China is really getting into vertical farming, and it’s pretty exciting to see. With cities growing like crazy and the need for food security becoming more important, these indoor farms are popping up everywhere. It’s not just about growing lettuce anymore; it’s about using new tech to grow more food, more efficiently, right where people live. This whole vertical farming in China movement is changing how we think about agriculture.
Key Takeaways
- Government support is a big deal for vertical farming in China, helping it grow fast to meet food needs.
- New technology, like AI and smart systems, is making vertical farms more efficient and productive.
- Combining vertical farms with greenhouses creates hybrid systems for better crop yields and control.
- Vertical farming helps cities feed more people and deal with climate change impacts by growing food locally.
- Challenges like energy use and costs are being tackled with new tech and smarter farming methods.
China’s Policy-Driven Vertical Farming Acceleration
China is really pushing forward with vertical farming, and it’s not just happening by accident. The government is playing a big role in making this happen, seeing it as a smart way to handle some major challenges. With cities growing super fast and not a lot of good farmland to go around, they need new ideas for feeding everyone.
Government Backing for Food Security
The government sees vertical farming as a key piece of the puzzle for making sure China has enough food, especially as more people move into cities. It’s about having a reliable food supply that isn’t totally dependent on weather or long-distance shipping. They’re putting money into it, creating special zones for agricultural tech, and generally making it easier for these farms to get started and grow. It’s a pretty clear strategy to build a more secure food future.
Integrating Vertical Farms into Urban Planning
This isn’t just about building farms out in the countryside. China is actively thinking about how to fit these vertical farms right into the fabric of its cities. Imagine farms being part of new buildings or set up in unused urban spaces. This approach helps cut down on how far food has to travel from farm to table, meaning fresher produce for city dwellers and less pollution from transport. It’s a smart way to use space and resources.
Rapid Market Growth Projections
All this government support and focus is really paying off in terms of market growth. The numbers show that China’s vertical farming market is expected to expand at a really fast pace. Some reports suggest it could grow by nearly 28% between 2024 and 2029. This kind of growth isn’t just about numbers; it means more investment, more jobs, and more innovation in the sector. It’s a sign that vertical farming is moving from a new idea to a major industry in China.
Technological Innovations Powering Vertical Farming
Vertical farming isn’t just about stacking plants; it’s about smart systems making it all happen. Think of it as a high-tech greenhouse, but indoors and way more controlled. The real magic happens when advanced tech meets agriculture, allowing us to grow food more efficiently than ever before.
Advancements in Lighting and Automation
Lighting is a big deal indoors. Gone are the days of just using whatever light was available. Now, we’ve got specialized LED lights that can be tuned to give plants exactly the spectrum they need to grow strong and fast. This means better yields and less wasted energy. Automation is another game-changer. Robots are starting to handle tasks like planting seeds, moving trays, and even harvesting. This not only speeds things up but also means fewer people are needed for repetitive, labor-intensive jobs. It also helps keep things running 24/7 without breaks.
AI and Smart Farming Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) is like the brain of the modern vertical farm. Sensors throughout the farm collect tons of data on things like temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and nutrient content in the water. AI systems take all this information and make tiny adjustments in real time. This means the plants always have the perfect conditions to thrive. It’s like having a super-attentive farmer for every single plant, all the time. This level of control helps prevent problems before they even start, leading to healthier crops and less waste.
Data-Driven Agriculture for Optimized Yields
This is where things get really interesting. Every bit of data collected by the sensors isn’t just used for immediate adjustments; it’s also stored and analyzed. Farmers can look back at this data to see what worked best for different crops or at different stages of growth. This helps them fine-tune their methods even further.
Here’s a look at what kind of data is collected and why it matters:
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and light intensity. Knowing these helps maintain optimal growth environments.
- Nutrient Levels: The precise mix of minerals in the water. This ensures plants get exactly what they need without excess.
- Plant Health Indicators: Things like leaf color, growth rate, and even early signs of disease. Early detection means quicker fixes.
- Energy Usage: Tracking power consumption helps identify areas for efficiency improvements.
By using this data, farms can reduce the amount of water and nutrients they use, cut down on energy costs, and ultimately grow more food in the same space. It’s all about making smarter decisions based on real information, leading to better results and a more sustainable operation.
Hybrid Systems: Integrating Vertical Farms and Greenhouses

The Jiashan Sino-Dutch Demonstration Center
China’s push for modern agriculture isn’t just about high-tech vertical farms or traditional greenhouses; it’s about finding smart ways to combine them. A prime example of this is the Jiashan Sino-Dutch Digital Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Demonstration Center. Located about an hour from Shanghai, this place is designed to show how different farming methods can work together. It’s a big project, with Dutch companies helping out, and it’s all about growing good quality vegetables right here in China.
Synergy Between Vertical and Greenhouse Cultivation
The core idea at Jiashan is to use a "hybrid" approach. Think of it like this: you start seeds in a vertical farm, where you can pack a lot of plants into a small space and control everything perfectly. This is great for getting strong, healthy young plants quickly. Then, these young plants are moved to a larger greenhouse for their main growing period. This setup uses the best of both worlds. The vertical farm handles the dense, controlled start, and the greenhouse provides more space for the plants to mature.
- Controlled environment for seedlings: Vertical farms allow precise management of light, temperature, and nutrients, creating ideal conditions for young plants.
- Space efficiency: High-density stacking in vertical farms means more seedlings can be produced in a smaller footprint.
- Scalability: Greenhouses offer the space needed for larger-scale cultivation and fruiting of plants.
High-Yield Production and Advanced Monitoring
This combined system is already showing impressive results. At the Jiashan center, they’ve reported yields of around 5300 kg of leafy greens per mu (which is about 8 kg per square meter). That’s a lot of food from a relatively small area. What’s also cool is that they’re using algorithms and real-time monitoring to manage the whole operation, from the plants themselves to the production process and the business side of things. This kind of integrated management is pretty new for Asia and helps make sure everything runs smoothly and efficiently. It’s this blend of controlled indoor growing and larger-scale greenhouse cultivation, all managed with smart technology, that’s paving the way for more productive and resilient food systems.
Addressing Urbanization and Climate Change Challenges
Meeting the Demands of Growing Urban Populations
Cities are getting bigger, and fast. In China, we’re looking at something like 920 million people living in urban areas soon. That’s a lot of mouths to feed, especially when space is tight and resources are stretched thin. Vertical farms are a pretty neat solution here because they grow food right where people are – smack dab in the middle of cities or nearby. This means less travel time for your veggies, fewer trucks on the road, and ultimately, fresher food on your plate. It’s a direct answer to the pressure that rapid city growth puts on our food supply.
Resilience Against Climate-Related Disruptions
Forget about worrying if the harvest will be ruined by a sudden hailstorm or a prolonged drought. Vertical farms operate indoors, so they’re not at the mercy of the weather. This climate-agnostic approach means they can keep producing food year-round, no matter what’s happening outside. This indoor, controlled environment significantly reduces the risk of food supply disruptions caused by extreme weather events. It’s a way to build a more stable food system that isn’t constantly at the whim of Mother Nature.
Reducing Food Miles and Enhancing Freshness
Think about how far your salad greens might have traveled before landing in your grocery bag. With vertical farms located in or near urban centers, that distance shrinks dramatically. This reduction in ‘food miles’ not only means less fuel is burned for transportation but also that the produce reaches consumers much faster. The result? Food that’s not only fresher but also retains more of its nutrients. It’s a win-win for both the environment and the quality of the food we eat.
Expanding Crop Diversity and Urban Integration
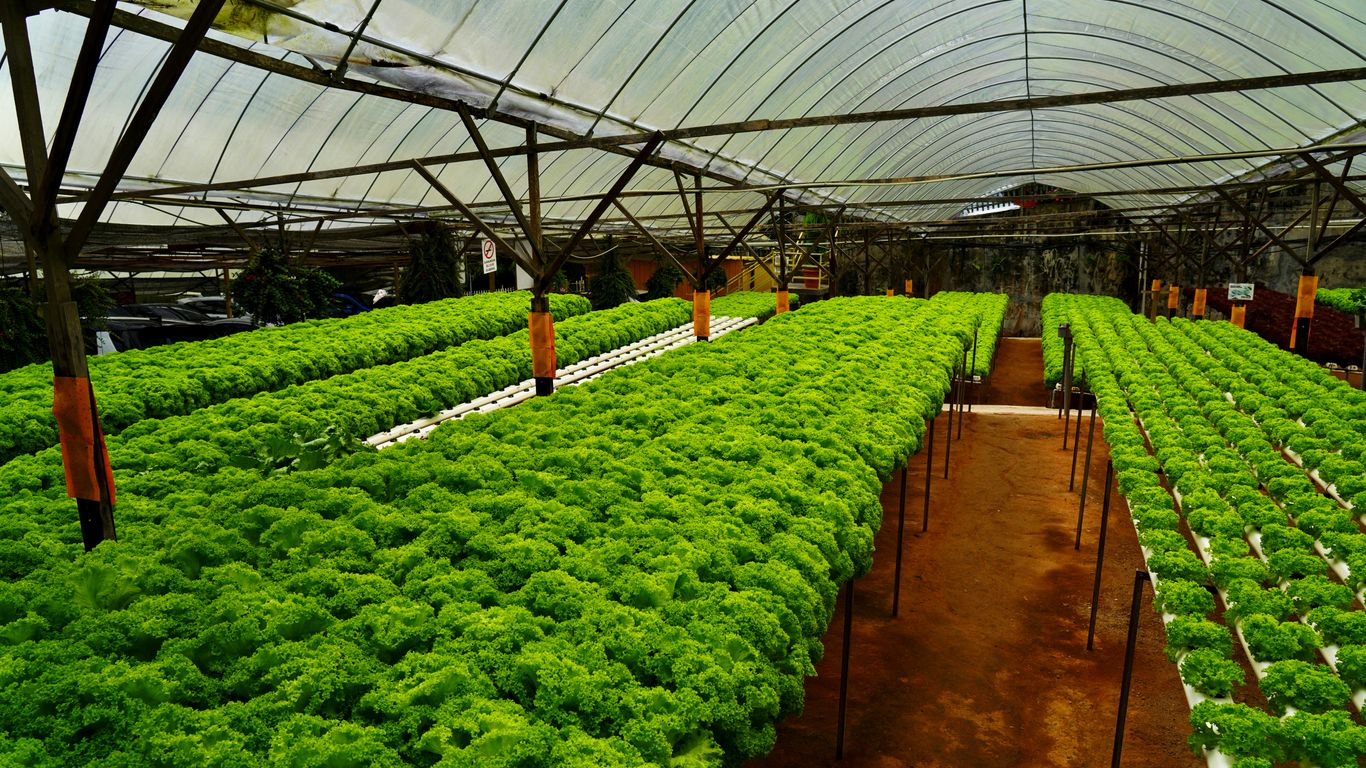

Moving Beyond Leafy Greens
For a while there, it felt like vertical farms were only good for growing lettuce and kale. And yeah, those are important, but the world needs more than just salad greens, right? Thankfully, things are changing fast. We’re seeing more and more vertical farms start to grow things like tomatoes, peppers, strawberries, and even cucumbers. Tomatoes, for instance, are already making up a pretty big chunk of the market’s earnings, showing just how much people want these other crops. With better lights and smarter ways to deliver nutrients, these farms are getting good at growing trickier stuff, like fruits and even some root veggies. This variety is a big deal because it means vertical farms can serve more people, meet different food needs, and just make more sense financially.
Integrating Farms into City Architecture
Cities are starting to get creative, building vertical farms right into apartment buildings, offices, and public spaces. It’s this idea of growing food right where people live, making it super easy to get fresh produce without needing tons of land or long truck rides. In China, this is becoming a part of how cities are planned. It helps grow more food locally while using less space. You might see these farms on rooftops, tucked into old warehouses, or even as part of new housing developments. This kind of setup makes our food system stronger. It means less pressure on farmland, shorter trips from farm to table, and a more direct connection between people and their food.
Community Impact and Food Deserts
Bringing farms into cities does more than just provide food; it helps communities. By growing food right where people live, these farms can help tackle the problem of ‘food deserts’ – areas where getting fresh, healthy food is tough. Plus, these urban farms create local jobs and cut down on the environmental impact of long-distance food transport. It’s a win-win: people get fresher food, and communities get a boost.
Overcoming Challenges in Scaling Vertical Farming
So, vertical farming sounds pretty great, right? Growing food indoors, year-round, using less water and space. But getting these high-tech farms to really take off on a large scale isn’t exactly a walk in the park. There are a couple of big hurdles that keep popping up.
Addressing High Energy Consumption
One of the main headaches is how much electricity these farms gobble up. All those lights, climate control systems, and pumps need a lot of power. It’s a big reason why the cost can be so high. Innovators are looking at ways to make this more efficient, like using LED lights that are specifically designed for plant growth and don’t waste as much energy. Some farms are even starting to hook up with renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, to offset their electricity use. It’s all about finding smarter ways to power these operations without breaking the bank or the planet.
Reducing Upfront and Operational Costs
Setting up a vertical farm from scratch costs a pretty penny. You’ve got the building, the racks, the lighting, the water systems – it all adds up fast. Then there are the ongoing costs, like paying for energy, nutrients, and skilled workers. To make it more accessible, companies are exploring modular designs. Think of it like building with LEGOs – you can start smaller and add more sections as you grow. This makes the initial investment less daunting. Plus, there’s a push for more public-private partnerships and funding to help new farms get off the ground. It’s a tough nut to crack, but people are working on it.
Knowledge Transfer and Market Education
It’s not just about the tech; it’s also about the know-how. Not everyone knows how to run a high-tech farm, and there’s a need for people trained in both agriculture and technology. So, there’s a growing effort to create training programs and share best practices. On top of that, many people – from investors to everyday shoppers – are still getting familiar with what vertical farming is all about. Explaining the benefits, like fresher food and less environmental impact, is key. It’s about building trust and showing people why this way of growing food is worth it. Think of it like this:
- Training Programs: Developing courses for new farm managers and technicians.
- AI Tools: Using smart software to help manage farm operations and predict issues.
- Public Outreach: Hosting open days or sharing information online to educate consumers.
- Industry Collaboration: Sharing research and development findings between different companies.
Looking Ahead
So, what does all this mean for the future? China’s push into vertical farming isn’t just about growing more lettuce indoors. It’s a big move towards making food systems tougher and more reliable, especially as cities keep getting bigger. We’re seeing a blend of smart tech, government backing, and new ideas that are really changing how we grow food. While there are still hurdles, like figuring out energy use and keeping costs down, the progress is clear. It feels like we’re on the edge of something big, where fresh food can be grown closer to home, using less land and water. Keep an eye on this space; it’s going to be interesting to see how these farms shape what we eat tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is vertical farming?
Vertical farming is a way of growing food indoors, often in cities. Instead of fields, plants are grown in stacked layers, like shelves in a tall building. This uses a lot less space than traditional farms.
Why is China investing so much in vertical farming?
China has a lot of people and not much farmland. They are also building many new cities. Vertical farming helps them grow food locally, which makes sure everyone has enough to eat and reduces the need to ship food long distances.
What kind of technology is used in vertical farms?
These farms use special lights, often LEDs, to help plants grow. They also use computers and robots for watering, feeding, and monitoring the plants. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps make sure the plants get exactly what they need to grow best.
Can vertical farms grow more than just lettuce?
Yes! While leafy greens like lettuce are common, vertical farms are now growing other things like tomatoes, strawberries, and peppers. Technology is improving so they can grow a wider variety of foods.
Are vertical farms good for the environment?
Vertical farms use much less water than regular farms. They also help reduce pollution from farm equipment and long-distance transportation because they are often located near where people live.
What are the biggest challenges for vertical farming?
One big challenge is that these farms use a lot of electricity for lights and climate control, which can be expensive. Also, setting up these high-tech farms costs a lot of money at first. But people are working on making them more energy-efficient and cheaper.