Discover the transformative potential of neural prosthetics in restoring motor and sensory functions for individuals with disabilities. Explore how these technological interventions work, their benefits, risks, and the types of conditions they can benefit. Stay informed about the latest advancements in neural prosthetics for a better quality of life. Imagine a world where lost motor and sensory functions can be restored through advanced technological interventions. This is no longer a distant dream but a reality, thanks to the groundbreaking field of neural prosthetics. Neural prosthetics are transforming medical interventions and offering new possibilities for individuals with spinal cord injuries or neurological disorders, improving their quality of life. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of neural prosthetics, understanding what they are, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and who can benefit from them.
Introduction
What are Neural Prosthetics?
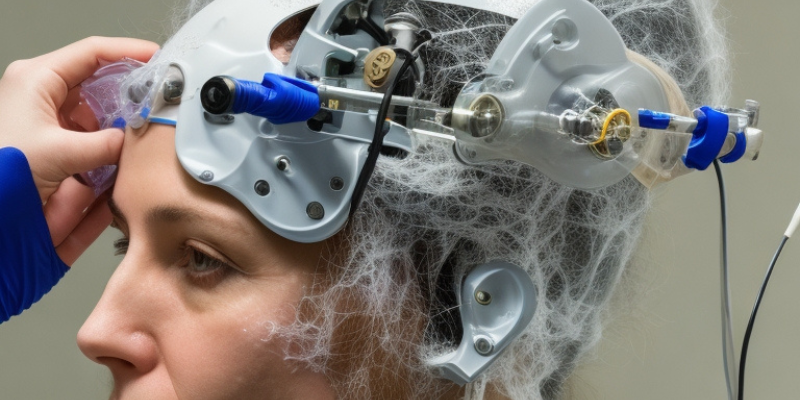
Neural prosthetics, also known as brain-machine interfaces, are technological interventions designed to restore motor and sensory functions in individuals with neurological disorders or injuries. These devices establish a connection between the nervous system and an external device, such as a computer or robotic limb.
The core idea behind neural prosthetics is to bypass damaged parts of the nervous system and create a new connection between the brain and the external device. This connection can be established through invasive methods, such as implanting electrodes into the brain, or non-invasive techniques, like using EEG sensors.
One of the significant advantages of neural prosthetics is their ability to decode signals from different areas of the brain associated with specific movements or sensations. By analyzing these signals, neural prosthetics assist individuals in regaining control over paralyzed body parts to some extent.
However, it’s crucial to note that neural prosthetics are still in the early stages of development, requiring further research before they become widely accessible. Nevertheless, this field holds tremendous promise for individuals living with disabilities caused by neurological disorders.
How Do Neural Prosthetics Work?
Neural prosthetics are devices that aim to restore motor and sensory functions in individuals with neurological injuries or disorders. The technology behind neural prosthetics is complex, but the basic concept involves creating an artificial link between the brain and a prosthesis, enabling communication between the two.
Invasive surgery is one method used to establish this link. In this procedure, electrodes are implanted directly into the brain’s cortex, picking up signals from neurons responding to specific movements or sensations. These signals are then translated by a computer algorithm into commands that control the movement of a robotic limb or other prosthetic device.
Another approach involves non-invasive techniques like electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). EEG measures electrical activity on the scalp, while fMRI detects changes in blood flow to different areas of the brain. By analyzing these patterns, scientists can determine an individual’s intended actions for their missing limb and translate those intentions into control signals for a prosthesis.
While still experimental, neural prosthetics offer hope for restoring function to individuals living with paralysis or amputations. However, developing effective devices that seamlessly integrate with our nervous system without causing harm or discomfort presents significant challenges. Nonetheless, ongoing research will undoubtedly lead to exciting advancements in this field.
Types of Neural Prosthetics
Several types of neural prosthetics have been developed to restore motor and sensory functions. One such type is the cochlear implant, which helps people who are deaf or hard of hearing regain their hearing. This device bypasses damaged parts of the ear and stimulates the auditory nerve directly, enabling sound signals to reach the brain.
Another type is the myoelectric prosthesis, which assists individuals who have lost their limbs in regaining some motor function. This device uses electrodes placed on the skin surface to detect muscle contractions in other parts of the body. These contractions are then translated into movements in the prosthetic limb.
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are another type of neural prosthetic that detects electrical activity in the brain and translates it into commands for a computer or other device. BCIs show promise in helping
individuals with conditions like paralysis or locked-in syndrome communicate and control devices using their thoughts alone.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution for neural prosthetics, as different technologies may be better suited to individuals based on their specific conditions and needs. Ongoing research and development expand our understanding of these innovative interventions and how they can best benefit those with disabilities or injuries affecting motor or sensory function.
Pros and Cons of Neural Prosthetics
Neural prosthetics are a remarkable technological intervention with the potential to restore motor and sensory functions in individuals with disabilities. While they offer several advantages, it’s important to consider their pros and cons before considering them as a viable option.
One significant benefit of neural prosthetics is their ability to enhance an individual’s quality of life by enabling independent daily activities. Moreover, these devices can reduce the need for medication or other medical interventions, leading to improved overall health outcomes.
On the flip side, there are some drawbacks associated with neural prosthetics. They can be expensive and not easily accessible to everyone who needs them. Additionally, there may be discomfort or pain during the initial stages of using these devices, as they require surgery and rehabilitation.
Another potential disadvantage is that while neural prosthetics can improve mobility and function in specific areas like limb movement or hearing abilities, they may not address underlying conditions such as muscle atrophy or nerve damage.
When assessing the suitability of neural prosthetics for an individual’s specific needs, it’s essential to carefully weigh both their merits and limitations. Ultimately, with proper utilization under professional guidance, these devices have shown great promise in helping people regain lost motor skills through innovative means.
Who Can Benefit from Neural Prosthetics?
Neural prosthetics are a revolutionary technological intervention with the potential to restore motor and sensory functions for people with disabilities. These devices have been designed to replace or supplement the function of damaged neural tissue, allowing patients to regain control over their bodies.
Individuals with spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and other neurological disorders can greatly benefit from neural prosthetics. These conditions often impose significant limitations on mobility and independence.
However, not all individuals with these conditions are suitable candidates for neural prosthetics. The eligibility for a neural prosthetic device depends on factors such as age, overall health status, and the severity of disability, among others.
For those who are considered suitable candidates by medical professionals, neural prosthetics can significantly improve their quality of life. Greater independence brings newfound freedom, which is crucial for living fulfilling lives.
Anyone experiencing limitations related to paralysis or impaired movement may find relief through neural prosthetics, offering hope where there was once none, and helping individuals rebuild a sense of normalcy after debilitating injuries or illnesses.
Are There Risks Associated with Neural Prosthetics?
As with any medical intervention, there are potential risks involved in using neural prosthetics. Although these devices offer a promising solution for restoring motor and sensory functions in individuals with severe injuries or diseases, their use is not without complications.
One primary risk associated with neural prosthetics is infection. Since these devices require direct contact with the nervous system, there is a risk of introducing bacteria into the body, leading to serious infections that may be challenging to treat.
Another risk is device malfunction. While rare, design or manufacturing errors could cause damage to surrounding nerves and tissues, resulting in further complications.
Additionally, some patients may experience discomfort or pain due to nerve stimulation provided by the prosthetic device. This discomfort can range from mild tingling sensations to more intense pain requiring medical attention.
Despite these potential risks, many patients have successfully used neural prosthetics without experiencing adverse effects. With proper planning and management by trained healthcare professionals, most of these issues can be effectively addressed and mitigated over time.
Conclusion
Neural prosthetics have revolutionized the field of medicine and transformed the lives of countless individuals. These technological interventions
have enabled people with motor and sensory impairments to regain their sense of independence. From cochlear implants to brain-computer interfaces, neural prosthetics come in various forms to cater to different needs.
While there are risks associated with these devices, proper patient selection and device regulations can manage them. Healthcare providers must stay updated on advancements in this field to provide optimal care to patients.
The potential benefits of neural prosthetics outweigh the drawbacks, as they continue to improve the quality of life for those who need them most. Ongoing research and development in this area will undoubtedly lead to more promising innovations in the future.