Beneath the surface of modern healthcare lies a remarkable array of technologies that aid doctors in diagnosing diseases and treating patients. Among these advancements, one method has truly revolutionized healthcare: Radioscopy. This groundbreaking imaging technique has transformed diagnostics, surgery, and treatment outcomes in ways previously deemed impossible. In this blog post, we will explore the profound impact of radioscopy on modern medicine, paving the way for unprecedented improvements in patient outcomes.
Introduction to Radioscopy
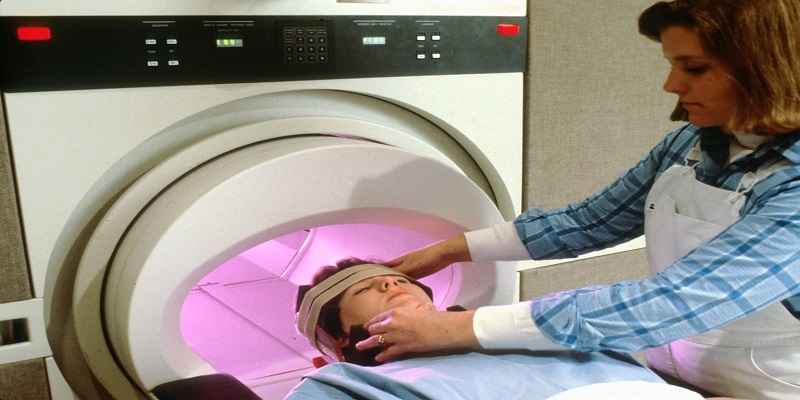
Radioscopy is an imaging technique that utilizes X-rays to create internal images of the human body. It plays a crucial role in disease diagnosis and treatment.
The origins of radioscopy can be traced back to Wilhelm Röntgen, a German physicist who developed the first radioscopy machine in 1895. During his exploration of electricity and magnetism, Röntgen discovered that electricity could generate invisible rays capable of penetrating human tissue, which he named “X-rays.”
Radioscopy swiftly gained popularity as it allowed doctors to visualize the human body without resorting to invasive surgery. Surgeons began utilizing radioscopy to guide them during operations. In the early 1900s, radioscopy proved instrumental in diagnosing tuberculosis and cancer.
Today, radioscopy is widely employed in diagnosing and treating a diverse range of diseases, making it an invaluable tool in modern healthcare.
Types Of Radioscopy
There are two types of radioscopy: digital and analog. Digital radioscopy, which uses computerized equipment to capture and store images, is more efficient and results in lower radiation exposure for patients. Analog radioscopy, which relies on traditional film-based methods requiring darkroom development, exposes patients to more radiation.
Benefits of Radioscopy for Patients
Radioscopy is a non-invasive medical imaging technique employing ionizing radiation to produce images of the human body. Its advantages for patients include:
- It is a non-invasive procedure, eliminating the need for surgery.
- It is quick, convenient, and can often be performed on an outpatient basis.
- It is relatively affordable and does not require specialized equipment.
- It is safe for individuals of all ages, including children.
- It enables the examination of almost any part of the body.
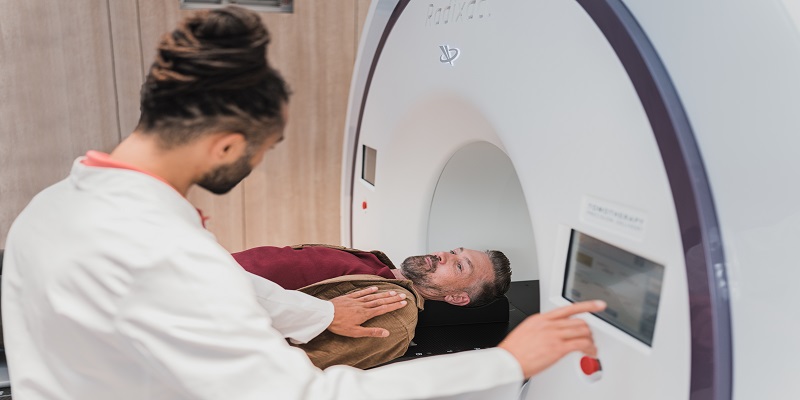
Procedure Mechanism
Although radio waves were initially utilized for medical purposes in the late 1800s, their potential for diagnosis and treatment was not fully realized until the early 1900s. In 1918, German engineer Karl Ferdinand Braun discovered that passing radio waves through the body generated an electrical current, allowing the detection of abnormalities. This breakthrough paved the way for the development of radioscopy, a revolutionary imaging modality that transformed healthcare.
Contemporary radioscopy is employed in diagnosing and treating a wide array of conditions, ranging from broken bones to cancer. The procedure is straightforward: a specialized radiology machine emits high-frequency sound waves that traverse the body, reflecting off organs, tissues, and bones. These reflections are captured by a computer and converted into images that can be viewed on a screen.
Radio waves pose no harm to the human body and cause no pain or discomfort. The procedure is swift and painless, providing doctors with detailed insights into a patient’s internal anatomy. Radioscopy has revolutionized healthcare by offering doctors a non-invasive means to diagnose and treat diseases. Thanks to this innovative technology, patients can receive necessary care without undergoing surgery or experiencing discomfort.
Types of Images Produced by Radioscopy and What They Tell Us
Radioscopy, a medical imaging technique utilizing X-rays, produces different types of images that provide valuable information for diagnosis. Wilhelm Röntgen, a German physicist, discovered X-rays in 1895 during his investigations of vacuum tubes. He named them “X-rays” due to their unknown nature at the time.
X-rays have since been extensively employed in medicine for diagnosing and treating various conditions. Similar to visible light but with higher energy levels, X-rays interact differently with tissues as they pass through the body. Dense tissues like bones absorb more X-ray photons than soft tissues such as organs or muscles. This discrepancy in absorption creates shadows on X-ray images, enabling the diagnosis of different conditions.
Radioscopy and radiography are two primary X-ray-based medical imaging techniques. Radiography captures images of bones and organs by directing X-rays through the body onto film or digital detectors. Darker areas on the image indicate higher X-ray absorption, revealing internal structural details of the tissues. Radioscopy, similar to radiography, incorporates special dyes that absorb X-rays to enhance the contrast between different tissues. This technique is often employed to…
When considering the use of radioscopy for imaging patients, there are important cost and safety considerations. Digital radioscopy has become the preferred standard in many medical facilities due to its high-quality images and relatively lower cost. However, the radiation dose is a critical factor to consider for patient safety. While digital radioscopy uses less radiation compared to traditional film-based radioscopy, the level of radiation exposure remains significant. It is crucial to thoroughly assess whether the benefits of radioscopy outweigh the potential risks associated with radiation exposure.
Another significant consideration is the cost of radioscopy equipment and services. Although digital radioscopy is generally more affordable than other imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), it still requires a substantial investment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that sufficient financial resources are available to cover the costs of radioscopy before deciding to use it for patients.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of the Procedure
Radioscopy, a procedure that employs X-rays to generate internal body images, like any medical procedure, carries potential risks and side effects that patients should be aware of before undergoing the process. Although these risks are generally low, it is essential to be informed.
The most common side effect of radioscopy is temporary skin reddening or irritation at the X-ray site, which typically resolves within a couple of days. Although rare, more serious side effects include burns, allergic reactions, and possible interference with implanted devices like pacemakers.
As with any medical procedure, there is a slight risk of complications arising from radioscopy. However, these risks are usually minimal and outweighed by the potential benefits of the procedure. Patients should have a thorough discussion with their doctor regarding all potential risks and side effects to make an informed decision about radioscopy.
Pros and Cons of Radioscopy for Patients:
Radioscopy, also known as X-ray imaging, utilizes low doses of radiation to capture images of the body for diagnostic purposes. While radiation exposure is a risk, the benefits of diagnostic radiology far outweigh the potential dangers. The radiation dose from a single diagnostic radiograph is typically very low and poses minimal risk to patients.
The advantages of radioscopy include its ability to diagnose a wide range of conditions and diseases, such as fractures, cancers, and other abnormalities. It is also valuable for monitoring the healing progress following injuries or surgeries.
While radioscopy generally carries low risks, there are potential side effects to consider. These may include allergic reactions to contrast materials used in certain procedures, as well as minor discomforts like headaches, dizziness, or nausea. Severe risks like cancer or organ damage are extremely rare.
Conclusion
Radioscopy has revolutionized modern healthcare, enabling accurate diagnoses and improving patient outcomes. It serves as a vital tool for various diagnostic imaging procedures, such as abdominal scans and mammograms. Radioscopy facilitates early disease detection and enhances treatment effectiveness. Through the use of advanced technology and specialized expertise, radiologists have made significant advancements in patient care, minimizing the risk of undetected diseases.