So, you want to know more about Jupiter? Good choice! This giant planet is seriously cool and has a ton of mysteries that even scientists are still trying to figure out. We’re talking about the biggest planet in our solar system, with crazy storms and a whole bunch of moons. If you’re curious about what makes Jupiter tick, you’re in the right place. We’ve put together 10 facts on Jupiter that are pretty mind-blowing and will give you a solid idea of just how amazing this gas giant really is.
Key Takeaways
- Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system, so huge that over a thousand Earths could fit inside it.
- The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is a massive, long-lasting storm, even bigger than Earth, though it seems to be shrinking over time.
- Jupiter’s atmosphere is mostly hydrogen and helium, with incredible, colorful bands of clouds and super-fast winds.
- Jupiter has a powerful magnetic field, the strongest in our solar system, which creates amazing auroras at its poles.
- Scientists are using new tools like the James Webb Space Telescope and missions like Juno and Europa Clipper to learn even more about Jupiter and its moons.
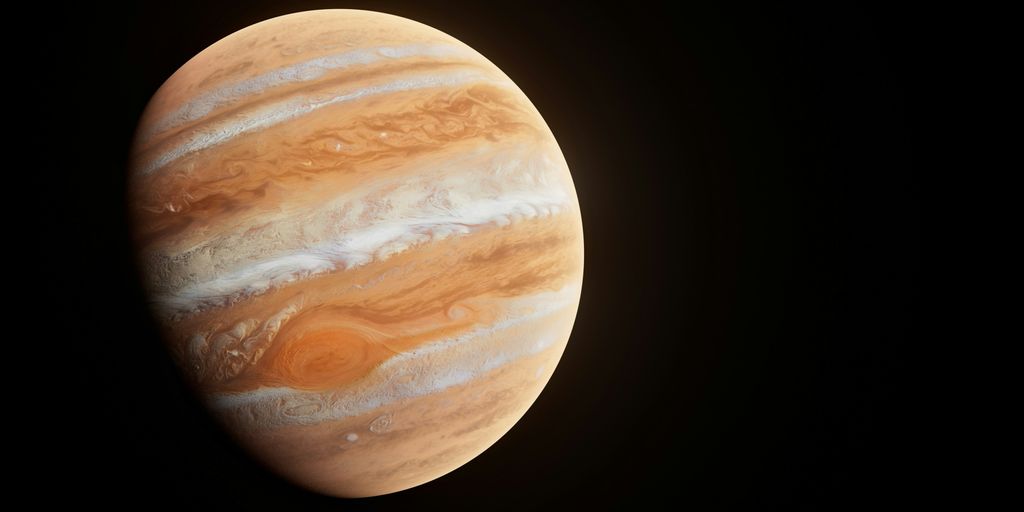
1. Jupiter
Jupiter, the solar system’s heavyweight champion, is a fascinating world. It’s the fifth planet from the Sun, and it’s a gas giant, meaning it’s mostly made of hydrogen and helium. You can even spot it with the naked eye sometimes! It appears as a bright object in the night sky. It’s pretty cool that you can see something so far away without needing a telescope.
Jupiter is so big that over 1,300 Earths could fit inside it! That’s mind-blowing when you think about it. Its gravity is also much stronger than Earth’s. If you weighed 100 pounds here, you’d weigh about 250 pounds on Jupiter. Imagine that!
Here are some quick facts about Jupiter:
- It takes Jupiter about 12 Earth years to orbit the Sun. That’s one long year!
- A day on Jupiter is only about 10 hours long. It spins super fast.
- Jupiter has a really strong magnetic field, way stronger than Earth’s. This magnetic field generates auroras at its poles, similar to Earth’s northern lights, but much more powerful.
Jupiter doesn’t actually orbit the Sun in the same way the other planets do. Because it’s so massive, Jupiter and the Sun orbit a point in space that’s just outside the Sun’s surface. It’s a weird fact, but it shows just how big Jupiter really is. Spacecraft like Pioneer 10 and Juno have given us amazing close-up views of this giant planet, revealing its secrets and mysteries.
2. Great Red Spot

Okay, so everyone knows about the Great Red Spot. It’s like, the thing about Jupiter, right? But there’s more to it than just being a big, red blob. It’s a massive storm, a swirling vortex of gas that’s been raging for centuries. Seriously, since telescopes were invented, we’ve been watching this thing. That’s a long time for a storm to stick around!
It’s been shrinking, which is kind of weird. At one point, you could fit three Earths across it. Now? It’s barely big enough for one. What’s up with that? Scientists are still trying to figure it out. Maybe it’s just calming down, or maybe it’s something else entirely. Jupiter’s atmosphere’s composition is still a mystery in many ways.
It’s not just shrinking, though. The winds inside the Great Red Spot are doing some crazy stuff too. It’s like the storm is getting more intense in some ways, even as it gets smaller. It’s all very confusing, but also super interesting. I mean, imagine a storm that’s been going on longer than your country has existed. Wild, right?
Here’s a quick rundown:
- It’s shrinking.
- It’s been around for centuries.
- The winds are getting faster.
- Scientists are still trying to figure out what’s going on with it.
It’s a reminder that even the things we think we know about space can still surprise us. The Great Red Spot is a testament to the power and mystery of Jupiter.
3. Atmosphere
Okay, so Jupiter’s atmosphere is wild. It’s not like Earth’s where you’ve got a pretty clear surface and then the air above it. Jupiter is basically all atmosphere, all the way down (or at least, as far down as we can tell). It’s mostly hydrogen (75%) and helium (24%), which is pretty similar to the composition of the Sun.
One of the coolest things about Jupiter’s atmosphere is how it’s banded. You see those colorful stripes? Those are caused by differences in wind speed and direction. The average wind speed is around 300 mph, which is insane! It also has the thickest atmosphere out of all the planets in our solar system. It’s a crazy, dynamic place, and scientists are still trying to figure out exactly what’s going on down there. It’s hard to imagine the physics of Jupiter, even for space scientists.
The zones and bands don’t move together, and their rotation and sizes change constantly.
It’s also worth noting that Jupiter’s atmosphere is incredibly deep. We’re talking thousands of kilometers deep. As you go deeper, the pressure and temperature increase dramatically. Eventually, the hydrogen turns into a metallic liquid, which is something you definitely don’t see on Earth. Juno’s work suggests that the interior may in fact move as a "nearly rigid body", which is opposite to how one would expect gases to behave. Figuring out the transition between the surface, fluid weather into this zone will be a task for Juno in its final years, as the interior of Jupiter may be indicative of the structure at Saturn and other gas giants.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the main components:
- Hydrogen: ~75%
- Helium: ~24%
- Other trace elements: ~1%
And here’s a table showing the atmospheric layers (as best as we understand them):
| Layer | Altitude (km) | Temperature (K) | Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Troposphere | -50 to 50 | 110-170 | 0.1-10 |
| Stratosphere | 50 to 200 | 170-200 | 0.1-0.001 |
| Thermosphere | 200+ | 200-1000+ | <0.001 |
It’s all pretty mind-blowing when you think about it. Jupiter’s atmosphere is a giant, swirling soup of gases, storms, and extreme conditions. It’s a place that continues to fascinate and challenge scientists, and there’s still so much we don’t know about it.
4. Magnetic Field
Jupiter’s magnetic field is seriously intense. Like, Earth’s magnetic field? Cute. Jupiter’s is about 20,000 times stronger. It’s so strong that it’s the biggest structure in the solar system – bigger than the sun itself if you could see it! It traps charged particles and flings them around, creating intense radiation belts. You definitely wouldn’t want to hang out there without some serious shielding.
The magnetic field is thought to be generated by metallic hydrogen deep within Jupiter. This metallic hydrogen conducts electricity, and Jupiter’s rapid rotation turns it into a dynamo, creating the powerful magnetic field. But here’s the thing: it’s not uniform. Juno’s data showed that the magnetic field is way more complex and asymmetrical than scientists initially thought. There are some weird variations between the northern and southern hemispheres that are still being investigated. Understanding Jupiter’s magnetic field could help us understand exoplanet studies and other gas giants.
It also drives some pretty spectacular auroras. These aren’t just your average northern lights; they’re supercharged by the intense magnetic field and the charged particles it funnels towards the poles. The auroras are visible in X-ray, ultraviolet, and infrared light, and they’re constantly changing and evolving. They’re way more powerful than Earth’s auroras, and they’re driven by different mechanisms, too. Figuring out what’s happening with Jupiter’s magnetism could help us understand Jupiter’s atmosphere better.
Here’s a quick rundown of some key features:
- Strength: Approximately 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s.
- Source: Metallic hydrogen layer and rapid rotation.
- Effects: Intense radiation belts and powerful auroras.
5. Moons

Jupiter’s got a whole posse of moons, like a planetary entourage. Seriously, it’s got a whopping 79 confirmed moons! That’s second only to Saturn in our solar system. Most of these are tiny, just little space rocks hanging around, but there are four big shots that everyone knows about: the Galilean moons. These are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They’re called Galilean moons because Galileo Galilei discovered them way back in 1610.
These moons are super interesting, and scientists are even looking into whether some of them could potentially support life. Jupiter’s complex environment has really shaped these moons, and they, in turn, affect Jupiter. It’s a whole cosmic dance!
Some mysteries scientists are trying to solve include how high-energy particles move around moons like Io, the nature of the moons’ auroras, and how Jupiter’s magnetic field (which extends around its moons) is shaped by the solar wind. The moons also influence each other through orbital resonances and tidal forces, adding even more complexity to this already fascinating system.
6. Solar System
Jupiter isn’t just a cool planet; it plays a big role in our solar system. It’s so massive that it affects the orbits of other planets and even helps protect us from space rocks. Seriously, it’s like the solar system’s bodyguard.
Think about it: Jupiter’s gravity is a huge deal. It’s got more than twice the mass of all the other planets combined. That’s a lot of pull! This gravity well can suck in asteroids and comets that might otherwise head toward Earth. It’s not a perfect shield, but it definitely helps. Plus, its position influences the asteroid belt, keeping things somewhat stable. Without Jupiter, the inner solar system might be a much more chaotic place. It’s kind of wild to think about how much this one planet impacts everything else around it. You can learn more about the gas giant and its characteristics on other pages.
- Jupiter’s gravity influences the asteroid belt.
- It deflects comets and asteroids.
- It helps stabilize the orbits of other planets.
Jupiter’s mass is a major factor in the solar system’s overall stability. It’s pretty amazing when you consider how one planet can have such a big impact on everything else. It’s like a cosmic domino effect, where Jupiter is the first and biggest domino.
7. Gas Giants
Gas giants are a fascinating class of planets, and Jupiter is the poster child for them in our solar system. But what exactly makes a planet a gas giant? Well, they’re big, for starters. Really big. And instead of having a solid, rocky surface like Earth, they’re primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Think of them as giant, swirling balls of gas.
Jupiter isn’t alone in this category; Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are also gas giants, though Uranus and Neptune are often referred to as "ice giants" due to their higher concentrations of heavier elements like oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur.
Gas giants are pretty different from the terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) that are closer to the Sun. They have no real surface to speak of, crazy fast winds, and intense magnetic fields. Plus, they tend to have a whole bunch of moons and rings orbiting them. Jupiter’s sheer size and mass also mean it technically doesn’t orbit the sun. Instead, Jupiter and the Sun orbit a point just outside the Sun.
It’s wild to think about these massive, gaseous worlds existing out there in space. They really put our own little rocky planet into perspective.
8. James Webb Space Telescope
Okay, so the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a big deal. Like, a really big deal. It’s not just taking pretty pictures (though it does that incredibly well); it’s giving us a whole new way to look at Jupiter and the rest of the universe. I remember when they first launched it; everyone was so hyped, and honestly, it’s lived up to it.
JWST’s infrared capabilities are unlocking secrets about Jupiter that we couldn’t even dream of before.
JWST is helping scientists understand Jupiter’s atmosphere, its storms, and even its moons in ways that weren’t possible with previous telescopes. It’s like going from watching a blurry TV to seeing everything in crystal-clear HD. The level of detail is insane.
Here’s what JWST is bringing to the table:
- Infrared Vision: JWST sees light that’s invisible to our eyes, revealing heat signatures and chemical compositions. This is super useful for studying Jupiter’s atmosphere and cloud layers.
- High Resolution: The telescope’s sharp images allow scientists to study Jupiter’s features in detail, like the Great Red Spot and the polar auroras.
- Spectroscopy: JWST can analyze the light from Jupiter to figure out what it’s made of, including trace gases and other elements. This helps us understand the planet’s composition and how it formed.
One of the coolest things JWST has shown us is the detail in Jupiter’s auroras. These are like the Northern Lights on Earth, but way more powerful. Webb’s advanced sensitivity has allowed astronomers to study them in detail, revealing new details and mysteries. It’s also helping us understand how Jupiter interacts with its moons and its magnetic field. It’s all connected, you know?
Basically, JWST is changing the game when it comes to studying Jupiter and other planets. It’s giving us a deeper understanding of our solar system and helping us learn more about planets around other stars too. It’s a really exciting time for space exploration!
9. Juno
Okay, so Juno. This mission has been a game-changer for how we understand Jupiter. Launched back in 2011, it arrived at Jupiter in 2016 and has been sending back incredible data ever since. It’s not just flying by; it’s orbiting, giving us a sustained, close-up look at the planet. It’s like having a permanent eye on Jupiter, which is pretty awesome.
Juno’s main goal is to figure out Jupiter’s origin and evolution. It’s doing this by investigating Jupiter’s:
- Composition
- Gravity field
- Magnetic field
- Polar magnetosphere
Basically, it’s trying to piece together the story of how Jupiter formed and how it impacts the rest of the solar system. And the findings? They’ve been wild. For example, Juno’s data reveals Jupiter’s cyclones have warmer, less dense tops and colder, denser bottoms. It’s stuff we never could have guessed from Earth-based observations. Plus, it’s helping us understand the high-energy particles flowing around Jupiter’s moons. Juno is really changing the game when it comes to gas giant exploration.
10. Europa Clipper
So, we’ve talked about Jupiter and its mysteries, but what about its moons? That’s where the Europa Clipper mission comes in. It’s all about exploring Europa, one of Jupiter’s icy moons, and figuring out if it could possibly support life. I mean, how cool would that be?
The main goal is to investigate whether Europa has the potential conditions for life. It’s not designed to find life directly, but to assess the moon’s habitability. Think of it as scouting for future missions that might actually look for little green aliens (or microbes, more likely).
Here’s what the Europa Clipper will be doing:
- Mapping Europa’s surface in high resolution. We’re talking detailed pictures to understand its geology.
- Analyzing the moon’s composition. What’s it made of? Is there water? What kind of chemicals are present?
- Searching for plumes of water erupting from the surface. These plumes could give us a sample of Europa’s ocean without having to drill through the ice. That’s a big deal.
- Studying Europa’s magnetic field and its interaction with Jupiter’s magnetic field lines.
It’s a pretty ambitious mission, and I’m excited to see what it discovers. It’s scheduled to launch soon, and it’ll take a few years to get to Jupiter, but the wait will be worth it. Who knows, maybe Europa Clipper will find something that changes everything we know about life in the solar system. It’s a long shot, but that’s what makes space exploration so exciting, right?
Conclusion
So, there you have it! Jupiter is just a super cool planet, full of weird and wonderful stuff. We’ve learned a lot about it, but there’s still so much more to figure out. It’s pretty amazing to think about how much we’ve discovered, and how much more is waiting for us out there. Keep looking up, because space is always doing something interesting!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Jupiter made of?
Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system, is mainly made of hydrogen and helium gas. It doesn’t have a solid surface like Earth. Instead, if you tried to land on it, you’d just sink deeper and deeper into its thick, swirling gases.
What is the Great Red Spot?
The Great Red Spot is a giant storm on Jupiter, much bigger than Earth! It’s like a hurricane that has been raging for hundreds of years. Scientists are still studying why it’s red and why it’s slowly shrinking.
Does Jupiter have a magnetic field?
Jupiter has a very strong magnetic field, much stronger than Earth’s. This field creates beautiful auroras (like the Northern Lights) at its poles. It also protects the planet from harmful particles from the sun.
How many moons does Jupiter have?
Jupiter has a lot of moons, at least 95 that we know of! The four biggest ones, called the Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto), are especially interesting because some of them might have oceans under their icy surfaces.
How big is Jupiter?
Jupiter is so huge that over 1,300 Earths could fit inside it! It’s the largest planet in our solar system by far, and it even weighs more than all the other planets combined.
How did Jupiter get its name?
Jupiter got its name from the Roman king of the gods, Jupiter, because it’s the largest and most powerful-looking planet in the sky. It’s been known since ancient times and is one of the brightest objects you can see without a telescope.