. It also helps with those annoying alarms that go off all the time – by looking at the data patterns, we can make them more useful and less of a nuisance.
Streamlining Clinical Workflows
Manual data entry is a real time-sink, isn’t it? Clinicians spend ages typing in readings from machines. MDI takes that away. Information flows automatically from the device to the patient’s electronic health record. This frees up staff to actually spend time with patients, which is what they’re there for. Plus, having all the information in one place, easily accessible within the patient’s record, means less time spent hunting for bits of data. It just makes the whole process smoother and helps everyone work more efficiently.
Achieving Economic Advantages
Beyond making things run better, MDI actually saves money. When you avoid manually entering data, you cut down on errors, which can prevent costly complications. Also, having accurate, up-to-date information can mean fewer repeat tests and potentially shorter hospital stays. Some estimates suggest that widespread adoption could save billions annually across the healthcare system. It’s not just about fancy tech; it’s about smart spending and better use of resources.
Integrating medical devices means we can get a much clearer picture of a patient’s health. This connected approach helps avoid duplicated efforts and ensures that the data we’re working with is accurate and timely, leading to better outcomes and more efficient use of hospital resources.
Navigating the Complexities of MDI Implementation
Getting medical devices to talk to each other and to your main hospital systems isn’t always straightforward. It’s a bit like trying to get everyone in a room to speak the same language when they all learned different ones. There are a few big hurdles to jump over.
Overcoming Interoperability Hurdles
This is probably the biggest headache. You’ve got devices from loads of different companies, all using their own ways of sending information. Making them all understand each other, and then making sure that information makes sense to your Electronic Health Record (EHR) system, is a real challenge. It often means you need special software or services to translate everything. Think of it like needing a universal adapter for all your plugs when you travel.
- Diverse Standards: Devices use different communication protocols, making direct connection difficult.
- Proprietary Systems: Many manufacturers keep their systems closed, limiting how data can be shared.
- Data Format Differences: Even when devices can connect, the way they structure data can vary wildly, requiring significant effort to normalise it.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
When you connect more devices, you open up more doors for potential security problems. Patient data is incredibly sensitive, and you have strict rules, like GDPR, to follow. Making sure that data is protected as it moves between devices and systems, and that only authorised people can see it, is absolutely vital. It’s a constant balancing act between making data accessible for care and keeping it locked down tight.
The expansion of connected medical devices significantly broadens the potential attack surface for cyber threats. Robust security measures are not just a good idea; they are a legal and ethical necessity to safeguard patient confidentiality and trust.
Addressing Integration Costs and Legacy Systems
Let’s be honest, this stuff isn’t cheap. There’s a significant upfront cost for the hardware, software, and the skilled people needed to set it all up. Then there are the ongoing costs for maintenance and updates. On top of that, many hospitals still rely on older equipment that wasn’t built with modern connectivity in mind. Trying to get these old devices to work with new systems can be a real pain, often requiring workarounds or even replacement, which adds to the expense.
Core Components of a Robust MDI Strategy
Right then, let’s talk about what actually makes a medical device integration (MDI) strategy work. It’s not just about plugging things in, you know. You need a solid plan that covers a few key areas. Think of it like building a house – you need the right materials, the right connections, and a good foundation.
Integrating Diverse Medical Device Types
First off, you’ve got to consider all the different gadgets you’re trying to connect. It’s a real mix out there. You’ve got your bedside monitors, the machines that help people breathe, even the pumps that deliver medication. Then there are the big imaging machines like MRI and X-ray, and don’t forget all the lab equipment. Even those smartwatches people wear for health tracking are part of it now, especially for keeping an eye on folks at home.
- Patient Monitoring: ECGs, ventilators, infusion pumps.
- Diagnostic Equipment: X-ray, CT scanners, lab analysers.
- Therapeutic Devices: Pacemakers, dialysis machines.
- Wearables & Sensors: Smartwatches, continuous glucose monitors.
Getting all these different types of devices to talk to each other and share information is a big part of the puzzle. Each one has its own way of doing things, and that’s where the real work begins.
Connecting with Essential Information Systems
Once you’ve got your devices sorted, you need to think about where all that data is going. The main place is usually the Electronic Health Record (EHR) or Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system. This is where doctors and nurses spend a lot of their time, so having the device data right there makes a huge difference. But it’s not just the EHR. You’ll also want to connect to systems that handle images (PACS), lab results (LIS), and the general hospital management systems (HIS).
The goal is to have all this information flowing smoothly, so healthcare professionals have a complete picture without having to jump between loads of different systems. It’s about making their jobs easier and, more importantly, improving patient care.
Leveraging Middleware and APIs
So, how do you actually make all these different devices and systems talk? That’s where middleware and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) come in. Think of middleware as a translator. It sits between your devices and your information systems, helping them understand each other, especially when they speak different ‘languages’. APIs are like specific instructions or doorways that allow different software applications to communicate and exchange data. Using well-defined APIs is key to building flexible and scalable integration solutions. Sometimes, you might need custom middleware or APIs, especially if you’re dealing with older equipment that wasn’t built with modern connections in mind. It’s all about creating those bridges so data can move reliably and securely.
MDI’s Role in Modern Cybersecurity

The Evolving Identity Threat Landscape
These days, the way bad actors try to get into systems has really changed. It’s not just about guessing passwords anymore. They’re using much smarter, more complex methods to get at people’s digital identities. Think about it – if they can get hold of your login details, maybe through a sneaky email or some dodgy software, they can often use those same details on other sites. It’s a bit like using the same simple password for your bank and your social media; if one gets out, the other’s at risk too.
Modern attackers are pretty good at finding ways to get credentials:
- Credential Stuffing: They take lists of usernames and passwords leaked from one breach and try them on many other services. It’s surprisingly effective.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Tricking people into giving up their login information, often by pretending to be someone trustworthy.
- Malware: Software designed to steal your passwords directly from your computer.
MDI’s Strategic Position in Defence
Microsoft Defender for Identity (MDI) is designed to keep a close eye on your organisation’s core digital identities, especially within Active Directory (AD) and hybrid environments. It’s constantly watching what users are doing, looking at network traffic, and checking system logs. By doing this, it can spot unusual behaviour that might signal an attack, like someone trying to move around your network undetected or trying to get higher-level access than they should have. This constant vigilance is key to catching threats early.
Even with newer cloud systems, many organisations still rely heavily on AD for managing who has access to what. MDI acts as a vital security layer for these systems, treating them with the high level of protection they deserve because they are so critical to your operations.
Key Features for Threat Detection
MDI has several clever features to help spot trouble:
- Behavioural Analytics: It learns what ‘normal’ looks like for your users and systems. If someone suddenly starts logging in at 3 AM from a strange location or accessing files they never touch, MDI flags it.
- Advanced Threat Detection: It’s built to spot specific, sophisticated attacks like Pass-the-Hash, Golden Ticket, and Kerberoasting, which are common ways attackers try to gain control.
- Lateral Movement Path Analysis: MDI can map out how an attacker might move from one compromised system to another within your network, helping you block those paths before they can do real damage.
Protecting digital identities is no longer just an IT task; it’s a fundamental part of patient safety in healthcare. When medical devices are connected, the security of the data they handle and the integrity of their operations become paramount. Any breach could have direct consequences for patient care, making robust security measures non-negotiable.
Practical Steps for MDI Deployment
Pre-Installation Planning Essentials
Before you even think about clicking ‘install’, a bit of groundwork is needed. It’s like getting ready for a big trip; you wouldn’t just hop on a plane without checking your passport or packing a bag, right? For MDI, this means getting a clear picture of what you’ve already got.
- Assess your current network setup: What devices are you using? How are they connected? Are there any old systems that might cause trouble?
- Identify your data needs: What information do you need to collect, and where does it need to go? Think about patient records, device status, and any alerts.
- Map out your security requirements: Patient data is sensitive. You need to know what rules you have to follow (like GDPR or HIPAA) and how you’ll keep everything safe.
- Check system compatibility: Make sure your existing IT systems, like electronic health records (EHRs), can actually talk to the new MDI system.
Proper planning here saves a lot of headaches down the line. It’s about making sure everything fits together before you start building.
Step-by-Step Deployment Guidance
Once the planning’s done, it’s time to get hands-on. This is where you actually put the pieces together. It’s usually best to do this in stages, especially in a busy hospital environment.
- Set up the core MDI software: Install the main system components. This might involve servers, databases, and the software itself.
- Connect your medical devices: This is the bit where you link up your monitors, infusion pumps, and other equipment. You might need special cables or network configurations.
- Integrate with information systems: Get the MDI system talking to your EHR or other hospital databases. This is key for making the data useful.
- Configure security settings: Double-check all the passwords, access controls, and encryption. Make sure only the right people can see the data.
- Test thoroughly: Run through various scenarios. Send test data, trigger alerts, and see if everything works as expected.
Post-Installation Verification
So, you’ve installed it all. Great! But are you sure it’s working correctly and securely? This final check is super important.
- Validate data accuracy: Is the data coming from the devices correct? Is it being recorded properly in your systems?
- Confirm system performance: Is the MDI system running smoothly? Is it slowing down other parts of your network?
- Review security logs: Check the system’s activity logs for any unusual or suspicious events.
- Gather user feedback: Talk to the doctors, nurses, and technicians who will be using the system. Are they finding it easy to use? Are there any issues they’ve noticed?
This verification stage is critical for confirming that the MDI system is not only functional but also secure and beneficial for daily operations.
Wrapping Up: Making MDI Work for You
So, we’ve gone through a lot about getting medical devices to talk to each other and to your main computer systems. It’s not always a walk in the park, with challenges like making different brands play nice and keeping all that sensitive patient information safe. But honestly, the benefits really do stack up. Better patient care, smoother days for your staff, and even saving a bit of money in the long run – it’s all on the table. Getting this right means your organisation is really looking ahead, ready for whatever comes next in healthcare. It’s about making sure the tech you have actually helps you do your job better, and ultimately, helps the people you’re looking after.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is Medical Device Integration (MDI)?
Think of MDI as a way to get different medical gadgets, like heart monitors or breathing machines, to talk to each other and to a hospital’s main computer system, especially the electronic patient records. It’s like building a bridge so that all the information from these devices can be easily shared and understood, helping doctors and nurses get a clearer picture of a patient’s health.
Why is MDI so important for hospitals?
MDI is super helpful because it makes patient care better and safer. When devices share information quickly, doctors can make smarter decisions faster. It also makes the jobs of nurses and doctors easier by cutting down on manual work, like writing things down by hand. Plus, it can save money by preventing mistakes and making things run more smoothly.
Is it hard to set up MDI?
Setting up MDI can be tricky sometimes. One big challenge is getting devices from different companies to work together, as they might use different languages. Keeping patient information safe and private is also really important. And, of course, there’s the cost of the technology and making sure it works with older equipment.
What kinds of medical devices can be connected using MDI?
Lots of different devices can be connected! This includes things like monitors that keep track of a patient’s heart rate and breathing, machines that help people breathe, pumps that give medicine, and even X-ray or MRI machines. Wearable gadgets that people use at home are also becoming a big part of this.
How does MDI help keep patient data safe from hackers?
MDI plays a big role in cybersecurity. It helps watch over who is accessing patient information and how they are doing it. It’s designed to spot unusual activity, like someone trying to log in when they shouldn’t be, or trying to access more information than they need. This helps protect sensitive data from being stolen or misused.
What are the first steps to putting MDI into place?
Before you start installing anything, you need to plan carefully. This means figuring out exactly what you want MDI to do, what devices need to be connected, and how it will fit with your existing computer systems. After installation, it’s important to check that everything is working correctly and securely.














