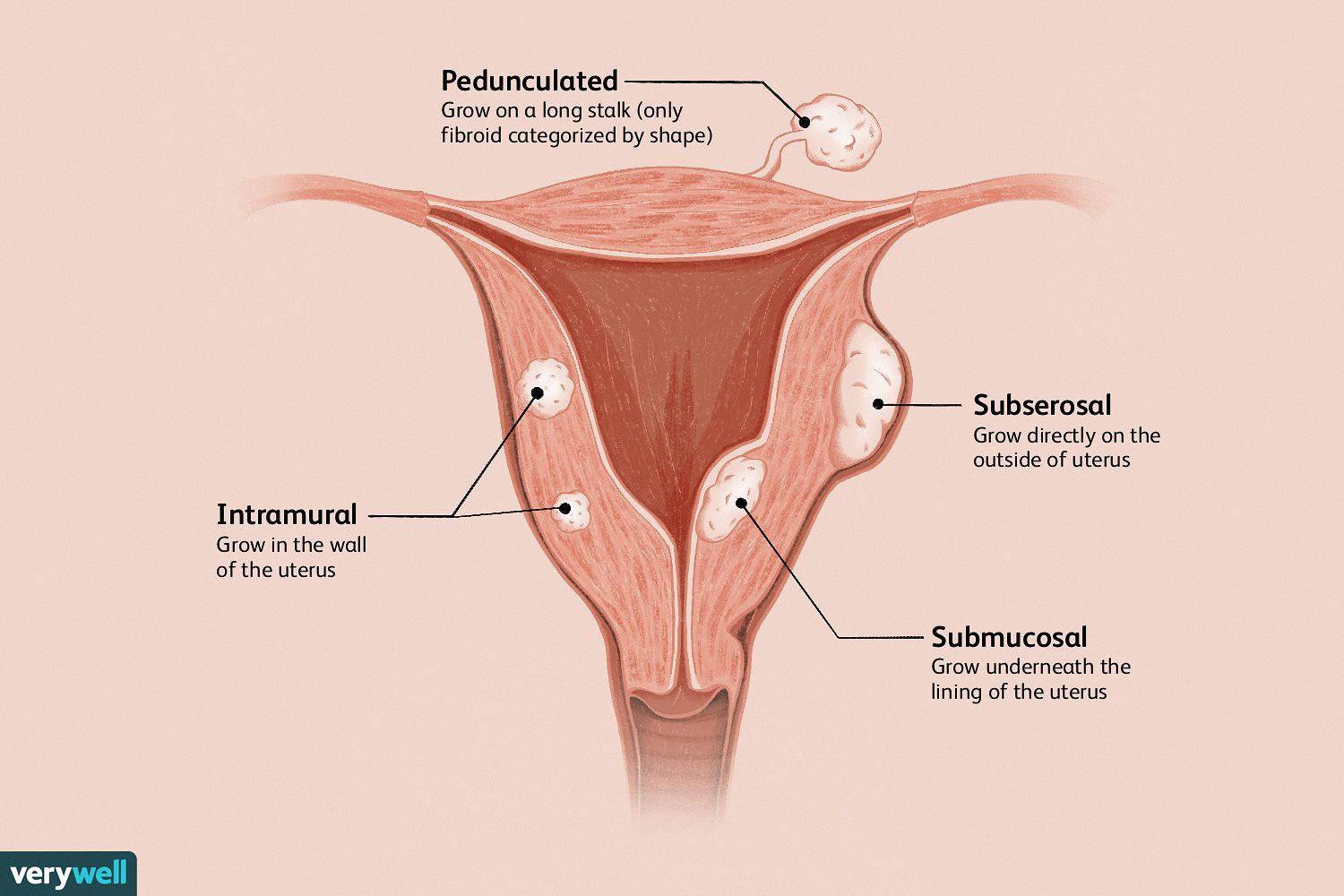
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the muscular wall of the uterus. These growths are quite common, with many women experiencing them at some point in their lives. While fibroids are typically benign and do not increase the risk of uterine cancer, they can cause discomfort and affect reproductive health. Read on to know everything about uterine fibroids, their causes, symptoms and treatments.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
The exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unclear, but they may be caused due to:
- Hormonal Influence: Estrogen and progesterone, hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, are believed to play a role in the growth of uterine fibroids. Fibroids tend to grow larger during periods of hormonal fluctuation, such as pregnancy and perimenopause, and often shrink after menopause when hormone levels decline.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors may predispose some women to develop uterine fibroids. Women with a family history of fibroids are more likely to develop them themselves.
- Other Factors: Other factors such as obesity, diet, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors may also contribute to the development of uterine fibroids. However, the exact interplay of these factors in fibroid formation requires further research. To find out more you can talk to a best gynecologist in rawalpindi.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
The symptoms of uterine fibroids can vary widely depending on their size, number, and location within the uterus. Some women may experience no symptoms at all, while others may experience:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation or difficulty with bowel movements
- Lower back pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Enlargement of the lower abdomen or uterus
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms is not necessarily correlated with the size of the fibroids. Some women with large fibroids may experience minimal symptoms, while others with small fibroids may experience significant discomfort.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing uterine fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans. Once diagnosed, the appropriate treatment plan depends on several factors, including the size and location of the fibroids, the severity of symptoms, and the woman’s age and reproductive goals.
Treatment options for uterine fibroids:
- Medications: Hormonal medications such as birth control pills, hormone-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists may help alleviate symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures such as uterine artery embolization (UAE), myomectomy, or focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) may be recommended to shrink or remove fibroids while preserving the uterus. These procedures are less invasive than traditional surgery and typically have shorter recovery times.
- Surgical Removal of the Uterus (Hysterectomy): In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) may be necessary to treat uterine fibroids. Hysterectomy is considered a definitive treatment for fibroids but is typically reserved for women who have completed childbearing or do not wish to have children.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids are common noncancerous growths that develop in the muscular wall of the uterus and can cause a range of symptoms depending on their size, location, and characteristics. While the exact cause of fibroids is not fully understood, hormonal factors, genetic predisposition, and other factors may contribute to their development. Treatment options for uterine fibroids depend on the severity of symptoms and may include watchful waiting, medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical intervention. If you experience symptoms suggestive of uterine fibroids, it’s essential to consult with a best gynecologist in lahore for evaluation, diagnosis, and appropriate management.