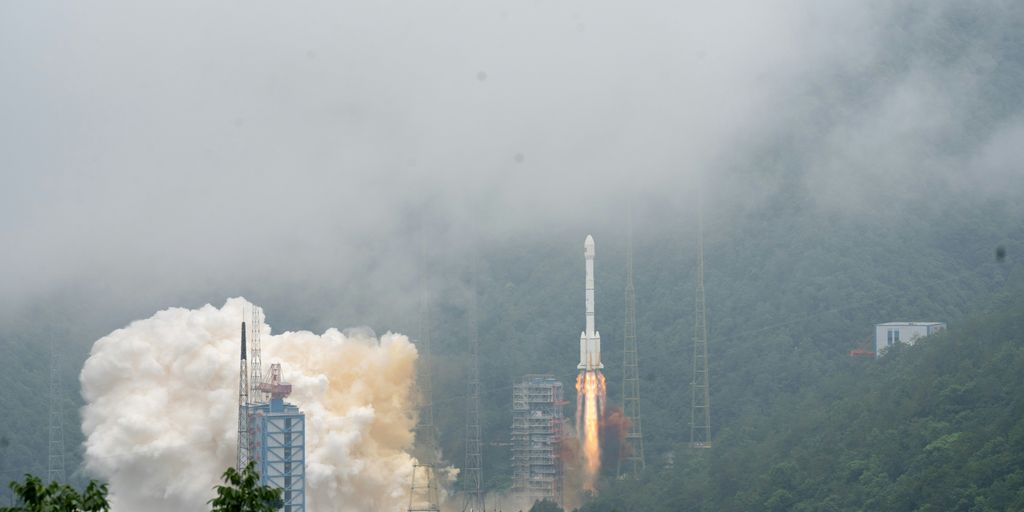
China’s space program is really picking up speed, making big moves that are changing how we think about space exploration. They’re not just doing a few things here and there; they’re working on a huge plan for the future. This includes everything from going to the Moon to setting up new space stations and even looking for life on other planets. It’s a busy time for china space news, with lots of new missions and discoveries happening all the time.
Key Takeaways
- China is setting up a big, long-term plan for its space science, moving into a faster development phase.
- New advancements in laser ranging technology are helping China with its Moon plans and future deep space trips.
- The country is focusing on five main science areas, like studying black holes and looking for planets where life could exist.
- Several important missions are planned before 2030, including a new X-ray observatory and work on the Tiangong Space Station.
- China is working with other countries on space projects and is actively looking to join more international efforts.
China’s Ambitious Space Program Vision
China’s space program is really taking off! It’s not just about getting into space; it’s about solidifying a major role in global space science. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) is overseeing an ambitious program that includes deep space exploration, a manned space station, and cutting-edge advancements. Let’s take a look at what’s driving this push.
Long-Term Space Science Roadmap
China is developing a medium- and long-term roadmap for future missions. This plan aims to transition China’s space science efforts into an accelerated development phase. The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) instructed the space science community to create this plan, and its release is expected soon. This roadmap identifies five main scientific themes for future breakthroughs, summarized as “One Black, Two Dark, Three Origins and Five Characterizations.”
Accelerated Development Phase
Space science in China is moving from an initial stage to a new era of accelerated development. This phase builds on successful missions like the DAMPE dark matter probe and the QUESS quantum science satellite. The release of the first national medium and long-term plan for space science is imminent, promising a series of new space science endeavors. The Tianwen-3 mission to return samples from Mars is a key part of this phase.
Strategic Priority Program Evolution
The Strategic Priority Program (SPP) is evolving into a national medium and long-term plan for space science. Missions launched under SPP include the Advanced space-based Solar Observatory (ASO-S) and the Einstein Probe. While some proposed missions under the SPP, like an E-type asteroid sample return and a Venus orbiter, didn’t gain approval, there’s a growing call for a strategic focus on asteroids. The International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) and experiments on the Tiangong Space Station will also contribute to this vision.
Breakthroughs in Deep Space Exploration

China’s space program is really starting to push the boundaries of what’s possible, especially when it comes to exploring deep space. They’ve got some seriously ambitious plans and have already achieved some impressive milestones. It’s not just about getting there, but also about what they can learn once they arrive. They are really focused on habitability and the search for extraterrestrial life, which is super cool.
Daytime Laser Ranging Advancements
Okay, so this might sound a bit technical, but it’s actually a pretty big deal. China managed to successfully fire a precision laser at a satellite orbiting the Moon during daylight hours. This laser ranging is a huge step forward because it improves the accuracy of lunar orbit determination. This advancement is crucial for future lunar missions, including landing and resource exploration. Think of it like this: it’s like having a super precise GPS for the Moon, even when the sun’s out.
Lunar Program Ambitions
China’s lunar ambitions are no secret. They’re aiming to land astronauts on the Moon by 2030, and they’re putting in the work to make it happen. The Chang’e program has already sent several successful missions to the Moon, including landers and rovers. These missions are not just about planting a flag; they’re about gathering data, testing technologies, and paving the way for a permanent lunar base. The Chang’e-7 mission is planned to land on the lunar south pole. The International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) is also in the works.
Future Deep Space Missions
Beyond the Moon, China has its sights set on even more distant targets. The Tianwen program is leading the charge, with missions planned for Mars, Jupiter, and even potentially Uranus and Neptune. These missions are designed to study the planets themselves, as well as their moons and surrounding environments. The Tianwen-3 Mars sample return mission is scheduled to launch around late 2028. The Tianwen-4 mission is scheduled to launch around 2029 and head to Jupiter. These missions face some serious challenges, like ultra-long deep space communication, planetary protection protocols, and developing spacecraft for extended mission lifetimes. They might need to make breakthroughs in nuclear power for deep space.
Key Scientific Themes Driving Innovation

China’s space program isn’t just about getting up there; it’s also about pushing the boundaries of science. The Chinese space community identified five key themes for future breakthroughs. It’s a pretty ambitious plan, aiming to make China a major player in space science.
Exploring the Extreme Universe
This theme focuses on studying some of the most intense objects in the cosmos. Think black holes, neutron stars, and other super-dense celestial bodies. Scientists are trying to understand the fundamental laws of physics under these extreme conditions. It’s all about testing our current theories and maybe discovering some new ones. This research could really change how we see the universe.
Investigating Habitable Planets
Are we alone? That’s the big question driving this theme. China’s looking at planets within our solar system and exoplanets far beyond, searching for signs of life or conditions that could support it. This involves studying planetary atmospheres, surfaces, and potential for liquid water. It’s a long shot, but finding another habitable planet would be a game-changer.
Biological and Physical Science in Space
Space is a unique laboratory. This theme uses the conditions of space – microgravity, radiation, etc. – to study how matter and life behave. Experiments range from testing new materials to understanding how space affects living organisms. Plus, they’re working on advancing quantum mechanics and general relativity. It’s a broad area, but the potential payoffs are huge.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the themes:
- Extreme Universe: Black holes, neutron stars, high-energy phenomena
- Habitable Planets: Exoplanet research, biosignatures, planetary environments
- Biological & Physical Science: Material science, space biology, fundamental physics
Upcoming Missions Before 2030
China’s space program is really gearing up for some exciting stuff before 2030. It’s not just about getting there; it’s about what they’ll do when they arrive. Let’s take a look at some of the missions on the horizon.
Approved Scientific Missions
Several missions have already gotten the green light, which is a big deal. These aren’t just ideas anymore; they’re actually happening. The long-term space science roadmap laid out some pretty ambitious goals, and these missions are a direct result. For example, there’s the Discovering the Sky at the Longest Wavelength (DSL) mission. It’s a wild idea involving a bunch of spacecraft using the moon as a shield to listen for faint signals from the early universe. How cool is that?
Enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarimetry
The Enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarimetry (eXTP) mission is another one to watch. It’s basically an X-ray observatory that will monitor the sky. This will help with multi-messenger studies, especially for gravitational waves and neutrino sources. Think of it as a super-sensitive ear to the cosmos, listening for the faintest whispers of the universe. It’s all about understanding the extreme physics out there.
Tiangong Space Station Contributions
Of course, we can’t forget about the Tiangong Space Station. It’s not just a place to hang out in space; it’s a working lab. A lot of science will be conducted there, contributing to the overall goals of China’s space program. Plus, missions like the Chang’e-7 lunar south polar landing mission and the Tianwen-2 near-Earth asteroid sample return will add to the data collected at Tiangong. It’s all connected, you know?
International Collaboration in Space
China’s space program isn’t going it alone. They’re actively seeking and building partnerships with other nations and organizations. This is a smart move, as space exploration is expensive and complex, and sharing resources and knowledge makes sense.
Einstein Probe Cooperation
The Einstein Probe launched in January is a great example. It’s a collaborative effort, showcasing China’s willingness to work with international partners on cutting-edge science. These kinds of projects not only advance our understanding of the universe but also build bridges between countries.
SMILE Mission Partnership
Another big one is the SMILE mission with the ESA (European Space Agency). SMILE, which stands for Solar wind Magnetosphere Ionosphere Link Explorer, will study the interaction between the Earth’s magnetosphere and the solar wind. This partnership highlights the global nature of space science and the benefits of combining expertise and resources. It’s cool to see different space agencies working together to tackle big scientific questions.
Active Participation in Global Projects
Beyond specific missions, China is also getting involved in broader international efforts. This includes things like:
- Contributing to the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS, a joint project with Russia). This is a long-term effort to establish a research base on the Moon.
- Sharing data and findings from its missions with the global scientific community. This helps to accelerate the pace of discovery and allows researchers from all over the world to benefit from China’s space program.
- Participating in international conferences and workshops to exchange ideas and best practices. This helps to build relationships and to coordinate efforts in space exploration.
It’s not always easy, of course. There are often political and logistical challenges to overcome when working with international partners. But the benefits of collaboration are clear, and China seems committed to playing an active role in the global space community.
Technological Advancements and Capabilities
China’s space program isn’t just about grand visions; it’s also about the nuts and bolts – the actual technology that makes it all possible. They’re pushing hard on multiple fronts to develop the capabilities needed for their ambitious goals. It’s a mix of building on existing tech and forging entirely new paths.
Cutting-Edge Technology Development
China is investing heavily in developing key technologies for space exploration. This includes advanced propulsion systems, high-performance computing, and communication technologies. They’re not just buying off-the-shelf; they’re aiming to create their own versions, tailored to their specific needs. For example, there’s a big push for more powerful and efficient rocket engines, which are essential for deep space missions. They’re also working on improving the accuracy and reliability of their navigation systems. The goal is to become self-sufficient in critical space technologies.
New Materials and Robotics
Space is a harsh environment, so new materials are a must. China is researching and developing materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, radiation, and micrometeoroid impacts. This includes things like advanced composites and heat-resistant alloys. Robotics also plays a huge role. They’re developing robots for lunar exploration, in-space construction, and even asteroid mining. These robots need to be autonomous and reliable, able to operate in remote and challenging conditions. Efficient lunar mining processes lunar mining processes are crucial to realizing these ambitions.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI is becoming increasingly important in space exploration. China is exploring ways to use AI for everything from spacecraft navigation to data analysis. For example, AI could be used to optimize flight paths, identify potential hazards, and even make decisions autonomously in case of communication delays. They’re also looking at using AI to process the massive amounts of data generated by space missions, helping scientists to make new discoveries. It’s all about making space missions more efficient and effective. Nvidia has unveiled new technology AI safety designed to enhance AI safety.
Milestones in Manned Spaceflight
China’s manned space program is really picking up speed! It’s exciting to see how far they’ve come in a relatively short time. From initial research to a fully operational space station, it’s been quite a journey. Let’s take a look at some of the key milestones and what’s coming up.
Shenzhou-20 Launch Significance
The Shenzhou-20 launch was a big deal. It marked another successful mission to the Tiangong Space Station, further solidifying China’s capabilities in long-duration spaceflight. It’s not just about getting there; it’s about staying there and conducting meaningful research. The crew is up there right now, doing experiments and keeping the station running smoothly. It’s a testament to the reliability of the Shenzhou program and the dedication of the astronauts and ground support teams. The human spaceflight program is really taking off.
Astronauts on the Moon by 2030
Okay, this is the big one. China wants to put astronauts on the Moon by 2030. That’s a pretty ambitious goal, but they seem serious about it. Think about it: humans walking on the lunar surface again, decades after the Apollo missions. It would be a huge achievement, not just for China, but for all of humanity. There are a lot of challenges, of course. Building a lunar lander, developing life support systems, and ensuring the safety of the astronauts are all major hurdles. But if they pull it off, it will be an incredible moment in space exploration. Here’s a quick breakdown of what needs to happen:
- Develop a new generation of rockets capable of lunar missions.
- Construct a lunar lander and ascent vehicle.
- Establish a lunar base for long-term habitation.
- Train astronauts for lunar surface operations.
Tiangong Space Station Operations
The Tiangong Space Station is the centerpiece of China’s manned space program right now. It’s not just a place for astronauts to live; it’s a fully equipped research laboratory in orbit. They’re conducting experiments in a variety of fields, from biology and medicine to materials science and engineering. The station is also a platform for international collaboration, with scientists from other countries participating in experiments and research projects. The Tiangong space station is a great achievement. The current crew is busy with a range of tasks:
- Conducting scientific experiments.
- Maintaining and upgrading the station’s systems.
- Performing spacewalks for external repairs and installations.
- Collaborating with ground control on research projects.
Wrapping Things Up
So, what’s the takeaway from all this China space news? Well, it’s pretty clear they’re not messing around. We’ve seen some really cool stuff happen, from new missions to big plans for the future. It feels like they’re just getting started, and it’s going to be interesting to see what they do next. They’re definitely making a name for themselves in space, and that’s something to pay attention to.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s new with China’s space program?
China is working on a long-term plan for space science, aiming to become a major player in space exploration. This plan includes new missions and research areas.
What are some of China’s achievements in deep space?
China is making big strides in deep space, like using lasers to measure distances to the Moon during the day. They have plans for more Moon missions and other far-off space trips.
What kind of science is China doing in space?
China’s space research focuses on several key areas: studying extreme parts of the universe, finding planets where life could exist, and doing science experiments in space.
Are there any new Chinese space missions coming soon?
Before 2030, China plans to launch several approved science missions, including one to study X-rays from space and others that will use the Tiangong Space Station.
Does China work with other countries in space?
Yes, China is working with other countries on space projects, like the Einstein Probe and SMILE missions with Europe. They want to be more involved in global space efforts.
What new technologies is China using in space?
China is developing advanced technology for space, such as new materials, robots, and artificial intelligence, to help with their ambitious space goals.