So, we’re talking about who’s really making the big moves in the AI chip world as we get closer to 2025. It’s kind of a wild scene, with some companies you expect and some that are really shaking things up. This whole AI chip market share by company thing is getting pretty interesting, and it’s not just about who has the fastest chip. It’s about who’s building the whole system, who’s got the best partnerships, and who’s really thinking about the future. We’ll look at the companies that are leading the pack and what makes them stand out in this super competitive space.
Key Takeaways
- Nvidia continues to dominate the AI chip market, especially in data centers, with its advanced GPU architectures.
- AMD is a strong challenger, focusing on competitive pricing and performance for AI workloads.
- Intel is making a comeback with its specialized AI accelerators and custom solutions.
- Google and Amazon are heavily invested in custom AI chips for their cloud services, leveraging vertical integration.
- The market is seeing innovation from specialized players like Graphcore and Cerebras, alongside mobile-focused Qualcomm and China’s Alibaba.
Nvidia Corporation
It’s hard to talk about AI chips without mentioning Nvidia. They’ve really cemented themselves as the go-to company for the hardware that powers so much of the AI revolution we’re seeing. Nvidia’s GPUs are basically the engine behind a lot of the big AI models out there, from the ones powering chatbots to the systems running self-driving cars. They’ve managed to build a really strong ecosystem around their products, which makes it tough for others to compete.
Market Dominance and Financials
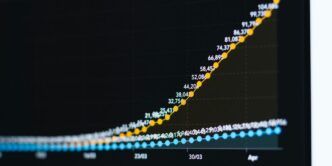
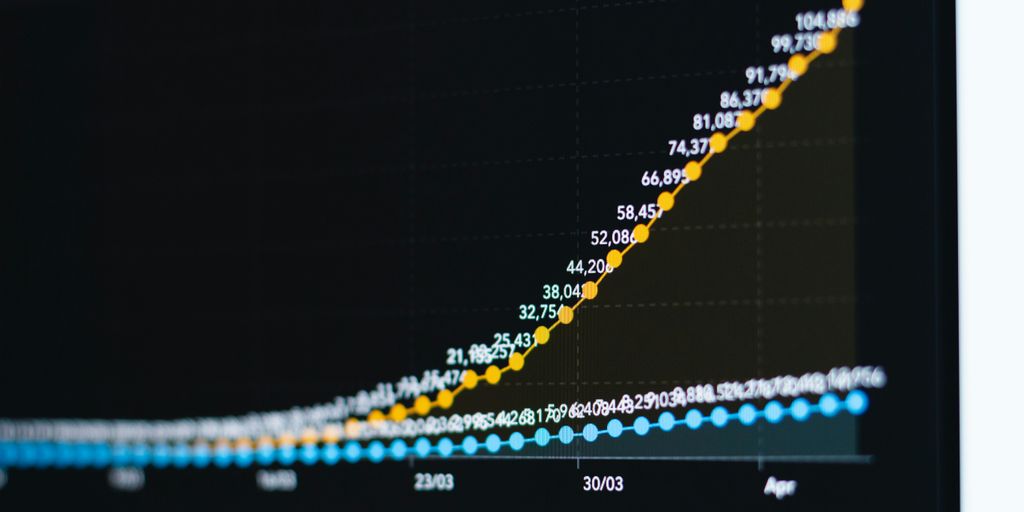
Nvidia has had a pretty incredible run. Back in July 2025, they actually became the first company to hit a $4 trillion market cap, which is just wild when you think about it. This wasn’t just a fleeting moment; it showed how much demand there is for their AI hardware. Their stock performance has been pretty stellar, and it’s a big reason why they’re such a major player in the semiconductor world right now. Some analysts are even talking about them potentially reaching $20 trillion in the future, which sounds almost unbelievable, but it shows the confidence people have in their continued growth, especially as they expand into areas like robotics and quantum computing.
Key Products and Technologies
Nvidia’s core strength lies in its Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). These aren’t just for gaming anymore; they’re incredibly powerful for the complex calculations AI requires. Beyond the hardware, they have a whole software stack, like CUDA, that makes it easier for developers to use their chips for AI tasks. This software integration is a big part of why they have such a strong hold on the market. They’re also making chips specifically for data centers, which is where a lot of AI training and processing happens. Even with some export restrictions affecting their business in China, they’re still finding ways to adapt and continue selling AI chips to China.
Industry Impact and Future Outlook
Nvidia’s influence extends beyond just selling chips. They’re actively partnering with companies in various sectors, including healthcare. For instance, they’ve worked with medical device companies to integrate their AI technology into surgical platforms and imaging devices. This shows how their hardware is becoming a foundational part of new medical innovations. They also have programs that support startups working on AI in healthcare, helping them get the computing resources they need. It’s clear that Nvidia isn’t just resting on its laurels; they’re pushing into new areas and solidifying their position as a leader in the AI hardware space.
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD)
AMD has really stepped up its game in the AI chip arena, becoming a major player to watch. They’ve been making smart moves, like buying up other companies and putting a lot of effort into research and development. This has really put them in a strong position by 2025, giving even the biggest names a run for their money.
CDNA 3 Architecture
AMD’s CDNA 3 architecture is specifically built for AI and machine learning tasks. It’s designed to be more efficient, meaning it uses less power for the same amount of work, which is a big deal for data centers. Plus, they’ve been pretty competitive with their pricing, which definitely helps them gain market share. It’s a smart strategy that seems to be paying off.
Market Strengths
AMD has a solid foothold in the business and data center markets. Their chips are often seen as a more budget-friendly option compared to some competitors, without sacrificing too much performance. The speed at which their AI chip performance is improving is pretty impressive, and it’s something that customers are noticing. They’re really making a name for themselves in this space, and it’s exciting to see how they continue to grow. You can see how their efforts are impacting the market, with AMD shares increasing in response to certain industry developments.
Strategic Innovations
- Optimized for AI/ML: The CDNA 3 architecture is tailored for AI and machine learning, making it a strong contender for these specific workloads.
- Energy Efficiency: AMD is focusing on making its chips more power-efficient, which is a key factor for large-scale deployments.
- Competitive Pricing: Their pricing strategy makes advanced AI technology more accessible to a wider range of businesses.
- Rapid Performance Gains: Continuous improvements in chip design are leading to faster and more capable AI processing.
Intel Corporation
Intel, a name that’s been around the semiconductor block for ages, is really trying to make a comeback in the AI chip game. They’ve poured a lot of money into their Habana Labs and custom AI accelerator divisions, and by 2025, these are looking like pretty important parts of their plan to get back to the top. They’re pushing their Gaudi3 AI Processors, which are built for training big machine learning models, and the Ponte Vecchio architecture is also part of the mix, aimed at super-powerful computing tasks.
Intel’s strategy seems to be about making custom AI chips for specific industries, using their existing factories, and leaning on their relationships with governments and big companies. It’s a different approach than just trying to be everything to everyone. They’re hoping this focus will help them carve out a solid niche. It’s a big shift from their past, and it’ll be interesting to see if it pays off. They’re definitely trying to show they can still innovate, kind of like how Richard Branson is pushing boundaries with space travel. It’s all about adapting to the new tech landscape.
Google (Alphabet)
Google, through its AI-first approach and significant investments in custom silicon, has carved out a substantial niche in the AI chip market by 2025. Their strategy centers on developing specialized hardware, primarily the Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) line, designed to power their extensive AI and machine learning operations. This custom silicon is not just for internal use; it’s a key component of their cloud and edge computing offerings, making them a significant player.
Custom Silicon Strategy
Google’s commitment to custom silicon, exemplified by their TPU development, allows them to tailor hardware specifically for AI workloads. This means their chips are optimized for the kinds of tasks that drive Google’s vast AI ecosystem, from search algorithms to advanced research projects. By controlling both the hardware and software stack, they can achieve performance gains that off-the-shelf solutions might not match. This focus on proprietary hardware is a major differentiator in the competitive AI chip landscape.
Key Health AI Applications
Beyond general AI acceleration, Google has made remarkable strides in applying its AI capabilities to healthcare. One of their most celebrated achievements is AlphaFold, an AI system that predicts protein structures with incredible accuracy. This has revolutionized biological research and is now a standard tool for drug discovery and biotechnology. The AlphaFold database, accessible to researchers globally, contains millions of protein structures, significantly speeding up the development of new medicines and our understanding of diseases. Google is also developing AI for medical imaging, aiming to detect conditions like diabetic retinopathy and various cancers from scans, often performing at or above human expert levels. Their work in digital pathology, assisting in the detection of diseases like breast cancer metastasis, further highlights their impact. Furthermore, Google is exploring generative AI for medicine with models like Med-PaLM 2, which can answer complex medical questions and assist clinicians with tasks like summarizing patient records. This broad application of AI in health showcases Google’s influence, making them a key innovator in the medtech sector.
Market Position and Future Outlook
By 2025, Google’s TPU strategy has positioned them as a major force, particularly in cloud computing and large-scale AI deployments. While they might not be selling chips directly in the same volume as some competitors, their internal use and cloud offerings mean their silicon is powering a significant portion of AI computation. Their ongoing research and development, especially in areas like generative AI and specialized hardware, suggest they will continue to be a dominant influence in the AI chip market for the foreseeable future. The company’s deep integration of AI across its product suite, from search to cloud services, provides a strong foundation for continued growth and innovation in AI hardware.
Apple Inc.
Apple’s approach to AI chips is all about making things work really well together, right on your devices. They’ve been quietly building up their custom silicon game for years, starting with the A-series chips in iPhones and iPads, and then really hitting their stride with the M-series chips for Macs. The real magic is how they integrate their Neural Engine directly into these processors. This isn’t just about raw power; it’s about making AI tasks, like image recognition or voice processing, super fast and efficient without draining your battery. It’s a big reason why features like on-device Siri requests or advanced photo editing feel so smooth.
Silicon Design Mastery
Apple’s custom silicon strategy, kicked off with the M-series chips, has really expanded into AI-specific processing. Their Neural Engine tech has become a benchmark for designing AI chips that are both efficient and powerful. They’re constantly pushing the boundaries here, focusing on making these chips better with each generation. It’s a smart move because it gives them a lot of control over performance and features.
Technological Highlights
- A-series and M-series Neural Engine advancements: Apple keeps improving the Neural Engine in its chips, making AI tasks faster and more capable.
- Industry-leading energy efficiency: A big win for Apple is how much AI processing they can do without using a ton of power. This means longer battery life for iPhones, iPads, and Macs.
- Tight hardware-software integration: Because Apple designs both the chips and the operating systems (like iOS and macOS), they can make them work together perfectly. This allows for optimizations that other companies often can’t match.
Market Approach
Apple’s main focus is on AI processing that happens directly on the device itself. They really emphasize privacy and keeping intelligence on your phone or computer, rather than sending lots of data to the cloud. This approach, combined with their continued vertical integration, sets them apart in the AI chip market. It’s interesting to see how this strategy plays out, especially with new innovations like the iPager, which aims to simplify communication through advanced tech. You can check out a video about it in the Apple store.
AI Chip Evolution
Apple’s journey with AI chips has been a steady build. They started by putting more AI smarts into their mobile chips and have now brought that power to their laptops and desktops with the M-series. The goal is always to make AI features feel natural and helpful, not like a separate, clunky addition. It’s all about making the user experience better, and their custom silicon is a huge part of that. It’s a strategy that seems to be working out pretty well for them, keeping them competitive in a fast-moving tech world.
Qualcomm
Qualcomm: Mobile and Edge AI Leadership
Qualcomm has really carved out a strong niche for itself in the AI chip market, especially when it comes to anything mobile or at the "edge." You know, like your smartphone, smart home devices, or even cars. They’ve built their business on being the go-to chip provider for these kinds of gadgets, and that’s paying off big time in the AI space. Their whole strategy is built around making AI work smoothly on these smaller, more power-conscious devices.
What’s really driving their success is the Snapdragon AI Engine. It’s not just one chip, but a whole system designed to handle AI tasks efficiently. This includes advanced neural processing units that are specifically built for machine learning workloads. Plus, they’re doing a great job integrating 5G connectivity with AI capabilities, which is pretty important for how we use devices today. It’s all about making these devices smarter and more responsive, right there on the device itself, without always needing to connect to the cloud. This focus on mobile and edge AI processing gives them a significant advantage, and they have really strong relationships with all the major smartphone makers. They’re not just selling chips; they’re providing a whole AI solution that works well within the existing ecosystem. You can see how this plays out when you look at the latest advancements in mobile technology, like those powering new smartphones.
Qualcomm’s market strengths are pretty clear:
- Dominance in mobile and edge AI processing.
- Strong partnerships with smartphone manufacturers.
- A comprehensive AI solution ecosystem that supports developers.
They’re really the company to watch if you’re interested in how AI is showing up in everyday devices.
Graphcore
Graphcore: The AI Chip Innovator
Graphcore has carved out a unique niche in the AI chip market with its distinctive approach to hardware design. Unlike many competitors who focus on refining existing GPU architectures, Graphcore developed the Intelligence Processing Unit (IPU). This processor is built from the ground up specifically for machine learning tasks, aiming to handle the complex computational graphs that are common in AI workloads.
Their strategy centers on offering a fundamentally different architecture that can accelerate AI development and research. By 2025, Graphcore has established itself as a significant player, particularly for those pushing the boundaries in AI research and demanding specialized hardware. Their chips are designed to be highly parallel and efficient for the specific types of calculations AI models require. This focus on a specialized architecture, rather than a general-purpose one, is what sets them apart. It’s an interesting path in a market often dominated by more traditional designs, and it’s worth keeping an eye on how this specialized approach performs against the broader market trends. You can find more about their work on Graphcore’s website.
Key technological innovations from Graphcore include:
- Colossus MK2 IPU Architecture: This is their latest generation of IPU, designed for even greater performance and efficiency in AI training and inference.
- Specialized Processor Design: The IPU’s architecture is optimized for the parallel processing and memory access patterns typical of machine learning algorithms.
- Unique Computational Graph Processing: Graphcore’s hardware is engineered to directly map and execute the computational graphs that define AI models, potentially leading to faster processing.
Graphcore’s market positioning is that of an innovator, targeting researchers and developers who need specialized hardware to explore new AI models and techniques. While they might not have the sheer volume of the larger players, their focus on a distinct architectural advantage makes them a company to watch in the evolving AI chip landscape.
Cerebras Systems
Cerebras Systems is really doing something different in the AI chip space. Instead of making chips that fit into existing servers, they went and built the biggest chip you’ve ever seen, called the Wafer-Scale Engine. It’s basically an entire wafer of silicon dedicated to processing AI tasks. Pretty wild, right?
Their whole approach is about tackling massive AI problems that just can’t be solved with traditional hardware. Think about training enormous AI models or running complex simulations – Cerebras is aiming to make that feasible. They’ve got this unique architecture that’s built for parallel processing, which is exactly what AI needs. It’s a big bet on the idea that more raw processing power, in a very specialized form, is the way forward for certain AI applications.
Wafer-Scale Engine Architecture
Market Positioning and Strategy
Cerebras is really focusing on places that need extreme computing power, like big research labs and national institutions. They’re not really competing head-to-head with the everyday AI chips you see in laptops or even most data centers. Instead, they’re carving out a niche for those who are pushing the absolute limits of what’s computationally possible. It’s a strategy that relies on partnerships and solving problems that others can’t even touch. They’ve got some interesting collaborations going on, which you can read more about on their website.
Key Technological Innovations
Future Outlook and Impact
Alibaba Group
Alibaba, a major player in China’s tech scene, has been making some serious moves in the AI chip space. They’re not just dabbling; they’re investing heavily and developing their own custom silicon, which is pretty cool. Their Hanguang 800 chip, for instance, is designed specifically for AI tasks and is integrated right into their massive cloud services. This means they’re not only building the hardware but also controlling the ecosystem where it’s used, which is a smart way to do things.
Hanguang 800 Neural Processing Unit
This is Alibaba’s flagship AI chip. It’s built for machine learning and is a big deal because it shows how serious they are about custom silicon. It’s used within their own cloud infrastructure, powering a lot of their AI services. Think of it as their answer to the specialized chips other big tech companies are making.
Custom AI Chips for Cloud and Edge Computing
Beyond the Hanguang 800, Alibaba is also working on other custom chips. These are aimed at both their cloud operations and edge devices – you know, the smaller computers and sensors that are out in the world. This dual focus is important because it covers a lot of ground in the AI market.
Strong Integration with Alibaba Cloud Services
This is where Alibaba really shines. They’re not just selling chips; they’re embedding them into their cloud platform. This tight integration makes it easier for their customers to use AI without having to worry too much about the underlying hardware. It’s a big advantage for anyone already using Alibaba Cloud.
Market Significance in China
In the Chinese market, Alibaba is a really significant force. They’re one of the leading domestic developers of AI chips, which is important given the country’s focus on technological self-sufficiency. Their investments in R&D are substantial, and they’re definitely a company to watch as the global AI chip landscape continues to shift.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Amazon Web Services, or AWS, has been quietly building its own AI silicon for a while now. They’ve got these chips called Inferentia and Trainium, and they’re pretty important for their cloud services. Think of them as custom-built parts that make machine learning tasks run smoother and faster right there in AWS’s data centers.
It’s a smart move because it means they can offer AI services without being totally dependent on other chip makers. Plus, they can tune these chips specifically for the kinds of jobs their customers are doing on the AWS platform. This tight integration is a big deal for performance and cost.
AWS is really focusing on making these chips work well for both inferencing (when an AI model makes a prediction) and training (when an AI model is being built). They’ve even got a new version, Inferentia 2, which is supposed to be even better. It’s all about providing a complete AI solution from the hardware up. You can find out more about their cloud infrastructure on AWS’s website.
Inferentia Chips
AWS’s Inferentia chips are designed for inference, which is the part of AI where a trained model is used to make predictions. These chips are optimized to handle a lot of these requests efficiently.
- Cost-effective inference: They aim to lower the cost of running AI models in the cloud.
- High throughput: Capable of handling many inference requests simultaneously.
- Integration: Built to work seamlessly with other AWS services.
Trainium Chips
Trainium chips are AWS’s answer for the heavy lifting of training AI models. Training AI can take a huge amount of computing power, and these chips are built to handle that.
- Performance for training: Designed to speed up the process of building AI models.
- Scalability: Allows users to scale their training jobs across many chips.
- Cost efficiency: Aims to make AI model training more affordable.
Market Impact
By developing its own AI chips, AWS is carving out a significant niche. They’re not just a cloud provider anymore; they’re also a hardware innovator in the AI space. This strategy helps them compete directly with companies that rely on third-party chips for their AI offerings. It also gives their customers more options and potentially better performance for their AI workloads within the AWS ecosystem.
Wrapping It Up: The AI Chip Race Continues
So, looking at where things stand in 2025, it’s pretty clear that AI chips are a really big deal. Companies like Nvidia are still leading the pack, but others like AMD and Intel are definitely making moves. It’s not just about who has the fastest chip anymore; it’s about who can make them efficiently, keep them cool, and tailor them for specific jobs. We’re seeing a lot of innovation, especially with specialized chips for things like self-driving cars or medical tech. The competition is fierce, and it’s happening all over the world. What’s next? Probably even more power-saving designs and chips that are even more specialized. It’s an exciting time, and these chips are really changing how we use technology every day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly are AI chips?
AI chips are like super-smart computer brains designed to handle tasks related to artificial intelligence. They help computers learn, understand images, and make decisions much faster than regular computer chips.
Why are AI chips so important for artificial intelligence?
Think of AI chips as the engines that power AI. They are special because they can do many calculations at once, which is exactly what AI programs need to learn and work efficiently. This makes them great for things like self-driving cars or smart assistants.
Which companies are leading the AI chip race right now?
Nvidia is currently seen as the leader because their chips are really good at the complex math needed for AI. Companies like AMD and Intel are working hard to catch up, and others like Google and Apple are making their own special chips for their products.
How big is the AI chip market expected to be?
The AI chip market is growing super fast! More and more companies are using AI, so they need these powerful chips. It’s expected to become a huge market, worth billions of dollars, as AI becomes a bigger part of our lives.
What are the main goals for new AI chip designs?
Companies are trying to make AI chips that are faster, use less electricity, and are cheaper to make. They are also creating specialized chips for different jobs, like one for understanding speech and another for recognizing faces.
Will AI chips start appearing in more regular devices soon?
Yes, AI chips are becoming more common in everyday devices like smartphones and smart home gadgets. They help these devices perform AI tasks right on the device, making them quicker and more private.